Google’s Threat Analysis Group (TAG) is tracking more than 270 government-backed threat actors from more than 50 countries.



As many as 130 different ransomware families have been found to be active in 2020 and the first half of 2,021 with Israel, South Korea, Vietnam, China, Singapore, India, Kazakhstan, Philippines, Iran, and the U.K. emerging as the most affected territories, a comprehensive analysis of 80 million ransomware-related samples has revealed.
Google’s cybersecurity arm VirusTotal attributed a significant chunk of the activity to the GandCrab ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) group (78.5%), followed by Babuk (7.61%), Cerber (3.11%), Matsnu (2.63%), Wannacry (2.41%), Congur (1.52%), Locky (1.29%), Teslacrypt (1.12%), Rkor (1.11%), and Reveon (0.70%).
Developing quantum-gravity technologies may elevate us to a “class A” civilization, capable of creating a baby universe.
facebook Share on Facebook Share on Twitter Share via Email.

WWhy Hasn’t Elon Musk Been To Space?: Jeff Bezos decided to mark the first success of the long-running New Shepard project with a flight to space, literally. And Richard Branson recently did the same with Virgin Galactic.
However, something is off with the CEO of SpaceX, Elon Musk. Despite having made so many breakthroughs in space travel, Elon Musk has never once taken a trip to space. But, Why is that? Well, we will find out in just a second.
Elon Musk was at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida on the day SpaceX’s first space tourists launched, clapping as the private astronauts walked past the Tesla that would transport them to suit.

Is Planetary Defense PI in the Sky?
In February of 2,013 skywatchers around the world turned their attention toward asteroid 2012 DA14, a cosmic rock about 150 feet (50 meters) in diameter that was going to fly closer to Earth than the spacecraft that bring us satellite TV.
Little did they realize as they prepared for the once-in-several-decades event that another bit of celestial debris was hurtling toward Earth, with a more direct heading. On February 15 2013, the Chelyabinsk meteor, a roughly 62-foot (19 meter)-diameter asteroid exploded over the city of Chelyabinsk, Russia, as it entered Earth’s atmosphere at a shallow angle. The blast shattered windows and damaged buildings, and nearly two thousand people were hurt, though thankfully no one died.
This looks familiar…
Robo Woman — 1,968 taken from the British Pathe reel “Miss Honeywell — World’s First Robotic Woman”. See this playlist of our best clips:
https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLF58DA24745914ADC
See the original Robo Woman video with its full Pathe commentary and extra shots here:
http://www.britishpathe.com/video/miss-honeywell/
The music is taken from a live art performance recorded by Pathe in Paris in 1964. You can watch the exciting piece here:
http://www.britishpathe.com/video/futuristic-music-and-dance-in-paris/ (The jazzy “electro” music in the middle is from the original reel, so you want the top link above for that)
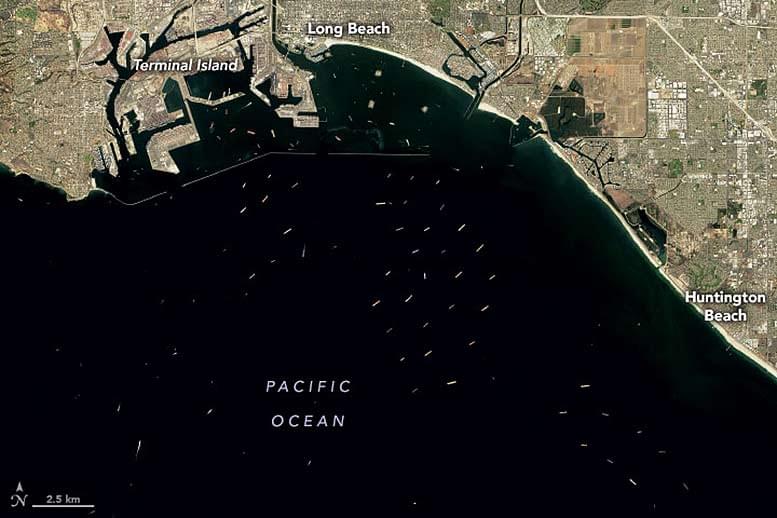
The pandemic has disrupted global supply chains and markets in ways that have led to backlogs of cargo ships at key ports.
Booming demand for consumer and goods, labor shortages, bad weather, and an array of COVID-related supply chain snarls are contributing to backlogs of cargo ships at ports around the world.
Among those seaports are the Port of Los Angeles and Port of Long Beach in Southern California, the two busiest container ports in the United States. On October 10 2021, the Operational Land Imager (OLI) on Landsat 8 captured this natural-color image of dozens of cargo ships waiting offshore for their turn to unload goods. On the same day, the Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) on NASA.
“This speed bag resupply feature is a game changer for the warfighter,” said in a statement Mike Goodwin, sales and strategy manager Bell. “With the ability to drop supplies quickly and efficiently in a drop zone or a remote location, we can get critical supplies delivered as soon as they’re needed.”
Bell claims the APT has already flown 420 times at U.S. Marine Corps Air Station Yuma, in Georgia, and other sites. Now, the company is seeking to demonstrate how the aircraft can drop supplies on demand at its cruising speed of 80 mph (129 km/h).
For now, the vehicle’s main advantage is that it will simply drop the transported goods quickly near the location, allowing personnel to immediately retrieve supplies without needing to wait for aircraft to land and takeoff. This allows the drone to conserve battery power by minimizing hover time, extending its mission range and time, and increasing the chances the aircraft will survive.
By contrast, Lewis’s studies suggest it is extremely difficult for B. burgdorferi to evolve resistance to hygromycin. The chemical resembles essential nutrients that spirochaetes cannot make themselves and take up using a specific transporter, so mutations that block the take-up of hygromycin would also deprive spirochaetes of these nutrients.
Lewis says his team isn’t the first to discover the value of hygromycin. It was studied as a potential treatment for a pig disease in the 1980s but abandoned.
Vaccines against Lyme disease are also being developed, but eradicating the disease would be an even better option.
