Advances make high-density, 5D optical storage practical for long-term data archiving.
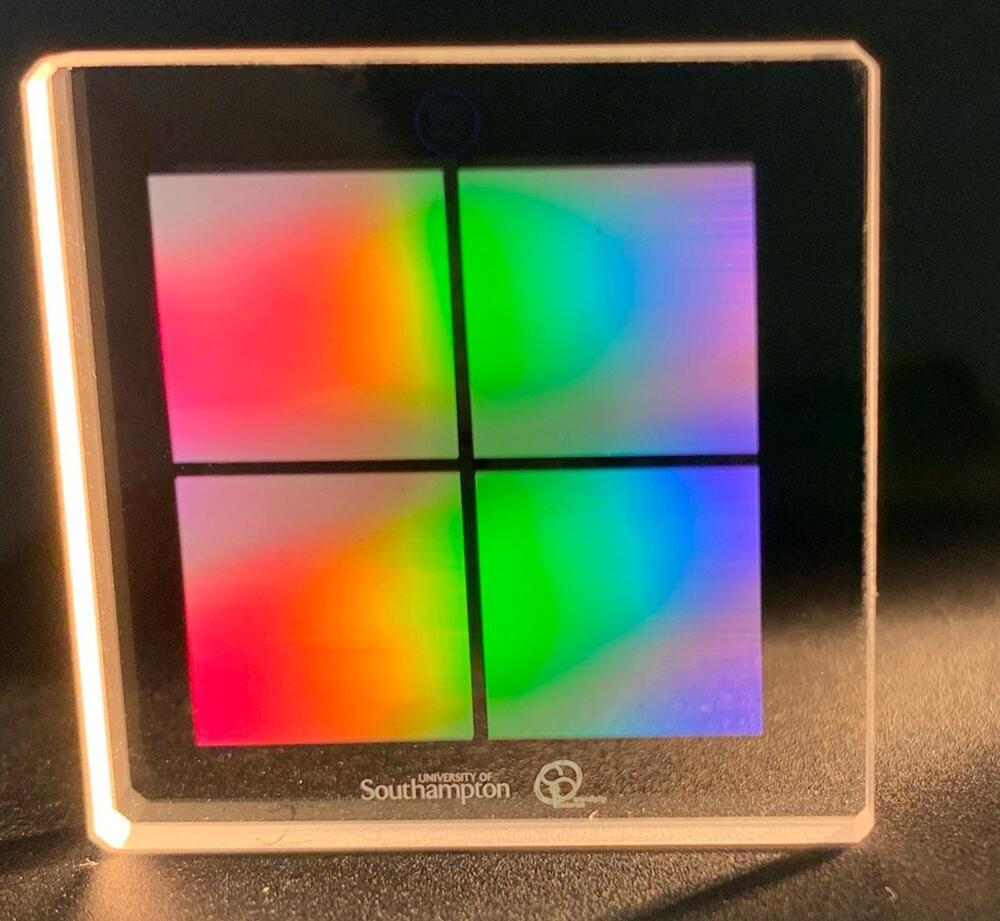
Researchers have developed a fast and energy-efficient laser-writing method for producing high-density nanostructures in silica glass. These tiny structures can be used for long-term five-dimensional (5D) optical data storage that is more than 10,000 times denser than Blue-Ray optical disc storage technology.
“Individuals and organizations are generating ever-larger datasets, creating the desperate need for more efficient forms of data storage with a high capacity, low energy consumption and long lifetime,” said doctoral researcher Yuhao Lei from the University of Southampton in the UK. “While cloud-based systems are designed more for temporary data, we believe that 5D data storage in glass could be useful for longer-term data storage for national archives, museums, libraries or private organizations.”