Who needs a boat?


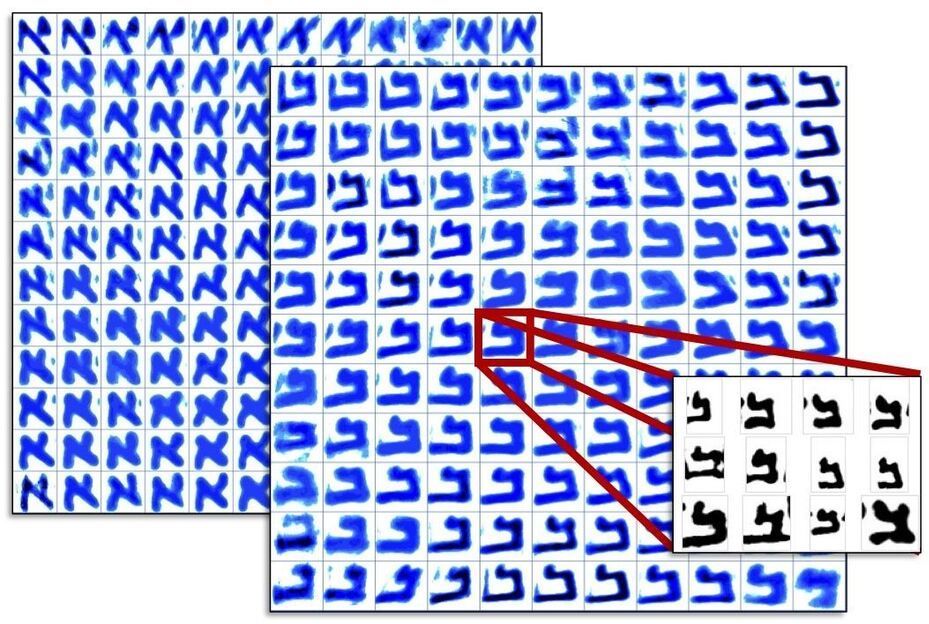
The Dead Sea Scrolls, discovered some seventy years ago, are famous for containing the oldest manuscripts of the Hebrew Bible (Old Testament) and many hitherto unknown ancient Jewish texts. But the individual people behind the scrolls have eluded scientists, because the scribes are anonymous. Now, by combining the sciences and the humanities, University of Groningen researchers have cracked the code, which enables them to discover the scribes behind the scrolls. They presented their results in the journal PLOS ONE on April 21, 2021.
The scribes who created the scrolls did not sign their work. Scholars suggested some manuscripts should be attributed to a single scribe based on handwriting. “They would try to find a “smoking gun” in the handwriting, for example, a very specific trait in a letter which would identify a scribe,” explains Mladen Popović, professor of Hebrew Bible and Ancient Judaism at the Faculty of Theology and Religious Studies at the University of Groningen. He is also director of the university’s Qumran Institute, dedicated to studying the Dead Sea Scrolls. However, these identifications are somewhat subjective and often hotly debated.
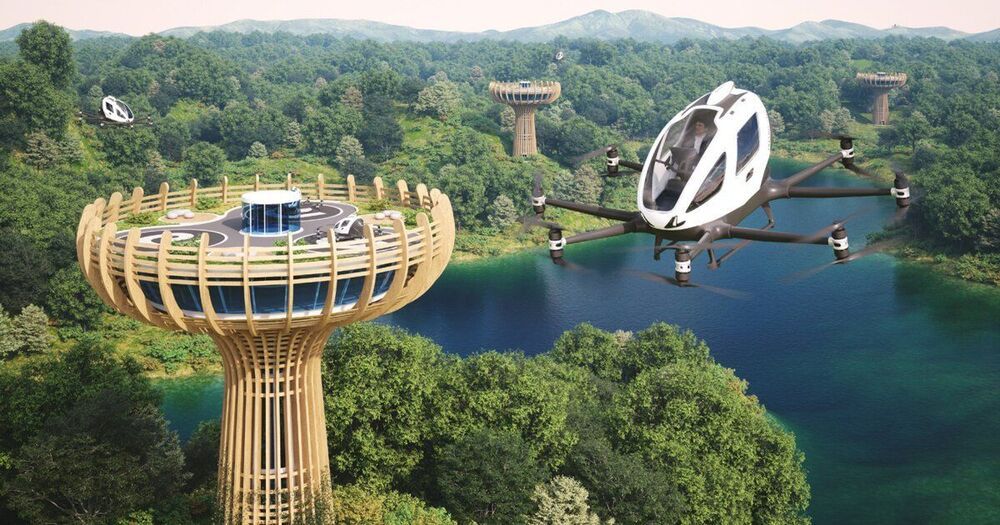

