Join us July 11th for our first fully crewed rocket powered test flight, and the beginning of a new space age. The countdown begins. #Unity22
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
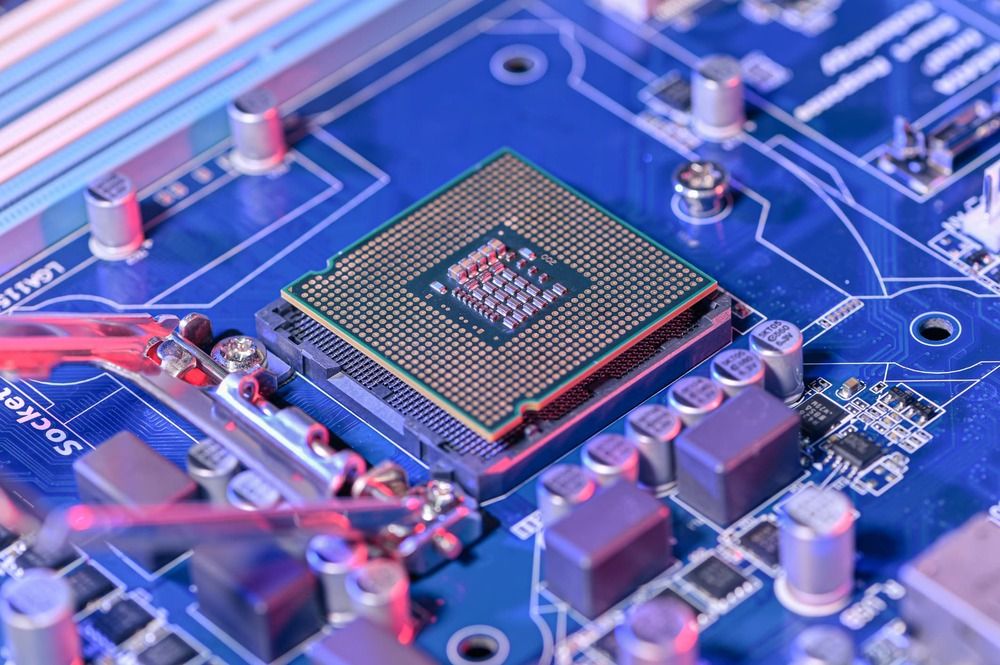
UK’s largest chip plant to be acquired
LONDON – Newport Wafer Fab, the U.K.’s largest chip producer, is set to be acquired by Chinese-owned semiconductor company Nexperia for around £63 million ($87 million) next week, according to two sources close to the deal who asked to remain anonymous because the information is not yet public.
Nexperia, a Dutch firm that is 100%-owned by China’s Wingtech Technology, told CNBC on Friday that the deal talks are ongoing.
Located in Newport, South Wales, privately-held NWF’s chip plant dates back to 1982 and it is one of just a handful of semiconductor fabricators in the U.K.
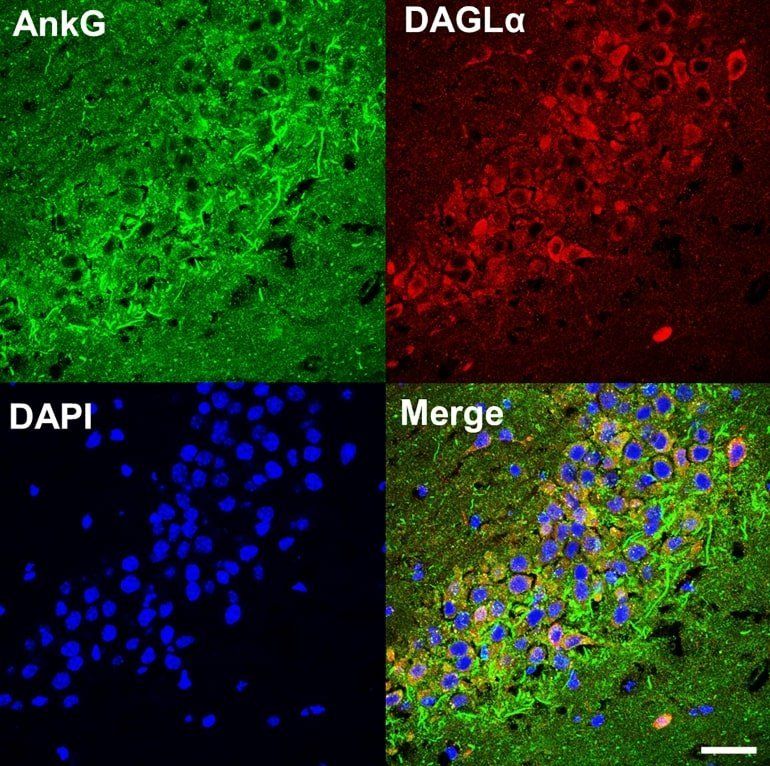
Cannabinoid Pathway Linked to Psychiatric Disorders
“Cannabis may contribute to increased risk for mental disorders, which has actually been shown in schizophrenia,” Penzes said. “Conversely, cannabis could be beneficial in some brain disorders, which prompted trials of medical marijuana in patients with autism.”
Summary: Findings reveal a role the endocannabinoid system plays in a range of psychiatric disorders, including schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and ASD.
Source: Northwestern University
Northwestern Medicine scientists discovered an unexpected connection between a synapse protein that has been implicated in neuropsychiatric disorders and the endocannabinoid pathway, according to a study published in Biological Psychiatry.
These findings suggest a role for the endocannabinoid system in conditions including bipolar disorder, according to Peter Penzes, PhD, the Ruth and Evelyn Dunbar Professor of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences, professor of Physiology and Pharmacology, and senior author of the study.


