Finger prosthetics We really are living in the future, wow GIFs | Search for More wow GIFs on www.GIF-VIF.com.


Finger prosthetics We really are living in the future, wow GIFs | Search for More wow GIFs on www.GIF-VIF.com.
NASA ’s Perseverance rover carries a device to convert Martian air into oxygen that, if produced on a larger scale, could be used not just for breathing, but also for fuel.
One of the hardest things about sending astronauts to Mars will be getting them home. Launching a rocket off the surface of the Red Planet will require industrial quantities of oxygen, a crucial part of propellant: A crew of four would need about 55,000 pounds (25 metric tons) of it to produce thrust from 15,000 pounds (7 metric tons) of rocket fuel.
That’s a lot of propellant. But instead of shipping all that oxygen, what if the crew could make it out of thin (Martian) air? A first-generation oxygen generator aboard NASA’s Perseverance rover will test technology for doing exactly that.
This video was made possible by Brilliant. Be one of the first 200 people to sign up with this link and get 20% off your premium subscription with Brilliant.org! https://brilliant.org/futurology.
Visit Our Parent Company EarthOne For Sustainable Living Made Simple ➤
https://earthone.io/
In videos past of this deep learning series, we have going from learning about the origins of the field of deep learning to how the structure of the neural network was conceived, along with working through an intuitive example covering the fundamentals of deep learning.
The focus of this video then will be to tie up many of the loose ends from those videos, and really delve into some of the complexities of deep learning!
Learn more about us here ➤
Forget Netflix and binge watch these awesome farm-bot videos.

It seems not everyone is happy about Microsoft’s productivity measuring tool. 😃
Watching, always watching.

A video on lab grown meat. Meat grown from cells taken from animals. 😃
How do you like your beef, the traditional way or 3D-printed? 🍖 🤔
Find out more at https://bit.ly/39kIeCN # engineering.
Excerpts from the Red Folder.
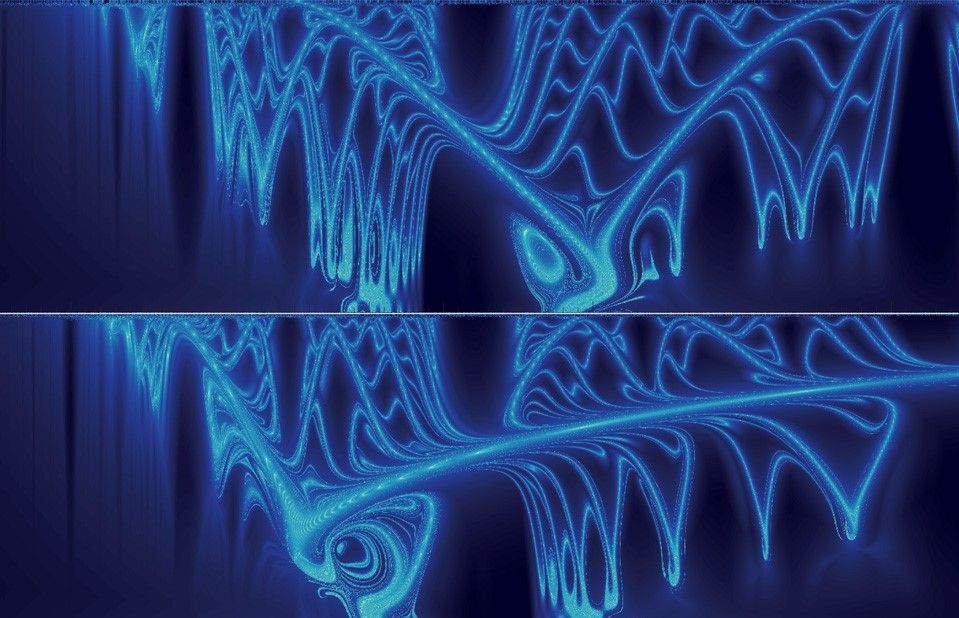
If we had a “Physics paper title of the year award”, the 2020 winner would surely have to be “The arches of chaos in the solar system”, which was published this week in Science Advances by Nataša Todorović, Di Wu and Aaron Rosengren. In their paper, the trio “reveal a notable and hitherto undetected ornamental structure of manifolds, connected in a series of arches that spread from the asteroid belt to Uranus and beyond”. These manifolds are structures that arise from the gravitational interactions between the Sun and planets. They play an important role in spacecraft navigation and also explain the erratic nature of comets.
The paper is beautifully written, describing the manifolds as “a true celestial autobahn,” and going on to say that they “enable ‘Le Petit Prince’ grand tour of the solar system”. And if that has not piqued your curiosity, the figures are wonderful as well – with the above image being “Jovian-minimum-distance maps for the Greek and Trojan orbital configurations”.
The luxury watchmaker Bremont has released the Hawking Limited Edition watch that contains bits of a wooden desk once used by the late Stephen Hawking. The “exquisite chromometer” also contains pieces of a meteorite and is etched with a view of the night sky as seen from Oxford on 8 January 1942, Hawking’s place and date of birth. What is more, the serial number of the watch is printed on paper from a 1979 paper by Hawking that was cowritten by Gary Gibbons.
With fall and winter holidays coming up, many will be pondering the relationship between food and sleep. Researchers led by Professor Masashi Yanagisawa at the University of Tsukuba in Japan hope they can focus people on the important middlemen in the equation: bacterial microbes in the gut. Their detailed study in mice revealed the extent to which bacteria can change the environment and contents of the intestines, which ultimately impacts behaviors like sleep.
The experiment itself was fairly simple. The researchers gave a group of mice a powerful cocktail of antibiotics for four weeks, which depleted them of intestinal microorganisms. Then, they compared intestinal contents between these mice and control mice who had the same diet. Digestion breaks food down into bits and pieces called metabolites. The research team found significant differences between metabolites in the microbiota-depleted mice and the control mice. As Professor Yanagisawa explains, “we found more than 200 metabolite differences between mouse groups. About 60 normal metabolites were missing in the microbiota-depleted mice, and the others differed in the amount, some more and some less than in the control mice.”
The team next set out to determine what these metabolites normally do. Using metabolome set enrichment analysis, they found that the biological pathways most affected by the antibiotic treatment were those involved in making neurotransmitters, the molecules that cells in the brain use to communicate with each other. For example, the tryptophan–serotonin pathway was almost totally shut down; the microbiota-depleted mice had more tryptophan than controls, but almost zero serotonin. This shows that without important gut microbes, the mice could not make any serotonin from the tryptophan they were eating. The team also found that the mice were deficient in vitamin B6 metabolites, which accelerate production of the neurotransmitters serotonin and dopamine.