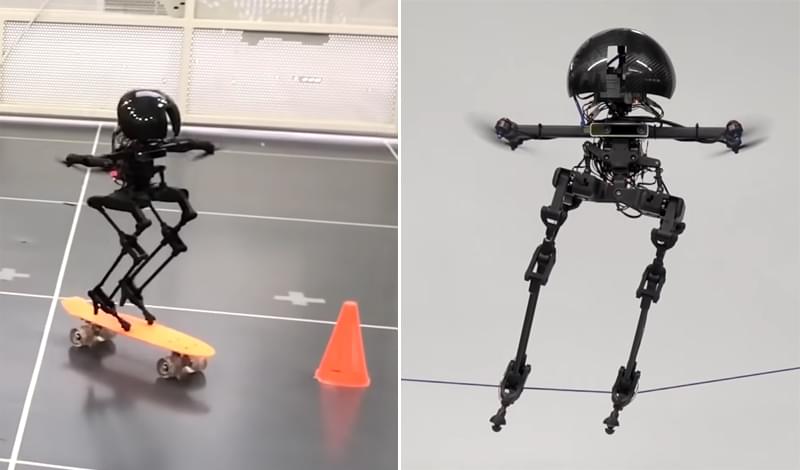
Researchers at the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) have built a bipedal robot that combines walking with flying to create a new type of locomotion, making it exceptionally nimble and capable of complex movements.
Part walking robot, part flying drone, the newly developed LEONARDO (short for LEgs ONboARD drOne, or LEO for short) can walk a slackline, hop, and even ride a skateboard. Developed by a team at Caltech’s Center for Autonomous Systems and Technologies (CAST), LEO is the first robot that uses multi-joint legs and propeller-based thrusters to achieve a fine degree of control over its balance.
“We drew inspiration from nature. Think about the way birds are able to flap and hop to navigate telephone lines,” explained Soon-Jo Chung, Professor of Aerospace and Control and Dynamical Systems. “A complex yet intriguing behaviour happens as birds move between walking and flying. We wanted to understand and learn from that.”