Quantum entanglement—spooky action at a distance—works differently inside the nuclei of atoms than it does in other systems.
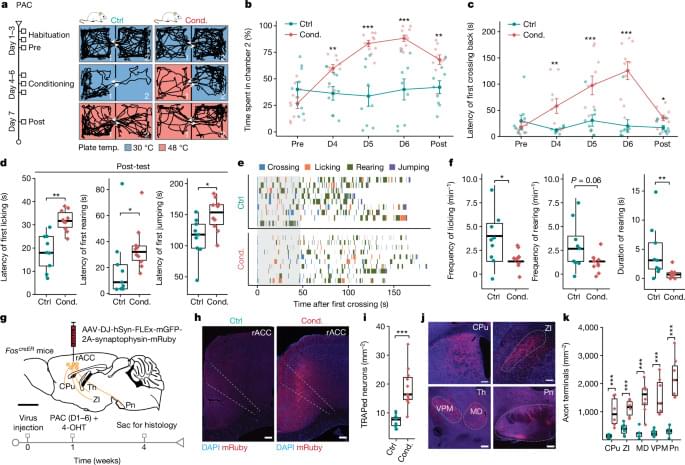
A study in @ Nature identifies using mouse models a neural circuit that may underpin pain relief caused by the placebo effect.
Analgesia from the expectation of pain relief is mediated by rostral anterior cingulate cortex neurons that project to the pontine nucleus.
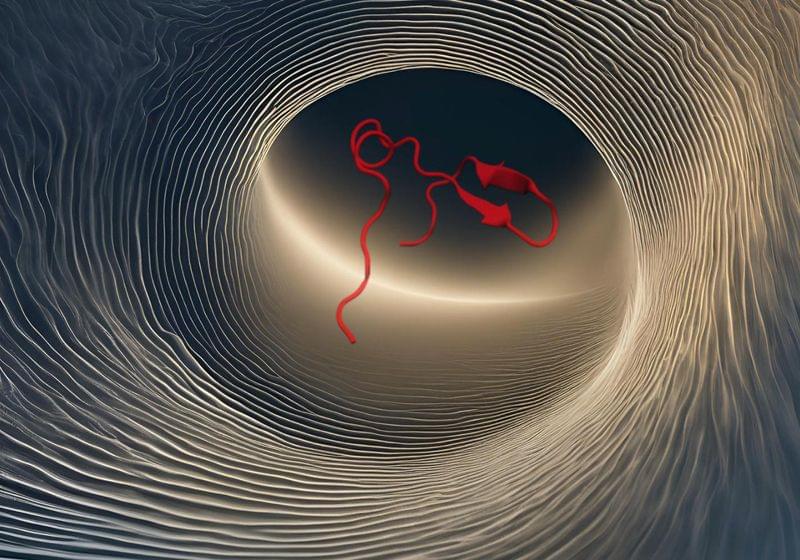
By assigning sounds to the dynamic bonds within proteins, scientists gathered new insights on protein folding.
Reversing Atherosclerosis
Posted in biotech/medical, media & arts
Enjoy the videos and music you love, upload original content, and share it all with friends, family, and the world on YouTube.
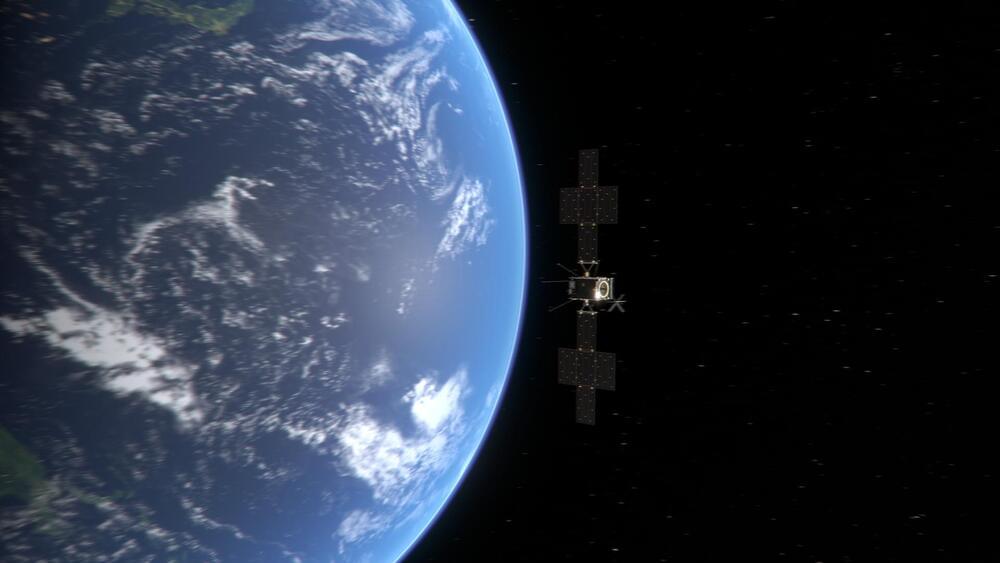
ESA’s Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer (Juice) has successfully completed a world-first lunar-Earth flyby, using the gravity of Earth to send it Venus-bound, on a shortcut to Jupiter through the inner Solar System.
