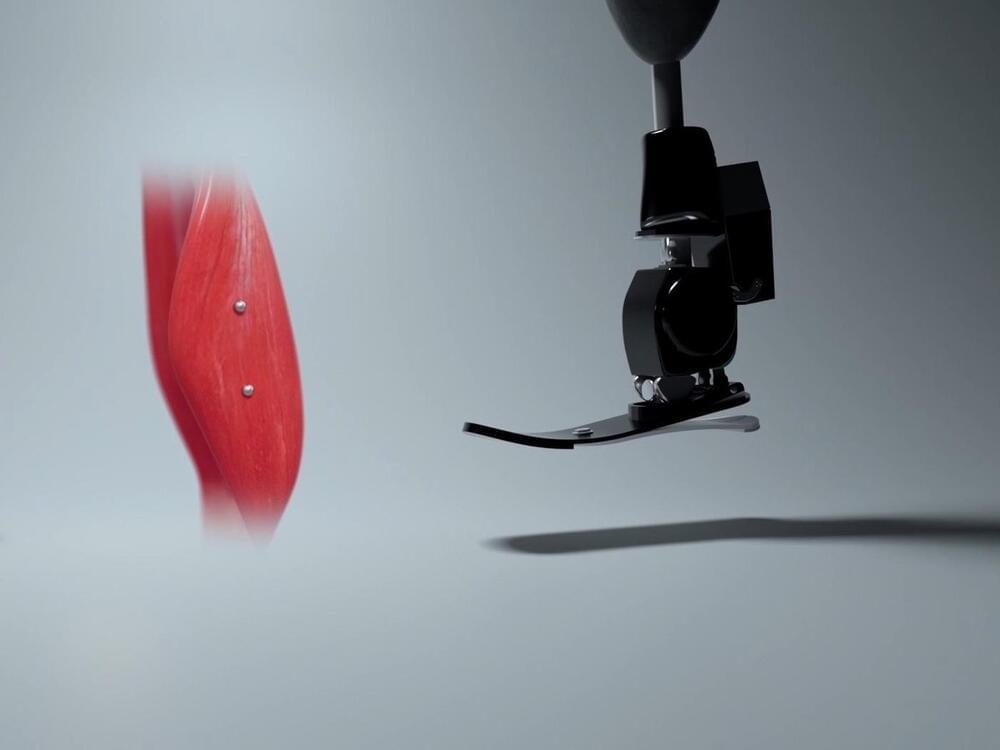
Why do so many people get frustrated with their “high-tech” prostheses? Though sophisticated robotics allow for prosthetic joints that can do everything a human can and more, the way we control robotic machines right now doesn’t allow us to operate them as naturally as you would a biological hand. Most robotic prostheses are controlled via metal pads on the skin that indirectly measure muscle action and then make some assumptions to determine what the person wants to do. Whil… See More.
We plan to use MM to provide natural control over prosthetic limbs by leveraging the human body’s proprioception. When you wiggle one of your fingers, your brain senses muscle lengths, speeds, and forces, and it uses these to figure out the position of that finger. This is called body awareness, or proprioception. When someone receives an amputation, if their muscle connections are maintained with what is called the “AMI technique,” their brain still perceives muscle flexion as it relates to joint movement, as if their limb was still present. In other words, they are sensing movement of a phantom limb. To give an amputee intuitive control over a robotic prosthesis, we plan to directly measure the muscle lengths and speeds involved in this phantom limb experience and have the robot copy what the brain expects, so that the brain experiences awareness of the robot’s current state. We see this technique as an important next step in the embodiment of the prosthetic limb (the feeling that it is truly part of one’s body).
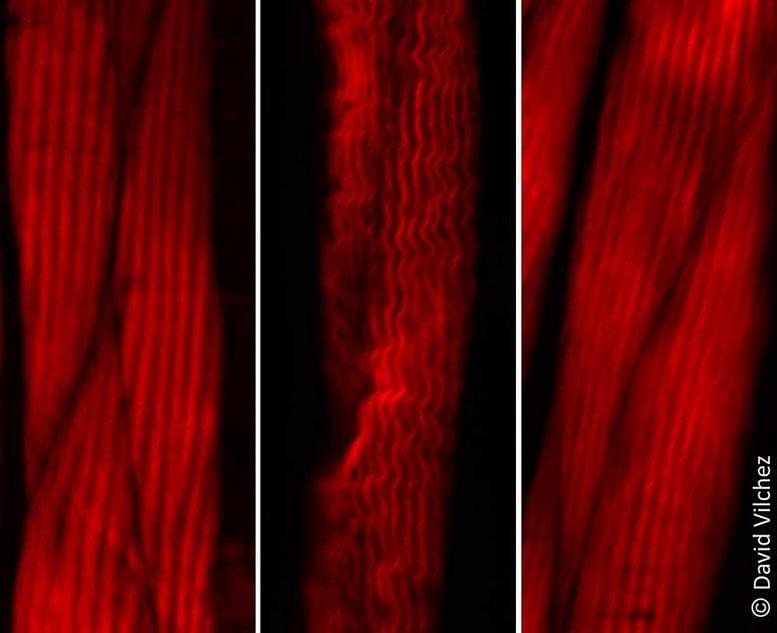
Notably, the tracking of magnetic beads is minimally invasive, not requiring wires to run through the skin boundary or electronics to be implanted inside the body, and these magnetic beads can be made safe to implant by coating them in a biocompatible material. In addition, for muscles that are close to the skin, MM can be performed with very high accuracy. We found that by increasing the number of compass sensors we used, we could track live muscle lengths close to the surface of the skin with better than millimeter accuracy, and we found that our measurements were consistent to within the width of a human hair (about 37 thousandths of a millimeter).
The concept of tracking magnets through human tissue is not a new concept. This is the first time, however, that magnets have been tracked at sufficiently high speed for intuitive, reflexive control of a prosthesis. To reach this sufficiently high tracking speed, we had to improve upon traditional magnet tracking algorithms; these improvements are outlined in our previous work on tracking multiple magnets with low time delay, which also describes how we can account for the earth’s magnetic field during portable muscle-length tracking. This is also the first time that a pair of magnets has been used as a distance sensor. MM extends the capabilities we currently have with wired-ultrasound-crystal distance sensing (sonomicrometry, SM) and tantalum-bead-based distance sensing via multiple-perspective X-ray video (fluoromicrometry, FM), enabling us to now wirelessly sense distances in the body while a person moves about in a natural environment.