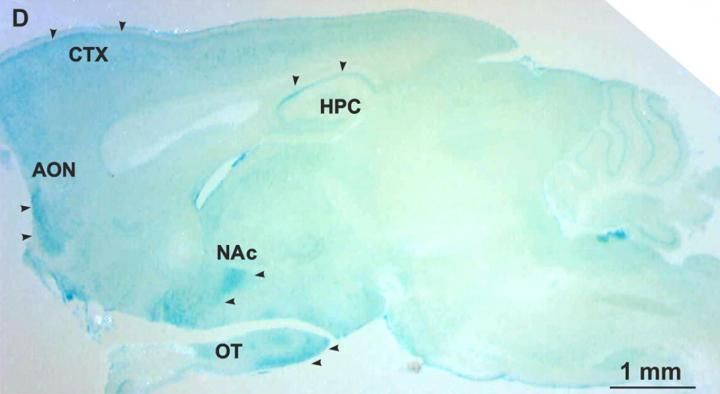
Within this system, the transmission of signals between neurons in the brain occurs via the trace amine-associated receptor 5 (TAAR5). The results of the study will allow the development of new types of drugs for depression, schizophrenia and anxiety disorders.
Treatment of Neuroterrorism
Posted in biotech/medical, military, terrorism
Bioterrorism is defined as the intentional use of biological, chemical, nuclear, or radiological agents to cause disease, death, or environmental damage. Early recognition of a bioterrorist attack is of utmost importance to minimize casualties and initiate appropriate therapy. The range of agents that could potentially be used as weapons is wide, however, only a few of these agents have all the characteristics making them ideal for that purpose. Many of the chemical and biological weapons can cause neurological symptoms and damage the nervous system in varying degrees. Therefore, preparedness among neurologists is important. The main challenge is to be cognizant of the clinical syndromes and to be able to differentiate diseases caused by bioterrorism from naturally occurring disorders. This review provides an overview of the biological and chemical warfare agents, with a focus on neurological manifestation and an approach to treatment from a perspective of neurological critical care.
The online version of this article (doi:10.1007/s13311-011‑0097-2) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Neuroterrorism, Bioterrorism, Warfare Agents.
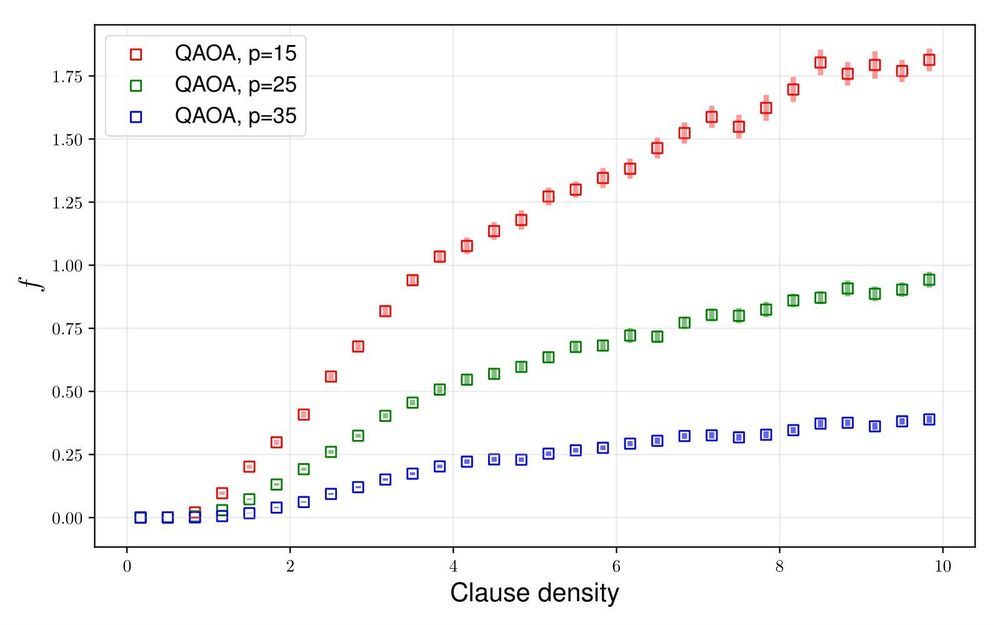
Google is racing to develop quantum-enhanced processors that use quantum mechanical effects to increase the speed at which data can be processed. In the near term, Google has devised new quantum-enhanced algorithms that operate in the presence of realistic noise. The so-called quantum approximate optimisation algorithm, or QAOA for short, is the cornerstone of a modern drive toward noise-tolerant quantum-enhanced algorithm development.
The celebrated approach taken by Google in QAOA has sparked vast commercial interest and ignited a global research community to explore novel applications. Yet, little is known about the ultimate performance limitations of Google’s QAOA algorithm.