The closest approach to the Moon was at 23:15 CEST (21:15 UTC) on 19 August, guiding Juice towards a closest approach to Earth just over 24 hours later at 23:56 CEST (21:56 UTC) on 20 August.
As Juice flew just 6,840 km above Southeast Asia and the Pacific Ocean, it snapped a series of images with its onboard monitoring cameras, and collected scientific data with eight of its ten instruments.
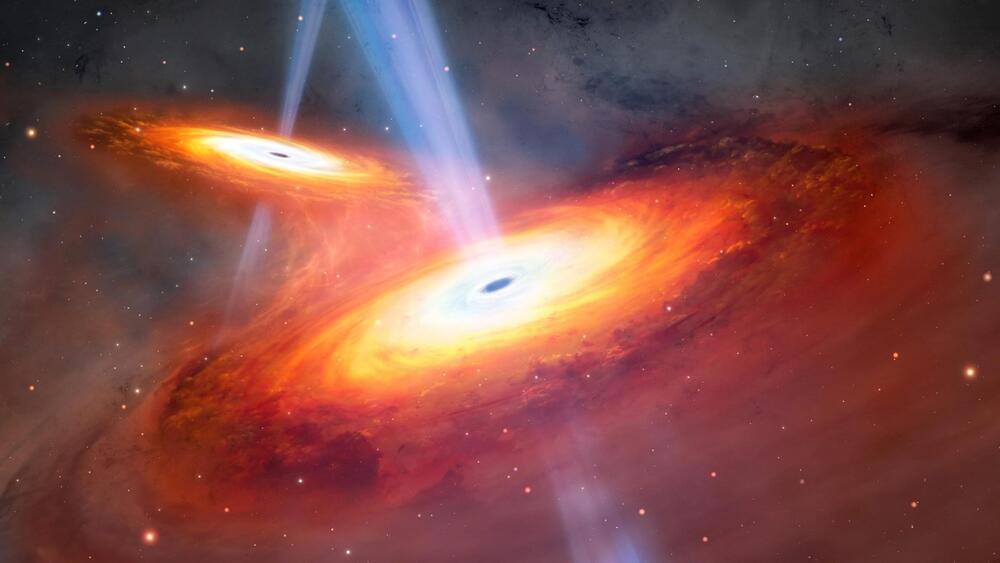
Astronomers have identified the earliest pair of quasars, shining 900 million years post-Big Bang, revealing insights into galaxy mergers and the reionization era of the Universe.
An international team of astronomers, including members from the Kavli Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the Universe (Kavli IPMU, WPI), has discovered the earliest known pair of quasars using the Subaru Telescope and Gemini North telescope, both situated on Maunakea in Hawai’i. These quasars, powered by actively feeding supermassive black holes, emit intense radiation. This significant discovery will provide insights into the early evolution of the Universe.
About 400 million to 1 billion years after the Big Bang, something, possibly a combination of sources, unleashed enough radiation to strip the electrons from most of the hydrogen atoms, completely altering the nature of the Universe. Quasars are one potential source of the radiation that caused this “reionization” of the Universe. When matter falls into the supermassive black hole at the center of a galaxy, the matter heats up and releases radiation in a phenomenon known as a quasar.
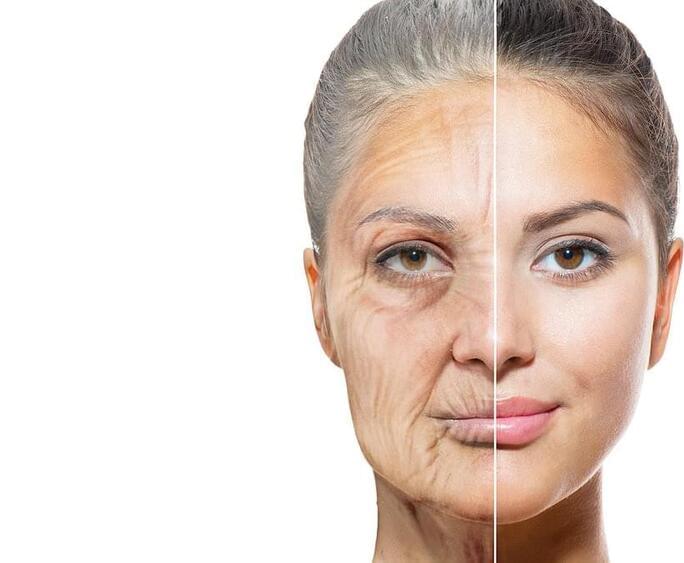
The new research harnesses previously unknown features of this ancient viral DNA, creating a biological clock to track a person’s age from the DNA’s chemical changes.
And the researchers now believe that new antiretroviral therapies, similar to those used to fight the HIV virus and AIDS, might one day help reverse the signs of aging.
