AI is already pretty powerful when humans show it what to do. As it gets better at drawing smart conclusions on its own, the technology will enter a new “age of self.”
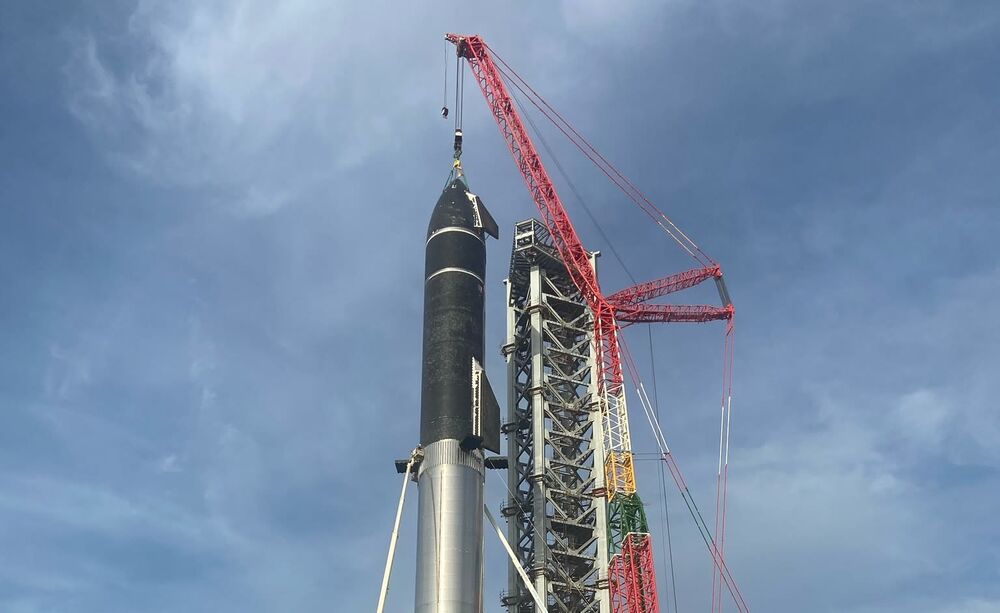



Elon Musk’s SpaceX stacked a Starship prototype rocket on top of a Super Heavy rocket booster for the first time Friday morning, giving a look at the scale of the combined nearly 400-foot-tall vehicle.
Musk, asked by CNBC what he thought of witnessing the milestone at the company’s facility in Boca Chica, Texas, responded simply.
“Dream come true,” Musk replied in a tweet.

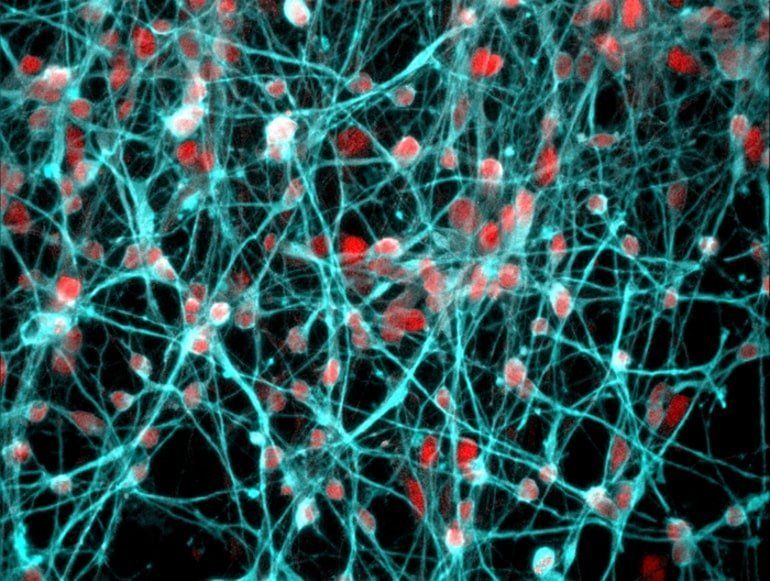
Summary: Study reveals a link between corticosteroid receptors and genes associated with ciliary and neuroplasticity in the hippocampus, an area of the brain associated with stress response, learning, and memory.
Source: University of Bristol.
Chronic stress is a well-known cause of mental health disorders. New research has moved a step forward in understanding how glucocorticoid hormones (‘stress hormones’) act upon the brain and what their function is. The findings could lead to more effective strategies in the prevention and treatment of mental health disorders.
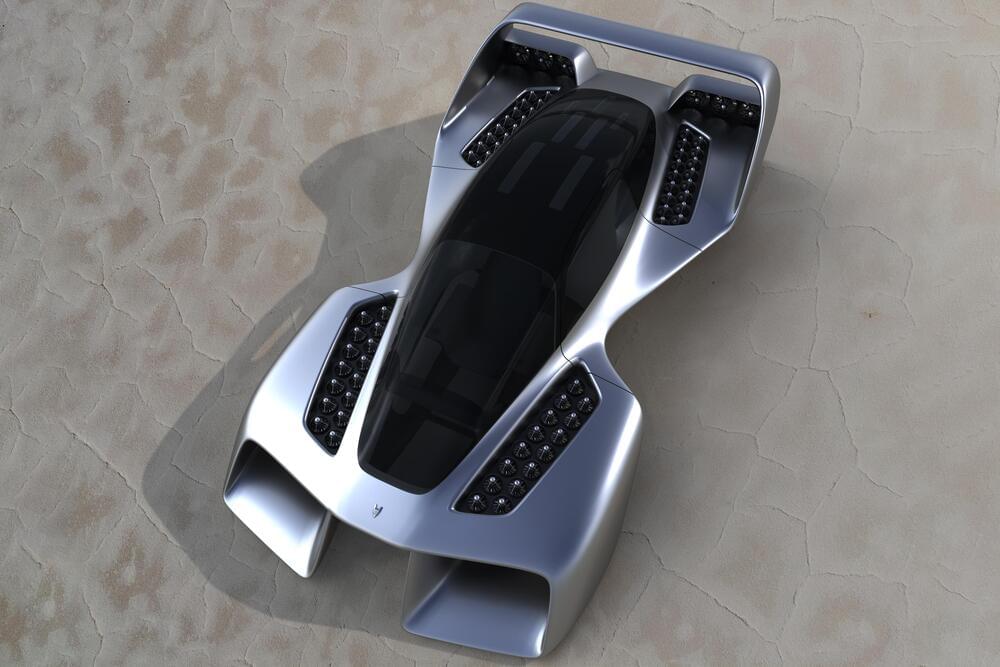

