Ordinarily, planning a mid-afternoon launch from Florida during the summer would be inadvisable, especially if there’s no margin for error. The heat and humidity can make for “dynamic” weather conditions (to use a word that came up frequently in forecasts last week) that make it difficult to predict if a launch can proceed.
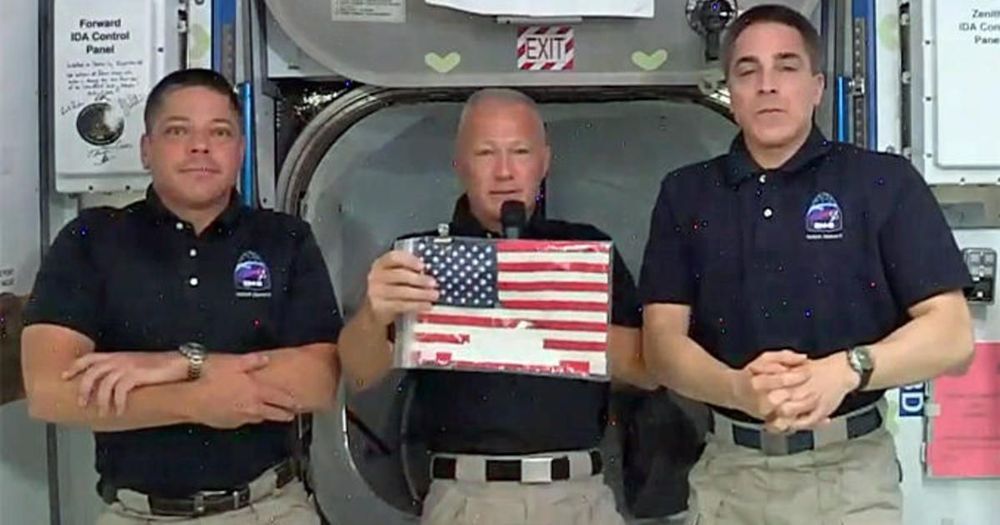
However, the schedule for the Demo-2 commercial crew mission was dictated not by Mother Nature but instead by Isaac Newton. The launch was tied to the orbit of the International Space Station so that the Crew Dragon spacecraft could reach the station after launch. That required an instantaneous launch window that, in late May, happened to be in the afternoon from the Kennedy Space Center.
Still, try explaining that to the boss. “I was told that the rocket you just witnessed had to be launched within one second, or it would be impossible for it to hit its target,” President Donald Trump said last Saturday, after a successful launch that he watched in person. He had been at the Kennedy Space Center three days earlier as well, when weather conditions didn’t quite clear in time to allow the launch.