‘Our findings indicate that retroelement clocks capture previously undetected facets of biological aging,’ said study co-author Dr Michael Corley, an assistant professor of immunology at Weill Cornell Medicine in New York.
While large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in extracting data and generating connected responses, there are real questions about how these artificial intelligence (AI) models reach their answers. At stake are the potential for unwanted bias or the generation of nonsensical or inaccurate “hallucinations,” both of which can lead to false data.
That’s why SMU researchers Corey Clark and Steph Buongiorno are presenting a paper at the upcoming IEEE Conference on Games, scheduled for August 5–8 in Milan, Italy. They will share their creation of a GAME-KG framework, which stands for “Gaming for Augmenting Metadata and Enhancing Knowledge Graphs.”
The research is published on the arXiv preprint server.
#bioink could be used to #Print and #Grow #Lung #Tissue.
Researchers describe their success in creating a mucus-based bioink for 3D printing lung tissue. This advancement could one day help study and treat chronic lung conditions. scitechupdates.com/mucus-based-bi…
Lung diseases kill millions of people around the world each year. Treatment options are limited, and animal models for studying these illnesses and experimental medications are inadequate. Now, writing in ACS Applied Bio Materials, researchers describe their success in creating a mucus-based bioink for 3D printing lung tissue. This advancement could one day help study and treat chronic lung conditions.
While some people with lung diseases receive transplants, donor organs remain in short supply. As an alternative, medications and other treatments can be used to manage symptoms, but no cure is available for disorders such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and cystic fibrosis. Researchers continue to seek better medications, often relying on testing in rodents. But these animal models may only partially capture the complexities of pulmonary diseases in humans, and they might not accurately predict the safety and efficacy of new drugs.
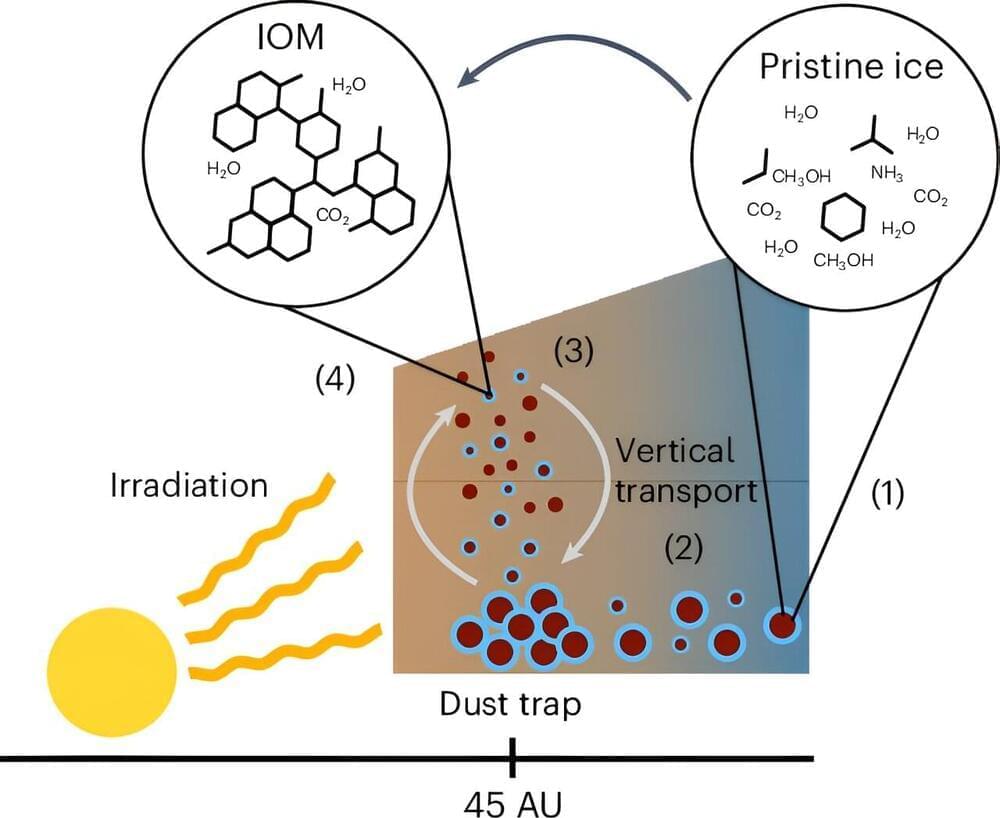
Computer modeling shows how macromolecules form quickly in gas & dust disks around young stars, aiding understanding of exoplanet.
Astronomers explain #Rapid #Formation of #Organic #Macromolecules in #Protoplanetary #Disks around #Young #Stars.
An international team of researchers led by the University of Bern has used observation-based computer modeling to find an explanation for how macromolecules can form in a short time in disks of gas and dust around young stars. These findings could be crucial for understanding how habitability develops around different types of exoplanets and stars.
Organic macromolecules are regarded as the building blocks of life, as they are of crucial importance for the life-friendly carbon and nitrogen composition of the earth.