Fasting, sprinting, and timing: a science-backed morning combo to trigger your body’s regeneration mode


A fireside with Elon Musk at AI Startup School in San Francisco.
Before rockets and robots, Elon Musk was drilling holes through his office floor to borrow internet. In this candid talk, he walks through the early days of Zip2, the Falcon 1 launches that nearly ended SpaceX, and the “miracle” of Tesla surviving 2008.
He shares the thinking that guided him—building from first principles, doing useful things, and the belief that we’re in the middle of an intelligence big bang.
Chapters:
00:00 — Intro.
01:25 — His origin story.
02:00 — Dream to help build the internet.
04:40 — Zip2 and lessons learned.
08:00 — PayPal.
14:30 — Origin of SpaceX
18:30 — Building rockets from first principles.
23:50 — Lessons in leadership.
27:10 — Building up xAI
39:00 — Super intelligence and synthetic data.
39:30 — Multi-planetary future.
43:00 — Nueralink, AI safety and the singularity.
Andrej Karpathy’s keynote at AI Startup School in San Francisco. Slides provided by Andrej: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1a0h1mkwfmV2PlekxDN8isMrDA5evc4wW…
Drawing on his work at Stanford, OpenAI, and Tesla, Andrej sees a shift underway. Software is changing, again. We’ve entered the era of “Software 3.0,” where natural language becomes the new programming interface and models do the rest.
He explores what this shift means for developers, users, and the design of software itself— that we’re not just using new tools, but building a new kind of computer.
More content from Andrej: / @andrejkarpathy.
Chapters and Thoughts (From Andrej Karpathy!)
