We are entering a period of change unlike anything we have ever experienced before, indeed, unlike anything that history has witnessed before.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
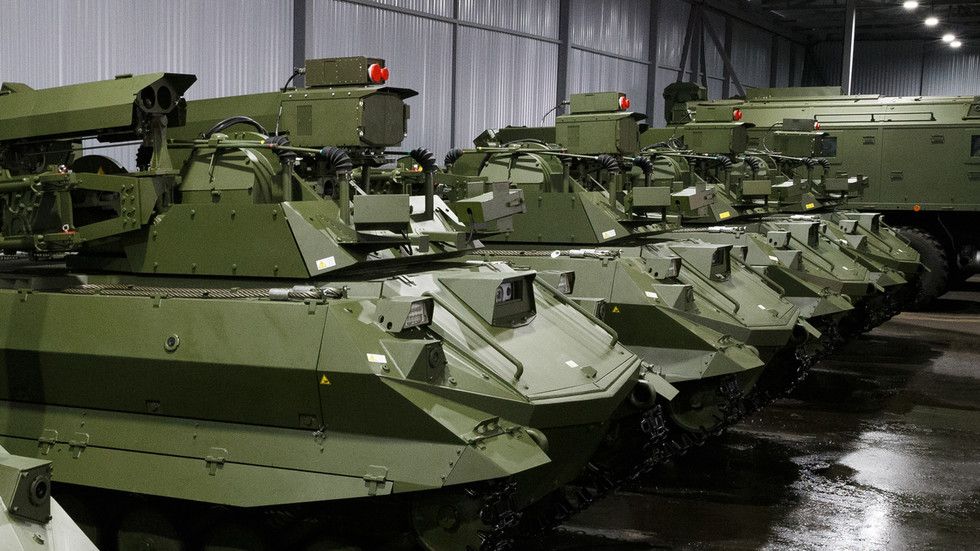

‘Weapons of the future’: Russia has launched mass production of autonomous high-tech WAR ROBOTS, Defense Minister Shoigu announces
The Russian military will soon be equipped with autonomous war robots capable of acting independently on the battlefield, Defense Minister Sergey Shoigu has said, adding that Moscow has launched mass production of such machines.
“These are not just some experimental prototypes but robots that can really be shown in sci-fi movies since they can fight on their own,” the minister told the Russian Zvezda broadcaster during the ‘New Knowledge’ forum, on Friday. Held in several Russian cities from May 20 to May 22, the forum is a series of educational events featuring top specialists in a variety of fields.
“A major effort” has been made to develop “the weapons of the future,” Shoigu said, referring to war robots equipped with artificial intelligence (AI). The bots, which are said to be capable of independently accessing a combat situation, are part of the new state-of-the-art arsenal that the Russian military is currently focused on.


