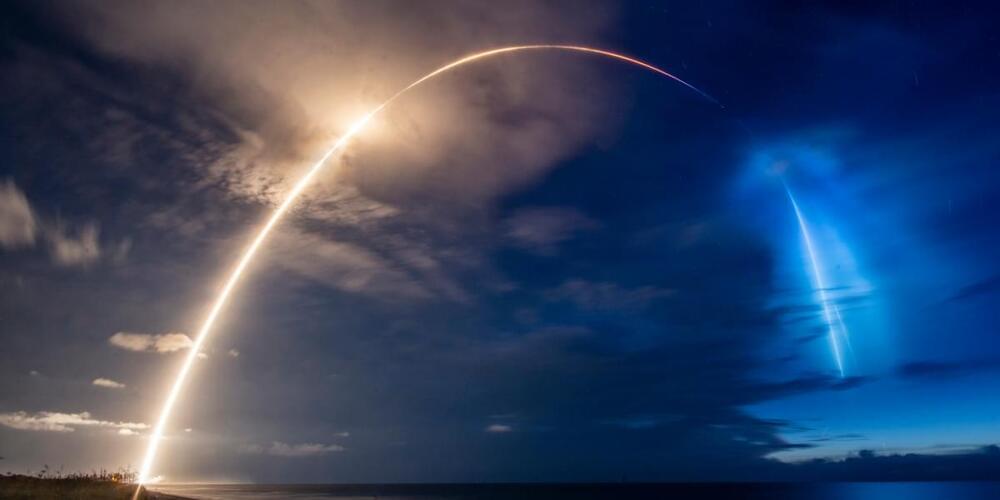
How to overcome reinforcement learning’s inherent selfishness.


Circa 23 March 2020
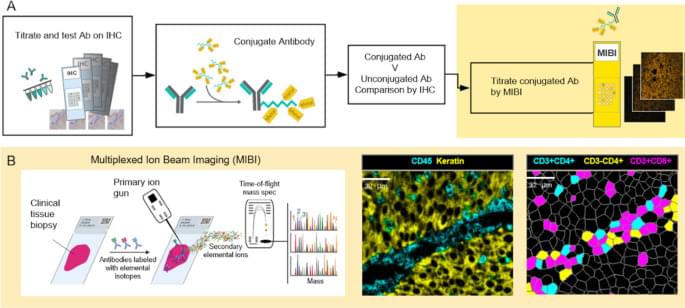
The ways in which a neoplastic cell arises and evades the immune system is the result of a departure from the systems biology that governs health. Understanding this biology requires methods that can resolve the heterogeneity of cell types, determine their states, whether they are activated (e.g., HLA-DR high) or suppressed (e.g., PD-1 high), and map their relationships or distances to one another. MIBI provides single cell resolution and sensitivity to phenotypically characterize the complex tissue environments including the TME. Executed similarly to IHC yet with the capability to profile 40+ markers simultaneously, MIBI is broadly applicable to a wide range of analyses performed in anatomic pathology including cell classification, spatial characterization, and assessment of marker expression. The MIBIscope produces data (multilayer TIFF files) that can be accessed by many analysis platforms currently available, such as those found in commercial software packages such as Fiji, Halo, and VisioPharm or freely available bioinformatic packages developed with open-source programming languages (e.g., R, Python).
All tumor types were stained, imaged, and analyzed using a single staining panel and standardized protocol. The workflow is flexible such that slides can be stained in batches and stored until imaged on the MIBIscope. Stained slides are typically stored under vacuum but protection from light is not necessary as the labels are stable metal isotopes rather than light-sensitive fluorophores. Once imaged it is possible to reimage the tissue as only a modest depth of the tissue is sputtered and analyzed during a single acquisition [16]. One limitation of the current project performed with an earlier version of the MIBIScope is the relatively small FOV size (500 μm by 500 μm) needed for images with 0.5 µm resolution. The current MIBIScope enables FOVs of 800 μm by 800 μm to be imaged in 70 min at fine resolution (650 nm). The resolution can be controlled at the instrument and acquisition at a slightly lower resolution than used in this study (1 μm) can be performed in 17 min. The 800 μm FOV captures 82% of a 1 mm TMA core. FOVs across cores of a TMA can be selected and then imaged in a single run. For whole sections it is possible to acquire adjacent images and stitch the images together using techniques commonly performed with other imaging technologies [22]. The need for tiling is particularly acute for imaging brain sections where multiple FOVs are collected to generate a larger image. Together with researchers at Stanford University, we are currently developing tiling methods to map large regions of brain tissue which will be described in a future publication. Because MIBI is still an early technology, the underlying methods for each stage of the processing pipeline are constantly evolving and improving, not just for accuracy but for generality. While the methods themselves are evolving, the pipeline tasks, at a high level, such as mass calibration, filtering, etc., are defined and have been automated through the MIBI/O software, and, as importantly, allows for appropriate user input when necessary. As more data becomes available, and the user base of MIBI grows, data processing should become more standardized.
The immediate utility of MIBI will be for understanding the biological mechanisms present in disease microenvironments. The results demonstrate the ability to detect a range of marker expression across many tumor types. The images can be segmented to define cell boundaries and then the expression of phenotypic markers used to classify cell instances into their cell class, such as proliferating tumor cells or nonproliferating tumor cells and various immune cells. Additional markers have been used on other sample sets to further define myeloid cell subsets, B cell subsets and stromal elements including vascular endothelial cells. This study also demonstrated the possibilities for calculating distances between different cell subsets including tumor and immune cells in addition to PD-1 and PD-L1 expressing immune cell subsets.
This tiny piece of rock will help solve one of the biggest mysteries of the universe.
NASA’s Perseverance rover collected its first Martian sample, which will help scientists determine if there is life beyond Earth.

