
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
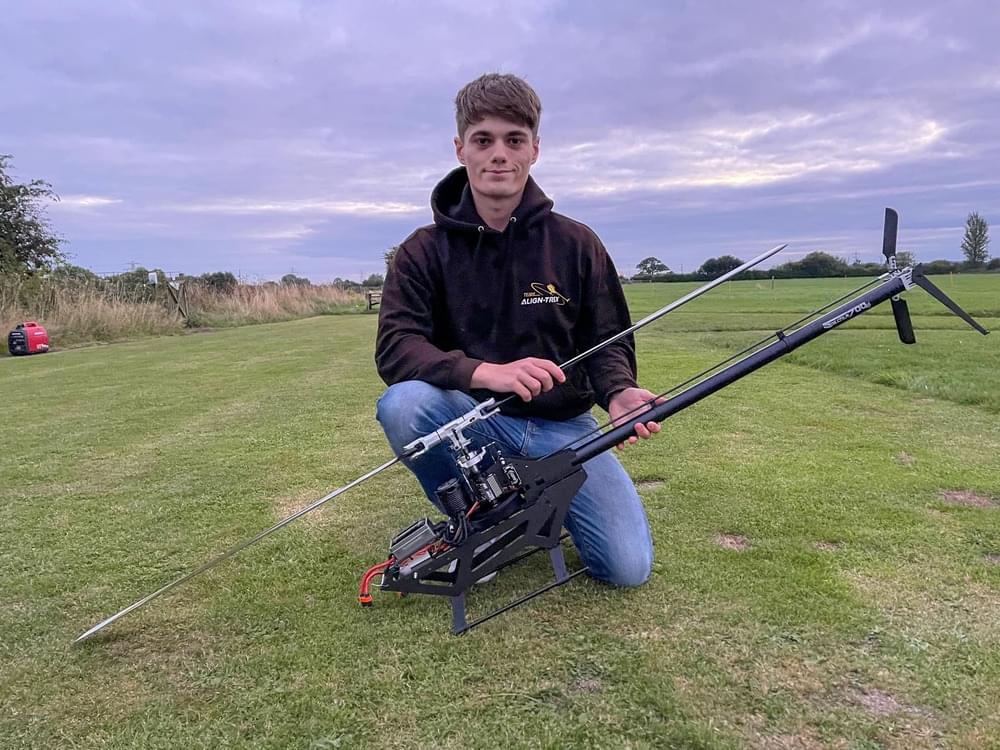




Here’s the new Specter 700 V2 all built and flight ready 😁
Sorry if I look a bit horrible, I’ve been a bit ill the past few days. But the V2 sure doesn’t look half bad. She does indeed fly as good as she looks.
As mentioned before the feeling of the tail is a big improvement, the head itself feels much tighter and more locked in, in part thanks to the more rigid frame. It also flips on a dime too, thanks to the lowered head and more central centre of gravity.
All in all I’m loving this model. It’s getting dark now, I should probably go home… one more flight maybe 😂
ALIGN TREX Models.
XLPower.
#TeamAT #Specter700V2 #XLpower #ATModels
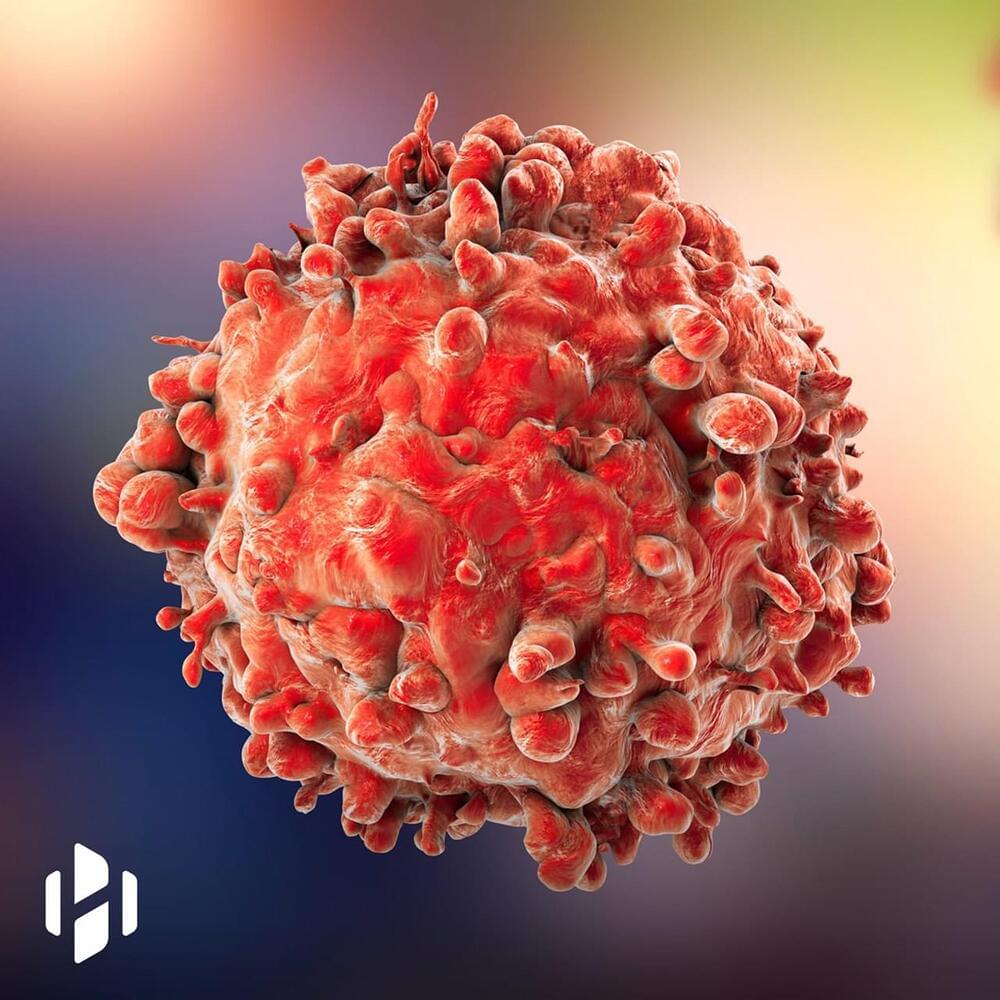
A Vaccine To Prevent Cancer Evolution
A cancer vaccine could be an effective way to prevent cancer from evolving and becoming resistant to treatment, new research suggests.
Scientists were investigating the use of a cancer-killing virus in clinical trials, and observed, as they had also seen in mice, that although some patients initially responded to the treatment, their tumours soon became resistant.
The researchers showed that the specific mutations causing tumour cells to become resistant to the viral treatment, could be anticipated and exploited using a vaccine which, when tested in mice, was shown to trigger the immune system to destroy treatment resistant tumour cells.
Scientists have developed a cancer vaccine that in mice was shown to trigger the immune system to destroy treatment-resistant tumor cells.

