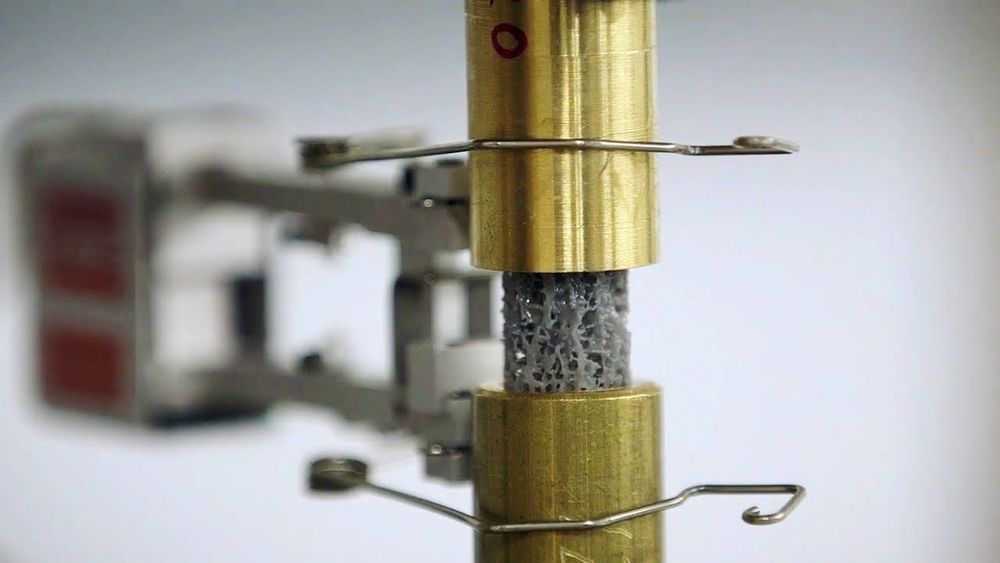
Cornell researchers have made a new discovery about how seemingly minor aspects of the internal structure of bone can be strengthened to withstand repeated wear and tear, a finding that could help treat patients suffering from osteoporosis. It could also lead to the creation of more durable, lightweight materials for the aerospace industry.
The team’s paper, “Bone-Inspired Microarchitectures Achieve Enhanced Fatigue Life,” was published Nov. 18 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. Co-authors include Cornell doctoral students Cameron Aubin and Marysol Luna; postdoctoral researcher Floor Lambers; Pablo Zavattieri and Adwait Trikanad at Purdue University; and Clare Rimnac at Case Western Reserve University.
For decades, scientists studying osteoporosis have used X-ray imaging to analyze the structure of bones and pinpoint strong and weak spots. Density is the main factor that is usually linked to bone strength, and in assessing that strength, most researchers look at how much load a bone can handle all at once.