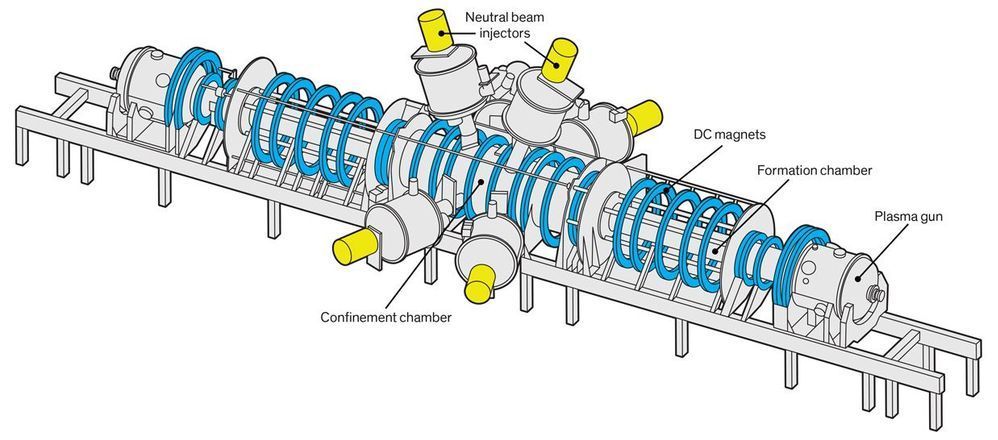
After decades of not happening, fusion power finally appears to be maybe possibly happening.
The joke has been around almost as long as the dream: Nuclear fusion energy is 30 years away…and always will be. But now, more than 80 years after Australian physicist Mark Oliphant first observed deuterium atoms fusing and releasing dollops of energy, it may finally be time to update the punch line.
Over the past several years, more than two dozen research groups—impressively staffed and well-funded startups, university programs, and corporate projects—have achieved eye-opening advances in controlled nuclear fusion. They’re building fusion reactors based on radically different designs that challenge the two mainstream approaches, which use either a huge, doughnut-shaped magnetic vessel called a tokamak or enormously powerful lasers.
What’s more, some of these groups are predicting significant fusion milestones within the next five years, including reaching the breakeven point at which the energy produced surpasses the energy used to spark the reaction. That’s shockingly soon, considering that the mainstream projects pursuing the conventional tokamak and laser-based approaches have been laboring for decades and spent billions of dollars without achieving breakeven.