An electric propulsion specialist and a supercar designer have partnered up on an eye-catching three-seat eVTOL, claiming 250-mph (400 km/h) top speeds and extraordinary 300-mile (483-km) range figures, as well as some extreme flight dynamics and some nifty ideas.
Pete Bitar has been working on vertical propulsion systems for decades now. He’s got a DARPA contract to develop his electric jetpack designs, his Verticycle is a competitor in the GoFly personal flight challenge, and he’s just won one of nine NASA “Future-Scaping Our Skies” awards for his work on ground infrastructure and air traffic control for the coming eVTOL age.
Now he’s partnered up with automotive designer Carlos Salaff to start an eVTOL company. Salaff was behind the outrageous Mazda Furai concept, and has in more recent years been showing his own outrageous coach-built creations at events such as Pebble Beach.

No, it’s not forbidden to innovate, quite the opposite, but it’s always risky to do something different from what people are used to. Risk is the middle name of the bold, the builders of the future. Those who constantly face resistance from skeptics. Those who fail eight times and get up nine.
(Credit: Adobe Stock)
Fernando Pessoa’s “First you find it strange. Then you can’t get enough of it.” contained intolerable toxicity levels for Salazar’s Estado Novo (Portugal). When the level of difference increases, censorship follows. You can’t censor censorship (or can you?) when, deep down, it’s a matter of fear of difference. Yes, it’s fear! Fear of accepting/facing the unknown. Fear of change.
What do I mean by this? Well, I may seem weird or strange with the ideas and actions I take in life, but within my weirdness, there is a kind of “Eye of Agamotto” (sometimes being a curse for me)… What I see is authentic and vivid. Sooner or later, that future I glimpse passes into this reality.
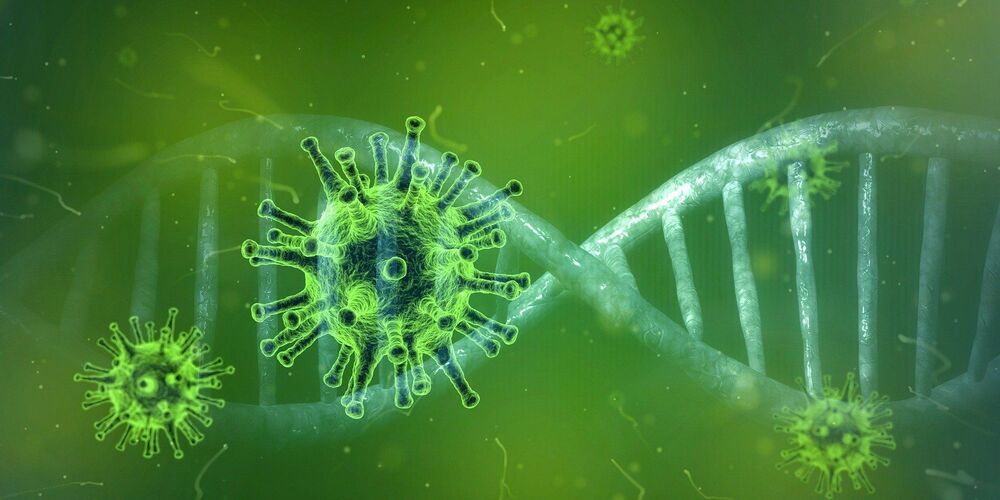


The same process that eliminates replication errors also eliminates antiviral agents delivered by the treatments commonly used to fight other RNA viruses, such as HIV, HCV and Ebola virus, which partially explains why SARS-CoV-2 has proven so difficult to treat, Yang said.
The coronavirus that causes COVID-19 has demonstrated a stubborn ability to resist most nucleoside antiviral treatments, but a new study led by an Iowa State University scientist could help to overcome the virus’s defenses.
The study, published recently in the peer-reviewed journal Science, details the structure of a critical enzyme present in SARS-CoV-2, the coronavirus that causes COVID-19. This enzyme, known as the proofreading exoribonuclease (or ExoN), removes nucleoside antiviral medications from the virus’s RNA, rendering most nucleoside analogs-based antiviral treatments ineffective. The new study presents the atomic structures of the ExoN enzyme, which could lead to the development of new methods for deactivating the enzyme and opening the door to better treatments for patients suffering from COVID-19.
“If we could find a way to inhibit this enzyme, maybe we can achieve better results to kill the virus with existing nucleoside antiviral treatments. Understanding this structure and the molecular details of how ExoN works can help guide further development of antivirals,” said Yang Yang, lead author of the study and assistant professor in the Roy J. Carver Department of Biochemistry, Biophysics and Molecular Biology at Iowa State University.

