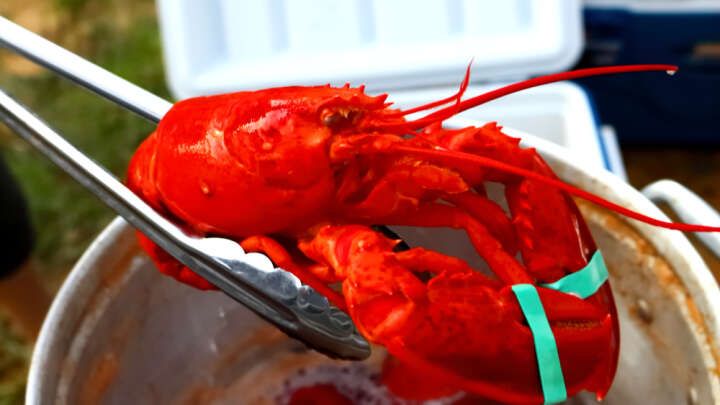
Boiling lobsters alive may be banned under a new law in the UK designed to protect the welfare rights of animals considered sentient beings. So, are lobsters sentient, do they feel pain, and what does science have to say about the moral quagmire of crustacean agony and cooking pots?
Back in May 2021, the UK government introduced a bill to formally recognize animals as sentient beings. Among the many facets of the bill, it aimed to limit the import of products from trophy hunting, push for fairer space requirements for farm animals, and stop people from owning primates as pets.
However, the bill only covered animals with a backbone and didn’t include any protections for non-vertebrates, which includes octopuses, squid, insects, and crustaceans. The Times reports that ministers are now preparing to back an amendment to the House of Lords, the upper house of the UK Parliament, to extend the legislation to shellfish and cephalopod mollusks. As per the report, this is likely to involve an outright ban on boiling lobsters alive.