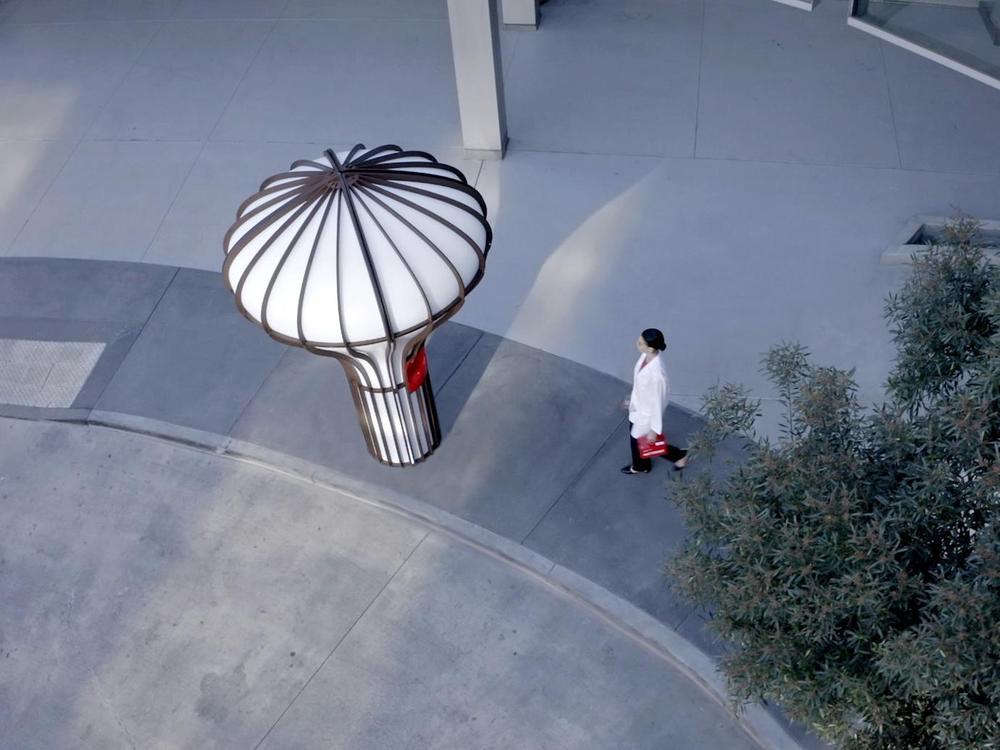
If drone delivery companies get to shape city streets to their liking, the curbside array of lamp posts, garbage cans and free magazine distribution boxes will be joined someday by docking stations for their aircraft. Matternet on Tuesday unveiled a 10-foot tall kiosk three years in the making that’s designed to safely integrate its medical delivery drones into urban environments — and to drastically reduce the number of employees the startup needs and achieve a breakthrough on costs.
Plenty of companies have developed docking stations for recharging drones and to shelter them when they’re idle. Matternet could be the first to field a system that automatically handles cargo.
After its M2 drone enters through the top and docks, the station loads and unloads payload boxes, swap batteries and assesses the condition of the drone. Medical workers will be able to retrieve and drop off boxes through a hatch after scanning their IDs.