Nov 7, 2019
Astronomers Have Found the Universe’s Missing Matter
Posted by Paul Battista in category: cosmology
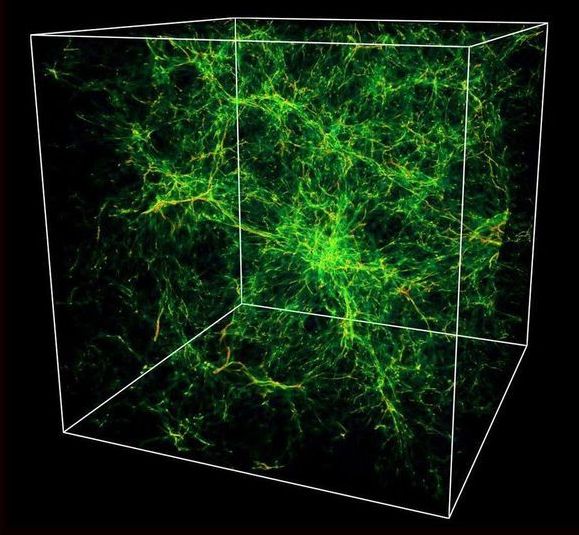
Astronomers have finally found the last of the missing universe. It’s been hiding since the mid-1990s, when researchers decided to inventory all the “ordinary” matter in the cosmos—stars and planets and gas, anything made out of atomic parts. (This isn’t “dark matter,” which remains a wholly separate enigma.) They had a pretty good idea of how much should be out there, based on theoretical studies of how matter was created during the Big Bang. Studies of the cosmic microwave background (CMB)—the leftover light from the Big Bang—would confirm these initial estimates.
So they added up all the matter they could see—stars and gas clouds and the like, all the so-called baryons. They were able to account for only about 10 percent of what there should be. And when they considered that ordinary matter makes up only 15 percent of all matter in the universe—dark matter makes up the rest—they had only inventoried a mere 1.5 percent of all matter in the universe.
Now, in a series of three recent papers, astronomers have identified the final chunks of all the ordinary matter in the universe. (They are still deeply perplexed as to what makes up dark matter.) And despite the fact that it took so long to identify it all, researchers spotted it right where they had expected it to be all along: in extensive tendrils of hot gas that span the otherwise empty chasms between galaxies, more properly known as the warm-hot intergalactic medium, or WHIM.