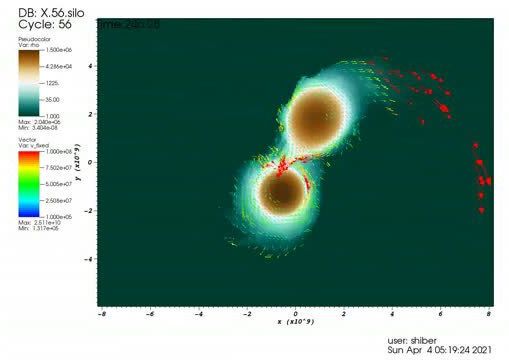
A breakthrough astrophysics code, named Octo-Tiger, simulates the evolution of self-gravitating and rotating systems of arbitrary geometry using adaptive mesh refinement and a new method to parallelize the code to achieve superior speeds.
This new code to model stellar collisions is more expeditious than the established code used for numerical simulations. The research came from a unique collaboration between experimental computer scientists and astrophysicists in the Louisiana State University Department of Physics & Astronomy, the LSU Center for Computation & Technology, Indiana University Kokomo and Macquarie University, Australia, culminating in over of a year of benchmark testing and scientific simulations, supported by multiple NSF grants, including one specifically designed to break the barrier between computer science and astrophysics.
“Thanks to a significant effort across this collaboration, we now have a reliable computational framework to simulate stellar mergers,” said Patrick Motl, professor of physics at Indiana University Kokomo. “By substantially reducing the computational time to complete a simulation, we can begin to ask new questions that could not be addressed when a single-merger simulation was precious and very time consuming. We can explore more parameter space, examine a simulation at very high spatial resolution or for longer times after a merger, and we can extend the simulations to include more complete physical models by incorporating radiative transfer, for example.”