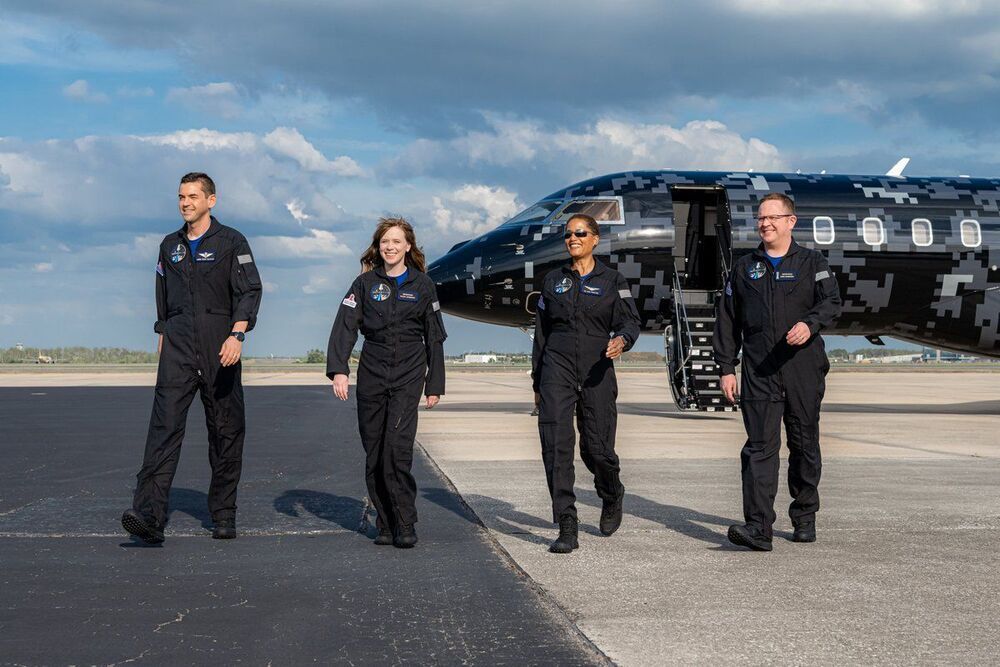
Four private astronauts have been strapped into a centrifuge, climbing mountains and learning how to fly a spacecraft ahead of their flight to space — the first-ever crewed space mission without any “professional astronauts” on board.
The crew is preparing to launch this upcoming September as part of the Inspiration4 mission aboard a SpaceX Crew Dragon spacecraft. The mission, privately chartered by billionaire Jared Isaacman to support St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital, recruited three crew members in addition to Isaacman for the trip which will fly around the Earth for several days. The crew includes Isaacman, St. Jude physician’s assistant and childhood bone cancer survivor Hayley Arcenaux, data engineer Chris Sembroski and geoscientist, science communicator and artist Sian Proctor.