Welcome to “The curious observer’s guide to quantum mechanics”–featuring particle/wave duality.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.


Researchers develop new one-step process for creating self-assembled metamaterials
A team led by University of Minnesota Twin Cities researchers has discovered a groundbreaking one-step process for creating materials with unique properties, called metamaterials. Their results show the realistic possibility of designing similar self-assembled structures with the potential of creating “built-to-order” nanostructures for wide application in electronics and optical devices.
The research was published and featured on the cover of Nano Letters, a peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the American Chemical Society.
In general, metamaterials are materials made in the lab so as to provide specific physical, chemical, electrical, and optical properties otherwise impossible to find in naturally occurring materials. These materials can have unique properties which make them ideal for a variety of applications from optical filters and medical devices to aircraft soundproofing and infrastructure monitoring. Usually these nano-scale materials are painstakingly produced in a specialized clean room environment over days and weeks in a multi-step fabrication process.
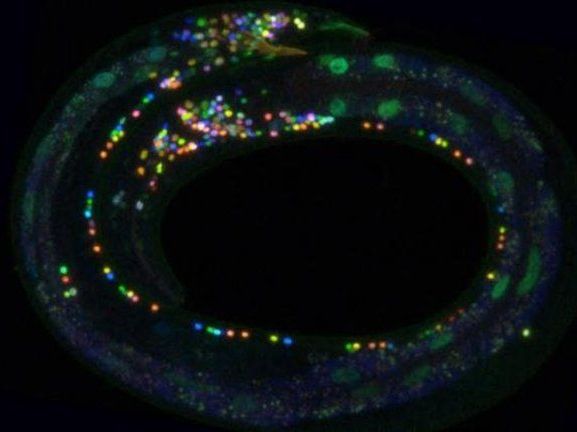
Scientists Paint Multicolor Atlas of the Brain
Summary: A newly developed technique dubbed NeuroPAL is helping researchers investigate the dynamics of neural networks in the nervous system of microscopic worms.
Source: Columbia University.
The human brain contains approximately 86 billion neurons, or nerve cells, woven together by an estimated 100 trillion connections, or synapses. Each cell has a role that helps us to move muscles, process our environment, form memories, and much more.
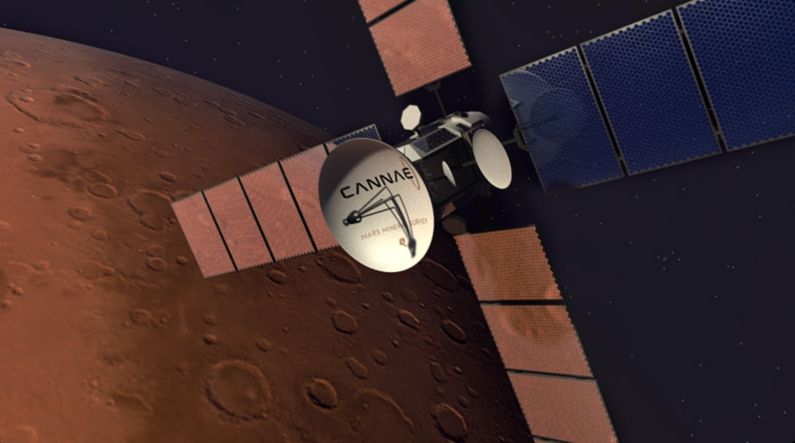


NASA says puzzling new space drive can generate thrust without propellant
Circa 2014
A NASA study has recently concluded that the “Cannae Drive,” a disruptive new method of space propulsion, can produce small amounts of thrust without the use of propellant, in apparent discordance with Newton’s third law. According to its inventor, the device can harness microwave radiation inside a resonator, turning electricity into a net thrust. If further verified and perfected, the advance could revolutionize the space industry, dramatically cutting costs for both missions in deep space and satellites in Earth orbit.
The basic principle behind space propulsion is very simple: for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. Use a rocket engine to throw mass one way, get propelled the other way. And according to the law of conservation of momentum, the more mass you throw behind you and the faster you throw it, the stronger your forward thrust will be.
One consequence for space travel is that, to counter Earth’s gravity and reach orbital velocity, rockets need to carry a very large amount of propellant: For instance, in the now-retired Space Shuttle, the mass of the fuel was almost twenty times greater than the payload itself. In satellites the impact is smaller, but still very significant: for geostationary satellites, fuel can make up as much as half the launch weight, and that makes them more expensive to launch and operate.



Dr. Tim R. Peterson — Moonshot Thinking For Aging, Mental Health, And Drug Re-Purposing
Moonshot Thinking For Aging, Mental Health, And Drug Re-Purposing — Dr. Tim R. Peterson.
Washington University in St. Louis.
Dr. Tim R. Peterson PhD. is Assistant Professor, in the Department of Medicine, at Washington University in St. Louis.
Dr. Peterson went to the Massachusetts Institutes of Technology (MIT) where he received his doctorate in biology.
Dr. Peterson’s lab is interested in quality of life issues that affect all people, indirectly or directly, and two critical conditions that his lab is especially interested in are aging (specifically research on health span – the healthy period of one’s life) and mental health / mental health equality for all people.