autonomous air vehicle company ehang unveils ‘baobab’, a large tree-like tower and landing platform for its EH216 passenger drones. designed by giancarlo zema design group (GZDG) with sustainability at the core, photovoltaic panels on the vertiports will generate energy and independent plug-and-play charging points will recharge the drones wirelessly. currently in the development stage, ehang and GZDG hope to enter the emerging global eco-tourism sector with hubs being planned for a lakeside site in china’s zhaoqing city as well as in the maldives, the united arab emirates, and italy.
Images courtesy of giancarlo zema design group (GZDG)

I believe that schizophrenia although an illness could be a quantum sense in the quantum realm essentially feeling different dimensions which still remain unknown. The minds developed by the military in different projects like the stranger things series is an example of such a wild reality we live in and how interesting dimensions beyond ours touch our reality.
To the average person, most quantum theories sound strange, while others seem downright bizarre. There are many diverse theories that try to explain the intricacies of quantum systems and how our interactions affect them. And, not surprisingly, each approach is supported by its group of well-qualified and well-respected scientists. Here, we’ll take a look at the two most popular quantum interpretations.
Does it seem reasonable that you can alter a quantum system just by looking at it? What about creating multiple universes by merely making a decision? Or what if your mind split because you measured a quantum system?
You might be surprised that all or some of these things might routinely happen millions of times every day without you even realizing it.
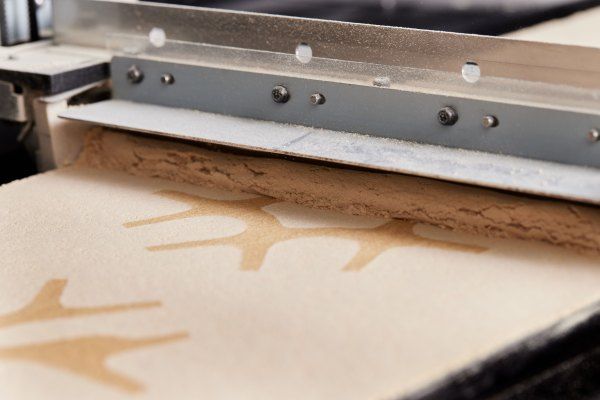

Desktop Metal today announced the launch of wood 3D printing tool, Forust. Founded in 2019, the company specializes in 3D printing for interior design. The company’s “non-destructive” printing methods have managed to largely fly under the radar, with minimal press coverage until now — making them a pretty ideal acquisition candidate.
In fact, the gross assets acquisition actually occurred back in October 2020, according to a filing, which pegs it at a price at $2.5 million, including $2 million in cash considerations. Since then, it seems, the two have been working together ahead of an official launch.
In a press release issued today, Desktop Metal is positioning Forust as the name of the new manufacturing process now in the company’s portfolio. The technology utilizes cellulose dust and lignin, byproducts from the wood and paper industries, respectively.