How China plans to win the future with its own international tech standards
China may have missed out on the opportunity to shape standards in the past, but it is quickly dominating fields that could drive the next industrial revolution, such as consumer internet, automation and green technology.
International technology standards are one reason for the West’s dominance over the last two centuries. China now has a plan for how to get the world to follow its rules.
Molecular Biologists Travel Back in Time – Over 3 Billion Years
A research group working at Uppsala University has succeeded in studying ‘translation factors’ – important components of a cell’s protein synthesis machinery – that are several billion years old. By studying these ancient ‘resurrected’ factors, the researchers were able to establish that they had much broader specificities than their present-day, more specialized counterparts.
In order to survive and grow, all cells contain an in-house protein synthesis factory. This consists of ribosomes and associated translation factors that work together to ensure that the complex protein production process runs smoothly. While almost all components of the modern translational machinery are well known, until now scientists did not know how the process evolved.
The new study, published in the journal Molecular Biology and Evolution, took the research group led by Professor Suparna Sanyal of the Department of Cell and Molecular Biology on an epic journey back into the past. A previously published study used a special algorithm to predict DNA sequences of ancestors of an important translation factor called elongation factor thermo-unstable, or EF-Tu, going back billions of years. The Uppsala research group used these DNA sequences to resurrect the ancient bacterial EF-Tu proteins and then to study their properties.
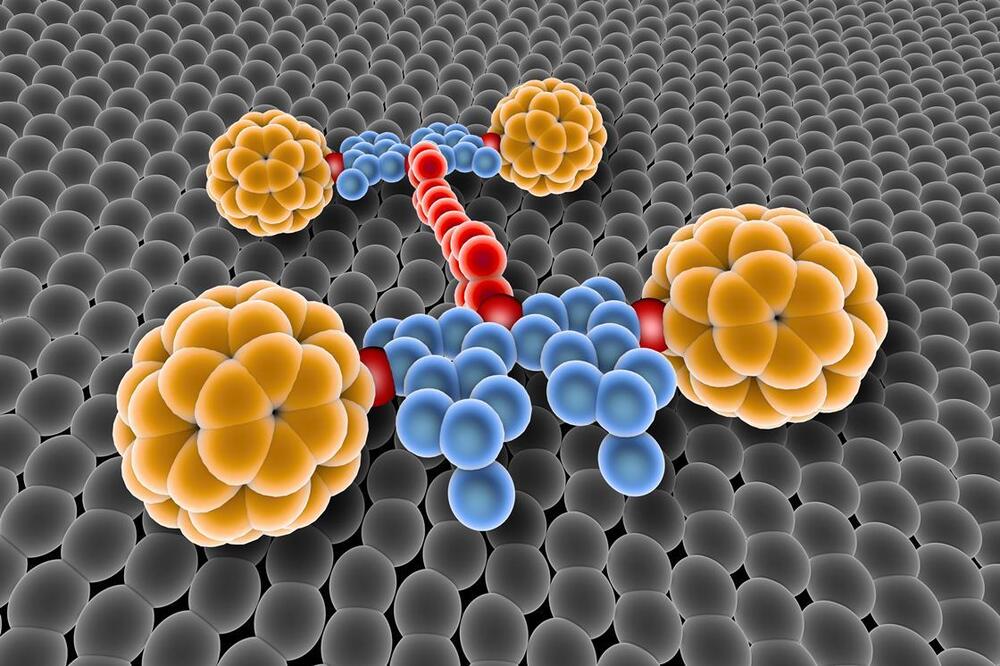
Exploring the potential of nanoarchitectonics
Combining self-assembly techniques from across scientific disciplines could allow us to precisely build any material structure.
Nanocars are an impressive achievement – but nanoarchitectonics can unlock a far greater range of material structures.
In a lecture at the American Physical Society in 1959 titled ‘There’s Plenty of Room at the Bottom’, Richard Feynman argued that huge possibilities come from working in the world of molecules and atoms. He dreamed of ultra-small computers, cars running under a microscope, and medical machines working in our body.
These dreams are now coming true. In 2017, we had the first World Nanocar Race in Toulouse, France. Six teams from around the world manipulated nanometre-size cars to run on a metal surface under a scanning tunnelling microscope. A nanocar is 2 billion times smaller than a usual car, corresponding to the size difference between a rice grain and the Earth. Feynman only imagined cars 4000 times smaller than normal. However, few of the nanocars resembled cars, and none were powered by their own motors. There’s still plenty of room for improvement.

Imiquimod Spurs Regression of High-Grade Cervical Lesions
Einstein, who was not involved in the study, noted that the number of LEEP procedures performed per year in the U.S. — approximately 500000 — indicates the scope of the disease. Additionally, he pointed out that due to the association between LEEP and preterm births, “it is truly important to explore these nonsurgical agents.”
Imiquimod directly activates innate immune cells through Toll-like receptors 7 and 8, resulting in production of cytokines and interferons.
Fonseca and colleagues evaluated the histologic response of cervical HSIL — defined as regression to cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) 1 — after topical application of 5% imiquimod cream.
Human-like robot creates creepy self-portraits
A robotic artist powered by AI algorithms has created realistic self-portraits that question the limits of artificial intelligence and what it means to be human.
Is Mars Heck?
Today we discuss Mars surface conditions with the villain from a 90s Kid’s movie. I also get mad (but not in a technical way). Apologies for this one.
The next one will be on Space Guns and Jules Verne which is more fitting for the channel.
Transition footage and thumbnail image are from the Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Perseverance and Ingenuity are nifty.
The Articles in Question (Don’t Contact the Authors):
“Mars is a Hellhole”
https://www.theatlantic.com/ideas/archive/2021/02/mars-is-no-earth/618133/

US Air Force autonomous drone Skyborg completes first flight
Last month, the United States Air Force successfully test flew an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) called Skyborg, operating on an autonomous hardware/software suite, for the very first time.
The military aims for this UAV to fuel collaboration among manned and unmanned aircraft. For its first test run, the Skyborg suite flew aboard a Kratos UTAP-22 Mako air vehicle in the first step of what’s known as the Autonomous Attritable Aircraft Experimentation Campaign.
By and large, the US Air Force Research Laboratory seeks a UAV solution that can carry out all of the functions of a manned aerial vehicle but also with the option of manned operation.