Jul 22, 2019
A Faster Way to Rearrange Atoms Could Lead to Powerful Quantum Sensors
Posted by Quinn Sena in categories: computing, engineering, particle physics, quantum physics
The fine art of adding impurities to silicon wafers lies at the heart of semiconductor engineering and, with it, much of the computer industry. But this fine art isn’t yet so finely tuned that engineers can manipulate impurities down to the level of individual atoms.
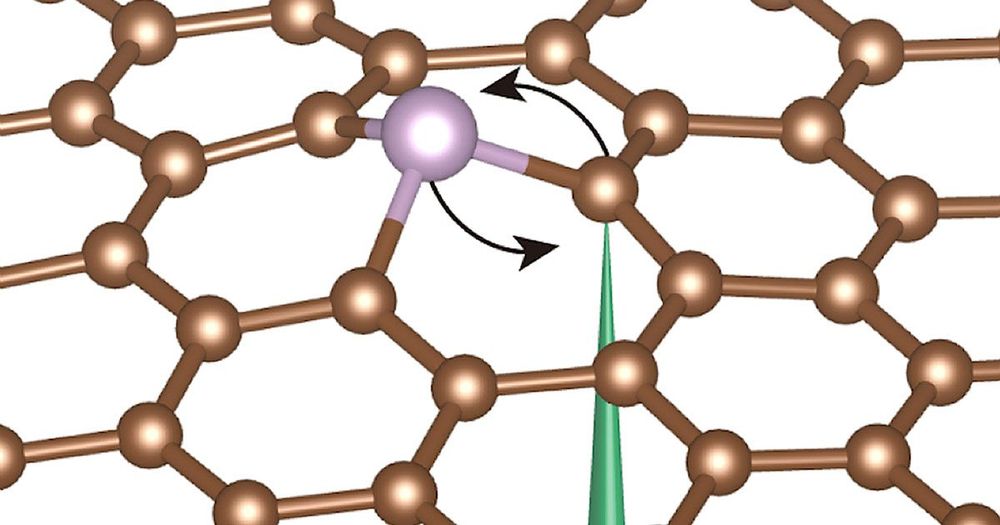
As technology scales down to the nanometer size and smaller, though, the placement of individual impurities will become increasingly significant. Which makes interesting the announcement last month that scientists can now rearrange individual impurities (in this case, single phosphorous atoms) in a sheet of graphene by using electron beams to knock them around like croquet balls on a field of grass.
The finding suggests a new vanguard of single-atom electronic engineering. Says research team member Ju Li, professor of nuclear science and engineering at MIT, gone are the days when individual atoms can only be moved around mechanically—often clumsily on the tip of a scanning tunneling microscope.