A team of scientists from Skoltech’s Deep Quantum Laboratory took up this contemporary challenge. The all-Skoltech team led by Prof. Jacob Biamonte discovered and quantified what appears to be a fundamental limitation in the widely adopted approach initiated by Google.
YouTuber Tom Scott has a new video where he stands in front of a laser and stops it in midair. “Can this burn me?” he asks the guest expert at one point. (The answer is just, “Yeah.”)
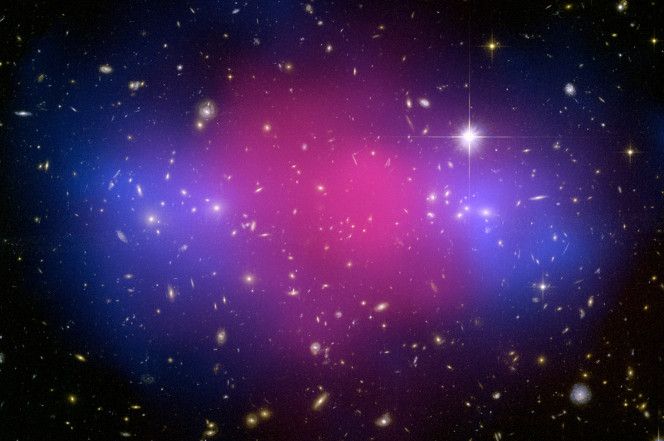
When astronomers gaze into space they can see many different things. Galaxies, stars, and even black holes can be spotted from our place here on Earth. However, one of the most abundant types of matter in the universe can’t actually be seen at all, or at least we’ve yet to invent the means to do so.
Dark matter may account for over three-quarters of all matter in the universe, but it can’t be observed directly. Instead, scientists have to infer its existence based on how other objects in the cosmos react to its gravity. But what is it, and will we ever be able to explain its origins? A new study by researchers at the University of York attempts to do just that, offering a potential explanation for what dark matter really is.
The researchers say that the secret of dark matter may rest in a type of particle called a d-star hexaquark. As SciTechDaily notes, it’s a particle made up of six quarks, which are the tiny bits that make up protons and neutrons, but because of their arrangement in a d-star, they are more versatile.
Watchdog Which? wants Google to be more transparent about security updates for old phones.
The race is on to identify an effective vaccine for the COVID-19 virus. Once discovered, the next challenge will be manufacturing and distributing it around the world.
My research group has developed a novel method to stabilize live viruses and other biological medicines in a rapidly dissolving film that does not require refrigeration and can be given by mouth.
Since the ingredients to make the film are inexpensive and the process is relatively simple, it could make vaccine campaigns much more affordable. Large quantities could be shipped and distributed easily given its flat, space saving shape.
CEO of the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations Dr Richard Hatchett explains the long-term dangers of the Covid-19 coronavirus — saying it’s the scariest outbreak he’s dealt with in his 20-year career. (Subscribe: https://bit.ly/C4_News_Subscribe)
——
Get more news at our site — https://www.channel4.com/news/
Follow us:
Facebook — https://www.facebook.com/Channel4News/
Twitter — https://twitter.com/Channel4News
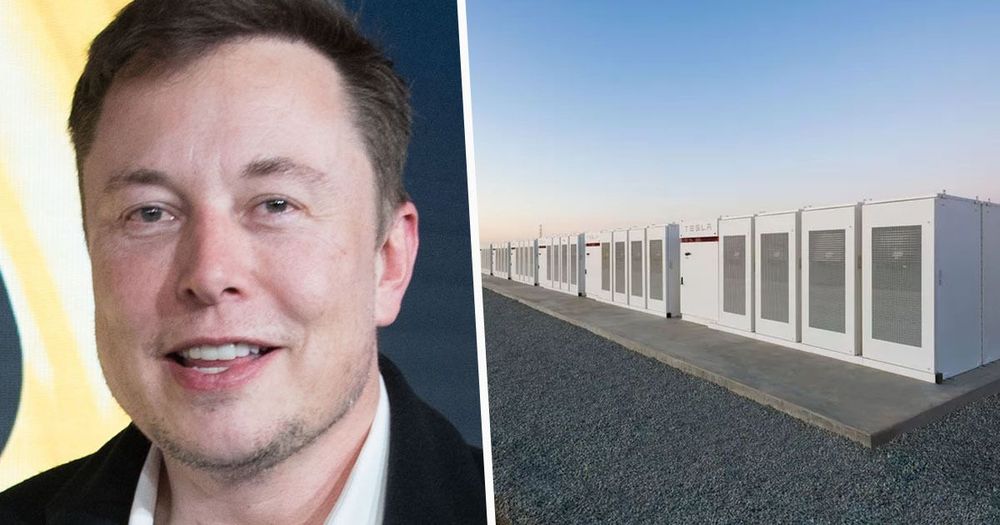
Elon Musk was challenged to fix South Australia’s energy problem in 2017, and just two years on he’s saved Australians millions.