Space needs a burdensome and expensive deep clean, and Woz’s Privateer apparently wants to take care of the mess.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.

Quantum mechanics for plants
Circa 2004
To what extent do photosynthetic organisms use quantum mechanics to optimize the capture and distribution of light? Answers are emerging from the examination of energy transfer at the submolecular scale.
The first law of photosynthetic economics is: “A photon saved is a photon earned.” Research into the factors behind this principle has been burgeoning, and has recently culminated in a paper in Physical Review Letters by Jang et al.1 in which the authors look at photosynthetic energy transfer at the quantum level.



Dr. Jean C. Accius, Ph.D. — Senior Vice President, AARP — Longer, Healthier, More Productive Lives
Longer, Healthier, And More Productive Lives — Dr. Jean Accius Ph.D., Senior Vice President, AARP
Dr. Jean C. Accius, PhD, is Senior Vice President, AARP Global Thought Leadership (https://www.aarp.org/). Dr. Accius leads a team in positioning AARP (formerly known as the American Association of Retired Persons) as a global thought leader, identifying emerging trends around the world, cultivating and elevating new ideas, forging global strategic alliances that become the foundation for collaboration and sparking bold solutions to change systems and improve the lives of the global population as it ages.
Dr. Accius is a passionate champion and catalyst for changing how the world sees and values aging. He is an internationally recognized thought leader on aging, longevity, equity, health systems transformation and modernizing the delivery and financing of long-term care. With tri-sector experience and deep knowledge, he has a strong track record of building high-performing teams, managing cross-functional operations and processes, and developing innovative and actionable solutions, policies, and programs to close the opportunity gap so that everyone can live longer, healthier and more productive lives.
A highly sought after author and speaker, Dr. Accius has been quoted by or appeared in numerous media outlets, including The New York Times, Forbes, TIME Magazine, USA Today, Reuters, Politico, Next Avenue, ESPN’s Undefeated, Rolling Out, NationSwell, Congressional Quarterly, and Huffington Post. In 2,020 he facilitated several sessions at the 50th annual World Economic Forum in Davos, Switzerland and also engaged nearly 300 leaders across industries and sectors, including 20 ambassadors and many delegates, at the United Nations.
Dr. Accius is a member of the National Association of Corporate Directors and has held a variety of board and advisory positions including Justice in Aging, the American Society on Aging, Leadership Maryland and the American University School of Public Affairs Board of Advisors.
Anna Kennedy Online
Anna’s guest at Women’s Radio was Dr Ian C E Hale I’m an Autistic person. It’s an indivisible part of who I am as an individual.
Annas guest at Women’s Radio was Dr Ian C E Hale ‘All things Autism will be aired at 1pm and 1am every day this week. Please see www.womensradiostation.com
Dr Ian C E Hale shared:
To be clear … it’s important to put my book and other work into context by knowing a little of their origins. I’m an Autistic person. It’s an indivisible part of who I am as an individual; it informs, goads and limits every thought and act of my life-but I refuse to let it define me. I’m a sportsman, poet, photographer, medical scientist and more-but first and foremost, a human being, with the same fears, hopes, weaknesses and feelings as everyone else.

NHS England announces large-scale trial of potential early cancer test
The NHS has launched the world’s largest trial of a potentially gamechanging blood test that aims to detect more than 50 types of cancer before symptoms appear.
More than 100,000 volunteers are being sought to provide blood samples at mobile test clinics in regions across England from Monday to assess how well the test works in the health service.
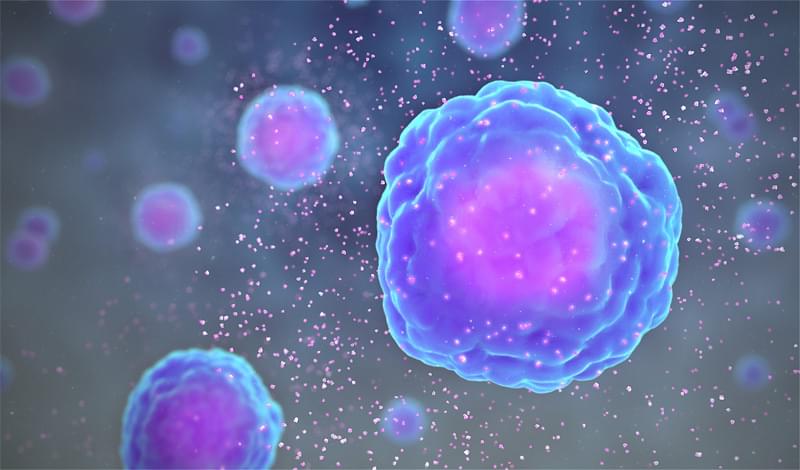
MRNA cancer therapy enters human trials after success in mice
BioNTech, the company that partnered with Pfizer to develop a COVID-19 vaccine, is now testing whether mRNA can be used to treat cancer.
Messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccines work by tricking our bodies into producing a small part of a virus. For the Pfizer–BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine, this involved isolating the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 (the virus that causes COVID-19). This protrudes from the outer surface of the virus and is used to latch onto specific cells in your body, infecting them and causing more copies of the virus to be made. Researchers obtained the spike protein’s RNA, then created mRNA based on these molecular instructions.
Once injected, the mRNA vaccine will instruct cells to build spike proteins in large volumes – not the virus itself, just the spike protein. This is enough to kickstart our immune response, training the body to recognise the spike protein, without making us sick. B-cells (also known as lymphocytes) can last for months or years and will “remember” the spike protein, making Y-shaped proteins called antibodies to destroy any SARS-CoV-2 encountered in the future.