A noninvasive technique for neurological conditions
Indiana University School of Medicine researchers are developing a new, noninvasive brain stimulation technique to treat neurological disorders, including pain, traumatic brain injury (TBI), epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease and more.
“Given the increasing use of brain stimulation in human brain study and treatment of neurological diseases, this research can make a big impact on physicians and their patients,” said Xiaoming Jin, Ph.D., associate professor of anatomy, cell biology and physiology.
When someone experiences a brain injury, nerve injury, or neurodegeneration, such as in epilepsy and TBI, there is damage to the brain which can lead to loss and damage of nerve or neurons and development of hyperexcitability that underlies some neurological disorders such as neuropathic pain and epilepsy.

Harvard, MIT researchers create COVID-19 diagnosing mask
Researchers from Harvard University and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, both based in Cambridge, Mass., have created small diagnostic biosensors that can be inserted into face masks and can diagnose COVID-19 within 90 minutes, The Mercury News reported June 29.
The insertable biosensors detect the virus from a wearer’s breath, producing easy to read results similar to those of an at-home pregnancy test. If the coronavirus is present, the system changes the pattern of lines in the readout strip.
To activate the test, the wearer pushes a button on the mask to release a small amount of water into the system, which activates the test.
The Technological Revolution (The 4th Industrial Revolution Explained)
This video was made possible by NordPass. Sign up with this link and get 70% off your premium subscription + 1 monrth for free! https://nordpass.com/futurology.
Visit Our Parent Company EarthOne For Sustainable Living Made Simple ➤
https://earthone.io/
The story of humanity is progress, from the origins of humanity with slow disjointed progress to the agricultural revolution with linear progress and furthermore to the industrial revolution with exponential almost unfathomable progress.
This accelerating rate of change of progress is due to the compounding effect of technology, in which it enables countless more from 3D printing, autonomous vehicles, blockchain, batteries, remote surgeries, virtual and augmented reality, robotics – the list can go on and on. These devices in turn will lead to mass changes in society from energy generation, monetary systems, space colonization, automation and much more!
This trajectory of progress is now leading us into a time period that is, “characterized by a fusion of technologies that is blurring the lines between the physical, digital and biological spheres”, called by many the technological revolution or the 4th industrial revolution — in which everything will change, from the underlying structure and fundamental institutions of society to how we live our day-to-day lives.
00:00 Intro.
AI Designs Quantum Physics Experiments Beyond What Any Human Has Conceived
This is only the Beginning.
Quantum physicist Mario Krenn remembers sitting in a café in Vienna in early 2016, poring over computer printouts, trying to make sense of what MELVIN had found. MELVIN was a machine-learning algorithm Krenn had built, a kind of artificial intelligence. Its job was to mix and match the building blocks of standard quantum experiments and find solutions to new problems. And it did find many interesting ones. But there was one that made no sense.
“The first thing I thought was, ‘My program has a bug, because the solution cannot exist,’” Krenn says. MELVIN had seemingly solved the problem of creating highly complex entangled states involving multiple photons (entangled states being those that once made Albert Einstein invoke the specter of “spooky action at a distance”). Krenn and his colleagues had not explicitly provided MELVIN the rules needed to generate such complex states, yet it had found a way. Eventually, he realized that the algorithm had rediscovered a type of experimental arrangement that had been devised in the early 1990s. But those experiments had been much simpler. MELVIN had cracked a far more complex puzzle.
“When we understood what was going on, we were immediately able to generalize [the solution],” says Krenn, who is now at the University of Toronto. Since then, other teams have started performing the experiments identified by MELVIN, allowing them to test the conceptual underpinnings of quantum mechanics in new ways. Meanwhile Krenn, Anton Zeilinger of the University of Vienna and their colleagues have refined their machine-learning algorithms. Their latest effort, an AI called THESEUS, has upped the ante: it is orders of magnitude faster than MELVIN, and humans can readily parse its output. While it would take Krenn and his colleagues days or even weeks to understand MELVIN’s meanderings, they can almost immediately figure out what THESEUS is saying.

Someone recently asked the question on Quora, How does AI affect social media?
Below is my Answer.
“There is big confluence between AI & Social Media. It is a two way thing, AI not only affects Social Media, Social Media also plays a great role in the development of AI.
The way AI is developed is through data, large data (big data) and one of the easiest ways to generate and source for data at this scale is from the contents and interactions on social media.
Most social media platforms operate at scale, so for issues such as monitoring or censorship of what is being posted, the admin of these platforms have to use automation and AI for its management and policing.
AI algorithms such as sentiment analysis or recommendation engines (used by Facebook & Youtube to recommend posts based on the AI understanding of what you will like) are very much an integral part of any social platform architecture.
AI is integral to how and when Adverts are delivered to you on social media. AI controls the engagement levels on your posts and ensures that people who are most likely interested in the topics or communities you belong to get recommended to you as connection; this is because engagement is key goal for every social media platform.
So as you can see, AI plays a very critical role in social media. But beyond this, it is also important to mention that not all the effects of AI on social media are positive ones. For example, AI ensures a never ending supply of content recommendation (recommendation engines) that can keep you engrossed in social media, using time in an unproductive way.

Nathan Seiberg on How Math Might Complete the Ultimate Physics Theory
Nathan Seiberg, 64, still does a lot of the electrical work and even some of the plumbing around his house in Princeton, New Jersey. It’s an interest he developed as a kid growing up in Israel, where he tinkered with his car and built a radio.
“I was always fascinated by solving problems and understanding how things work,” he said.
Seiberg’s professional career has been about problem solving, too, though nothing as straightforward as fixing radios. He’s a physicist at the Institute for Advanced Study, and over the course of a long and decorated career he has made many contributions to the development of quantum field theory, or QFT.