Car of the Week: The 2,040 HP Estrema Fulminea Hypercar May Be a Lightning Strike on the EV Market
New marque Automobili Estrema plans for its first model to reach 200 mph in less than 10 seconds and have a 325-mile range.
Automobili Estrema is a marque soon to become synonymous with extreme technology and performance in the hypercar stratosphere. Founded in 2020—a challenging year by any measure—the company is Italian through and through, though its team members and partners represent a global Who’s Who of leaders within the energy and automotive industries. Founder and CEO Gianfranco Pizzuto, an entrepreneur with an international business background, was the first investor and cofounder of Fisker Automotive in 2007. It was a bold venture into uncharted territory at a time when EVs were experiments and the first Tesla Roadster was still a year away. Now, as head of Automobili Estrema, he and his team have spent a year in virtual collaboration and accomplished what is nothing less than remarkable.
Headless, Two-Legged Robot Digit Is Now Ready to Take Over Your Duties
It was “born” in 2019 when its creator, Agility Robotics, first introduced it as a highly-capable robot with legs and arms, suited for both indoor and outdoor use. Now Digit is available for purchase and ready to take over your tedious duties.
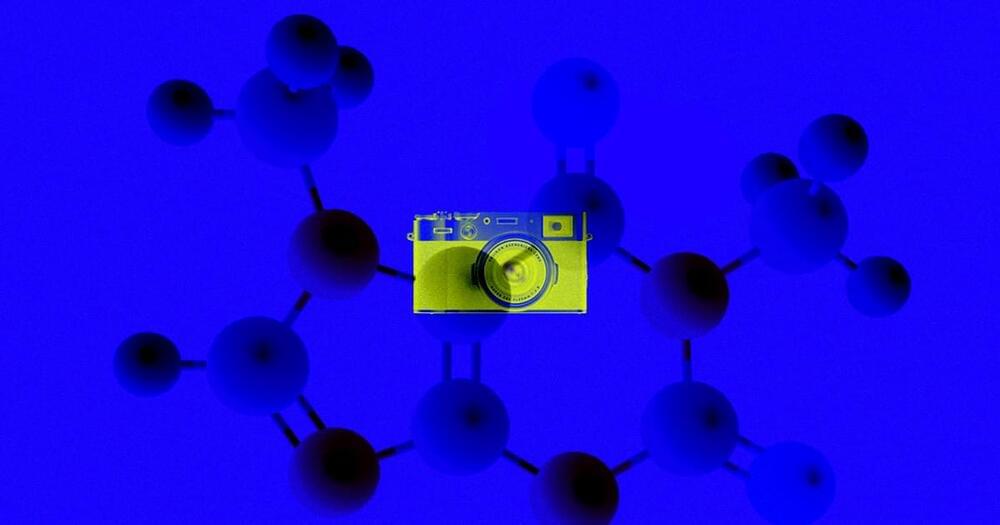

Scientists Build Molecule-Sized “Camera” To Watch Chemical Reactions in Real-Time
The device offers a far simpler way of monitoring how various chemical compounds form during reactions than the methods currently available to scientists, and the team that built the “camera” says it’s already using it to improve the technology behind solar cells.
Controlling the specific order and process of molecular assembly is notoriously difficult, especially at such tiny scales. Thankfully, the scientists realized that they merely had to plunk its components into room-temperature water — along with whatever molecules they wanted to study — and it would piece itself together automatically.
“We were surprised how powerful this new tool is, considering how straightforward it is to assemble,” first study author and Cambridge chemist Kamil Sokolowski said in a press release.