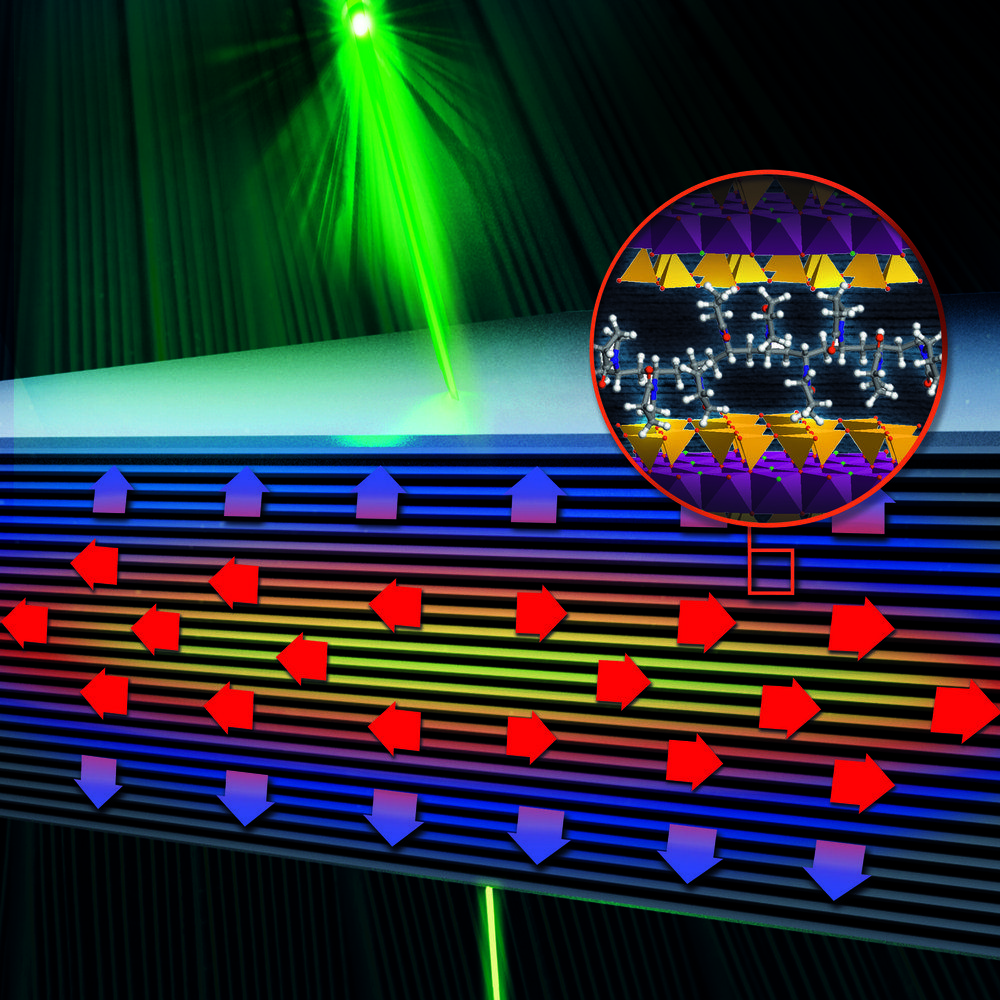
Styrofoam or copper—both materials have very different properties with regard to their ability to conduct heat. Scientists at the Max Planck Institute for Polymer Research (MPI-P) in Mainz and the University of Bayreuth have now jointly developed and characterized a novel, extremely thin and transparent material that has different thermal conduction properties depending on the direction. While it can conduct heat extremely well in one direction, it shows good thermal insulation in the other direction.
Thermal insulation and thermal conduction play a crucial role in our everyday lives—from computer processors, where it is important to dissipate heat as quickly as possible, to houses, where good insulation is essential for energy costs. Often extremely light, porous materials such as polystyrene are used for insulation, while heavy materials such as metals are used for heat dissipation. A newly developed material, which scientists at the MPI-P have jointly developed and characterized with the University of Bayreuth, can now combine both properties.
The material consists of alternating layers of wafer-thin glass plates between which individual polymer chains are inserted. “In principle, our material produced in this way corresponds to the principle of double glazing,” says Markus Retsch, Professor at the University of Bayreuth. “It only shows the difference that we not only have two layers, but hundreds.”