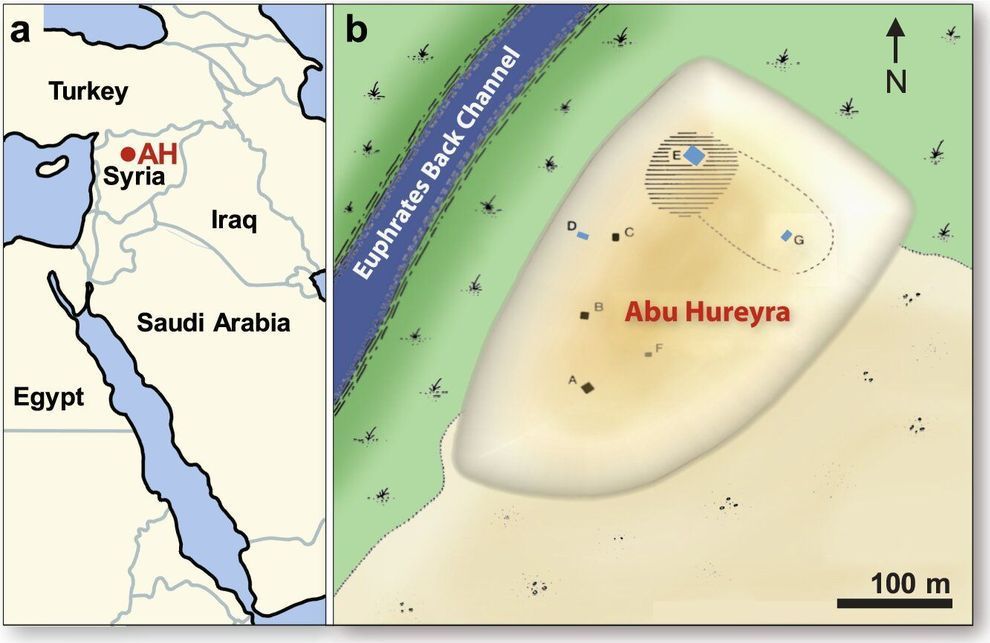
Before the Taqba Dam impounded the Euphrates River in northern Syria in the 1970s, an archaeological site named Abu Hureyra bore witness to the moment ancient nomadic people first settled down and started cultivating crops. A large mound marks the settlement, which now lies under Lake Assad.
But before the lake formed, archaeologists were able to carefully extract and describe much material, including parts of houses, food and tools—an abundance of evidence that allowed them to identify the transition to agriculture nearly 12,800 years ago. It was one of the most significant events in our Earth’s cultural and environmental history.
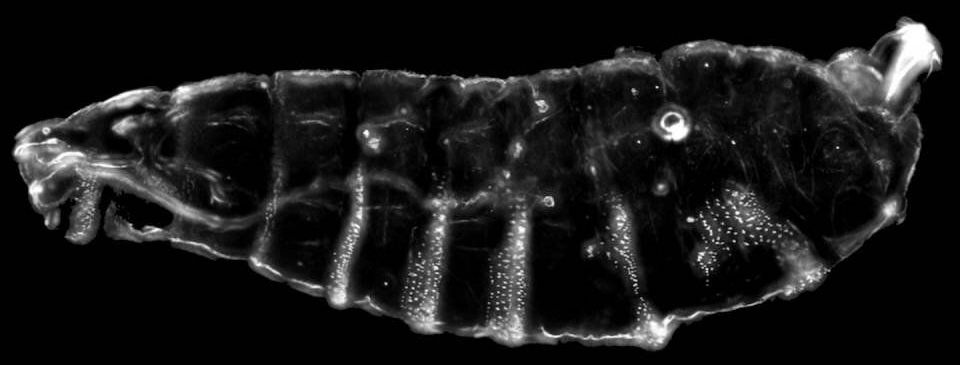
Abu Hureyra, it turns out, has another story to tell. Found among the cereals and grains and splashed on early building material and animal bones was meltglass, some features of which suggest it was formed at extremely high temperatures—far higher than what humans could achieve at the time—or that could be attributed to fire, lighting or volcanism.