0:00 — Imo fair to say that software is changing quite fundamentally again. LLMs are a new kind of computer, and you program them *in English*. Hence I think they are well deserving of a major version upgrade in terms of software.
6:06 — LLMs have properties of utilities, of fabs, and of operating systems → New LLM OS, fabbed by labs, and distributed like utilities (for now). Many historical analogies apply — imo we are computing circa ~1960s.
14:39 — LLM psychology: LLMs = \.
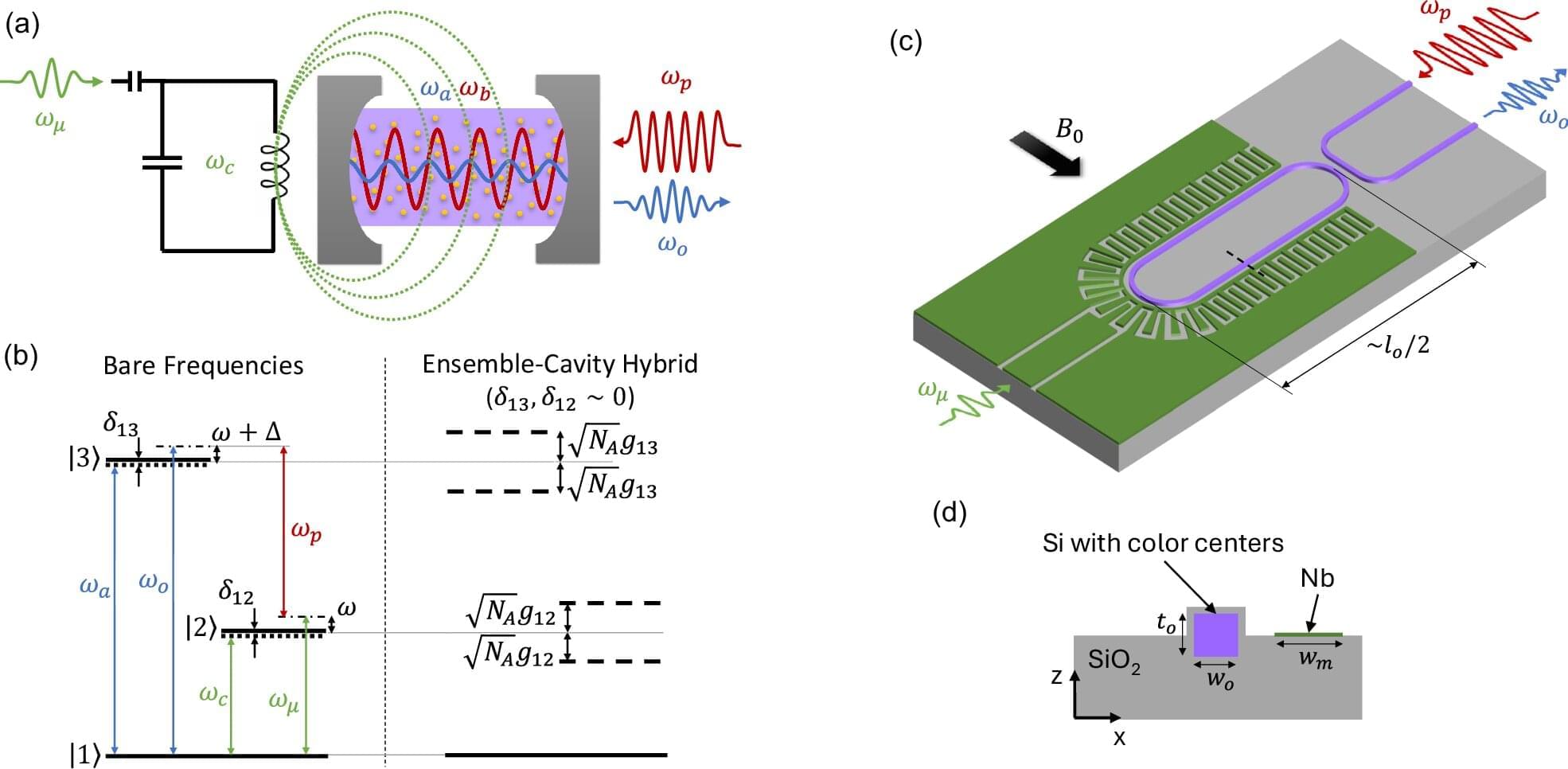
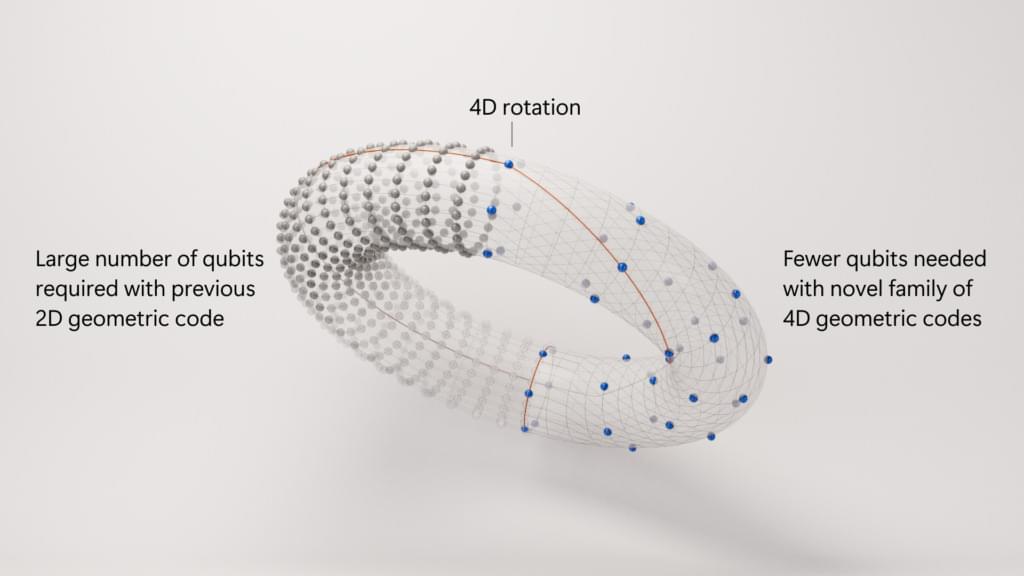
UBC researchers are proposing a solution to a key hurdle in quantum networking: a device that can “translate” microwave to optical signals and vice versa.
The technology could serve as a universal translator for quantum computers—enabling them to talk to one another over long distances and converting up to 95% of a signal with virtually no noise. And it all fits on a silicon chip, the same material found in everyday computers.
“It’s like finding a translator that gets nearly every word right, keeps the message intact and adds no background chatter,” says study author Mohammad Khalifa, who conducted the research during his Ph.D. at UBC’s faculty of applied science and the Stewart Blusson Quantum Matter Institute (SBQMI).
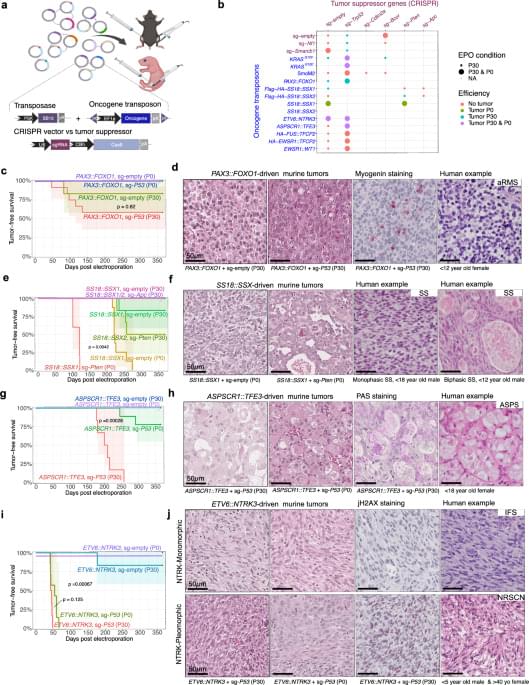
Sarcomas are a group of mesenchymal malignancies which are molecularly heterogeneous. Here, the authors develop an in vivo muscle electroporation system for gene delivery to generate distinct subtypes of orthotopic genetically engineered mouse models of sarcoma, as well as syngeneic allograft models with scalability for preclinical assessment of therapeutics.