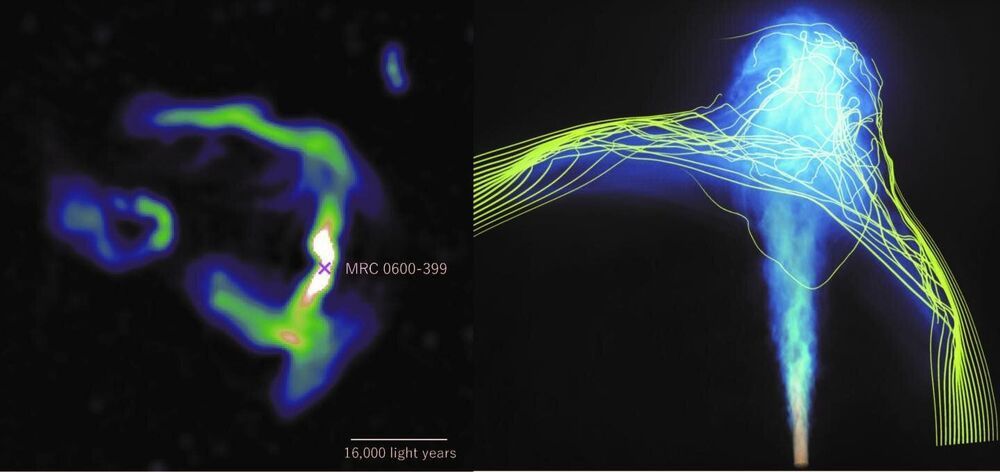
New observations and simulations show that jets of high-energy particles emitted from the central massive black hole in the brightest galaxy in galaxy clusters can be used to map the structure of invisible inter-cluster magnetic fields. These findings provide astronomers with a new tool for investigating previously unexplored aspects of clusters of galaxies.
As clusters of galaxies grow through collisions with surrounding matter, they create bow shocks and wakes in their dilute plasma. The plasma motion induced by these activities can drape intra–cluster magnetic layers, forming virtual walls of magnetic force. These magnetic layers, however, can only be observed indirectly when something interacts with them. Because it is simply difficult to identify such interactions, the nature of intra-cluster magnetic fields remains poorly understood. A new approach to map/characterize magnetic layers is highly desired.
An international team of astronomers including Haruka Sakemi, a graduate student at Kyushu University (now a research fellow at the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan—NAOJ), used the MeerKAT radio telescope located in the Northern Karoo desert of South Africa to observe a bright galaxy in the merging galaxy cluster Abell 3376 known as MRC 0600–399. Located more than 600 million light-years away in the direction of the constellation Columba, MRC 0600–399 is known to have unusual jet structures bent to 90-degree angles. Previous X-ray observations revealed that MRC 0600–399 is the core of a sub-cluster penetrating the main cluster of galaxies, indicating the presence of strong magnetic layers at the boundary between the main and sub-clusters. These features make MRC 0600–399 an ideal laboratory to investigate interactions between jets and strong magnetic layers.

And as well as producing less waste, insects can also live off food and biomass that would otherwise be thrown away, says Collins, contributing to the circular economy, where resources are recycled and reused. Insects can be fed agricultural waste, such as the stems and stalks from plants that people don’t eat, or scraps of food waste. To complete the recycling chain, their excrement can be used as fertiliser for crops.
Insects are a nutrition-dense source of protein embraced by much of the world. Why are some of us so squeamish about eating them?
Starship has an explosive flight record, but SpaceX may finally be mastering the spaceship’s landing. That’s crucial to making it reusable.
Physics has long looked to harmony to explain the beauty of the Universe. But what if dissonance yields better insights?
Quantum physics is weird and counterintuitive. For this reason, the word ‘quantum’ has become shorthand for anything powerful or mystical, whether or not it has anything whatsoever to do with quantum mechanics. As a quantum physicist, I’ve developed a reflexive eyeroll upon hearing the word applied to anything outside of physics. It’s used to describe homeopathy, dishwasher detergents and deodorant.
If I hadn’t first heard of Quantum Music from a well-respected physicist, I would have scoffed the same way I did at the other ridiculous uses of the word. But coming from Klaus Mølmer it was intriguing. In the Quantum Music project, physicists and musicians worked together to unite ‘the mysterious worlds of quantum physics and music for the first time’. They developed a device that attaches to each key of a piano so that, when the pianist plays, the information is piped to a computer and synthesiser, which plays ‘quantum’ tones in addition to the familiar reverberations in the piano.
Among the tones used are those that represent a very quantum object: a Bose-Einstein condensate (BEC). This is a cloud of atoms that have been cooled down to just above absolute zero. At this low temperature, the microscopic quantum properties of the individual particles can all be treated collectively as a single, macroscopic quantum entity. Studying BECs is a way of examining the consequences of quantum mechanics on a larger scale than is typically possible.