An international team of planetary scientists led by astronomers at AOP have found an asteroid trailing behind Mars with a composition very similar to the moon’s. The asteroid could be an ancient piece of debris, dating back to the gigantic impacts that formed the moon and the other rocky planets in our solar system like Mars and the Earth. The research, which was published in the journal Icarus, also has implications for finding such primordial objects associated with our own planet.
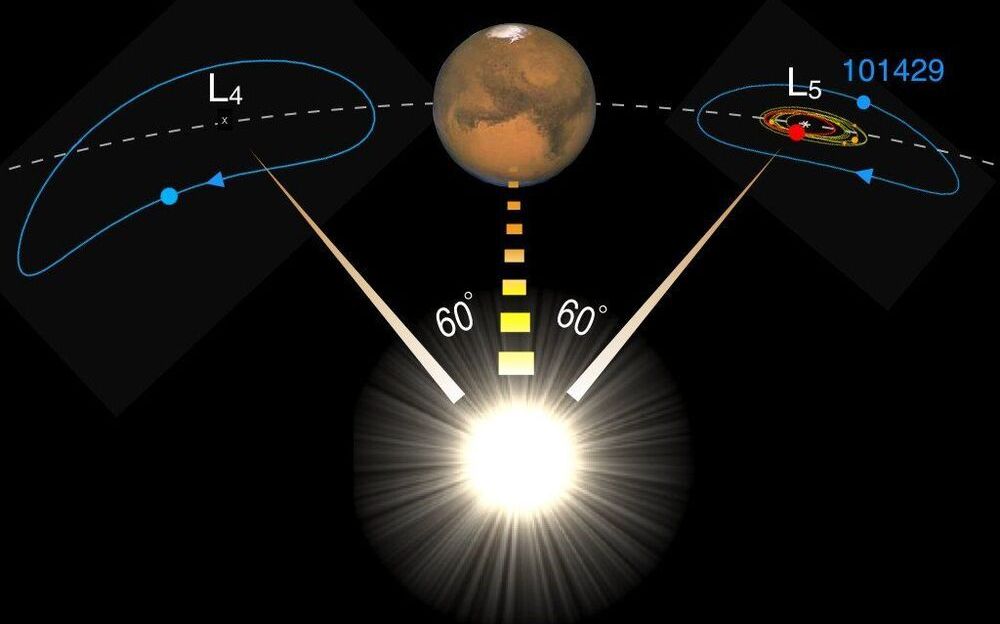
Trojans are a class of asteroid that follows the planets in their orbits as a flock of sheep might follow a shepherd, trapped within gravitational “safe havens” 60 degrees in front of, and behind, the planet (Figure 1). They are of great interest to scientists as they represent leftover material from the formation and early evolution of the solar system. Several thousands of those Trojans exist along the orbit of the giant planet Jupiter. Closer to the Sun, astronomers have so far discovered only a handful of Trojans of Mars, the planet next door to Earth.
A team including scientists from Italy, Bulgaria and the US and led by the Armagh Observatory and Planetarium (AOP) in Northern Ireland has been studying the Trojans of Mars to understand what they tell us about the early history of the inner worlds of our solar system—the so-called terrestrial planets—but also to inform searches for Trojans of the Earth. Ironically, it is much easier to find Trojans of Mars than for our own planet because these Earth Trojans, if they exist, sit always close to the Sun in the sky where it is difficult to point a telescope. An Earth Trojan, named 2010 TK7, was found a decade ago by NASA’s WISE space telescope, but computer modeling showed it is a temporary visitor from the belt of asteroids between Mars and Jupiter rather than a relic planetesimal from the Earth’s formation.