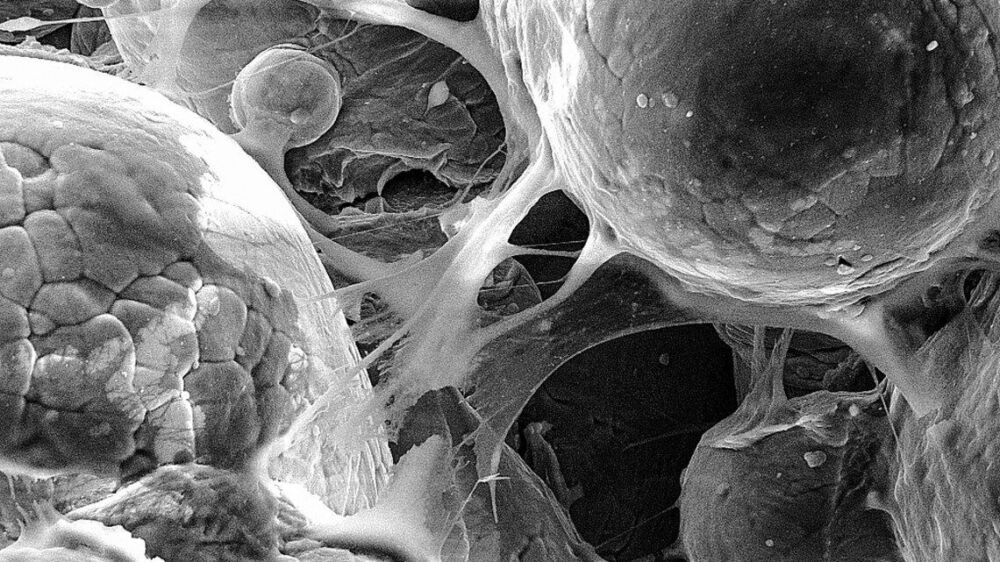
Forget glue, screws, heat or other traditional bonding methods. A Cornell University-led collaboration has developed a 3D printing technique that creates cellular metallic materials by smashing together powder particles at supersonic speed.
This form of technology, known as “cold spray,” results in mechanically robust, porous structures that are 40% stronger than similar materials made with conventional manufacturing processes. The structures’ small size and porosity make them particularly well-suited for building biomedical components, like replacement joints.
The team’s paper, “Solid-State Additive Manufacturing of Porous Ti-6Al-4V by Supersonic Impact,” published Nov. 9 in Applied Materials Today.