Toyota Motor Corporation announced on Tuesday that it will spend a massive $13.6 billion, or 1.5 trillion yen, on battery supply systems and research and development of electric vehicle battery technology by 2030. The investment will help the Japanese automaker establish a system for the development and supply of batteries for electrified models.
In April, Toyota debuted the bZ4X BEV concept and announced plans to roll out 15 BEVs under the bZ (Beyond Zero) family. Toyota surged into sustainable transportation with the development and release of the Prius Hybrid years ago, but the company has not significantly contributed to the development or sale of fully electric powertrains. Toyota CEO Akio Toyoda has not been in any hurry to develop electrified models for customers and still believes that the company remains light years ahead of EV competitors like Tesla due to size, experience, and production.
Toyota debuts bZ4X SUV concept, kicking off its 15 electric vehicle lineup

The electric vehicle sector would be wise to brace for an insane expansion of the Tesla Supercharger Network. As reported by local media outlets on Tuesday, Tesla’s Supercharger V3 Factory in Shanghai had been fully completed as of August 20 2021. The facility, which is capable of producing 10,000 Supercharger V3 stalls per year, would play a key role in the company’s aggressive expansion of its rapid-charging network.
With the facility fully completed, Tesla’s ramp of the Supercharger Network would likely become much faster than ever before. This would be incredibly advantageous for the company, particularly as CEO Elon Musk has noted that Tesla would be opening its Supercharger Network to non-Tesla EVs around the end of the year. To avoid overcrowding in its existing Superchargers, the company must have a way to ensure that it has a steady supply of rapid charging stalls to install.
This is where the Supercharger V3 factory in China comes in. Tesla currently operates about 25,000 Superchargers worldwide. And while this number seems incredibly small compared to the number of gas stations across the globe, the Supercharger Network already stands as one of the most expansive and reliable rapid charging systems for electric vehicles in the market. Having a facility that could add 10,000 more Superchargers every year would then be extremely beneficial.
Private orbital debris removal company Astroscale has validated its magnetic capture system that is designed to tackle the problem of space debris. Its End-of-Life Services by Astroscale-demonstration (ELSA-d) servicer satellite managed to capture a simulated piece of space debris in orbit for the first time using the system.
Space debris is a serious and growing problem as popular orbits around the Earth become increasingly cluttered with defunct satellites, boosters, and other flotsam that present the hazard of an increased probability of a bit of debris striking a working spacecraft at hypersonic speeds.
In recent years, there have been a number of proposals put forward to deal with this, including devices installed on satellites to increase atmospheric drag as well as experimental capture devices. In general, the most promising technology has involved end-of-life systems installed in new spacecraft, or spacecraft that can rendezvous with aging satellites still capable of maintaining attitude to deorbit them.


If the state of the planet is getting you down or you’re just terrified that ducks can now speak human words 0 then I advise you to stop what you’re doing for a few moments and gaze in awe at this photo by Thomas Pesquet, a French astronaut currently residing inside the International Space Station.
Pesquet, an engineer with the European Space Agency, is one of the members of the SpaceX Crew-2 mission and member of NASA’s Expedition 65, which launched to the station in April. It’s his second spaceflight and he’s become known around these parts for delivering some absolutely surreal images of our home planet.
This may be his best yet.
