Nov 11, 2019
The mysterious ‘Tully Monster’ fossil just got more mysterious
Posted by Genevieve Klien in category: futurism
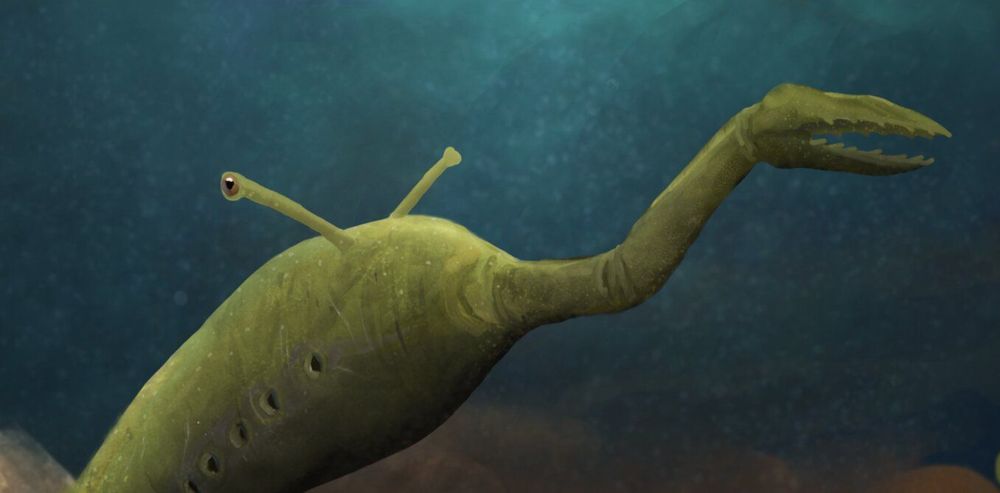
Every now and again, scientists discover fossils that are so bizarre they defy classification, their body plans unlike any other living animals or plants. Tullimonstrum (also known as the Tully Monster), a 300m-year-old fossil discovered in the Mazon Creek fossil beds in Illinois, US, is one such creature.
At first glance, Tully looks superficially slug-like. But where you would expect its mouth to be, the creature has a long thin appendage ending in what looks like a pair of grasping claws. Then there are its eyes, which protrude outward from its body on stalks.
Tully is so strange that scientists have even been unable to agree on whether it is a vertebrate (with a backbone, like mammals, birds, reptiles and fish) or an invertebrate (without a backbone, like insects, crustaceans, octopuses and all other animals). In 2016, a group of scientists claimed to have solved the mystery of Tully, providing the strongest evidence yet that it was a vertebrate. But my colleagues and I have conducted a new study that calls this conclusion into question, meaning this monster is as mysterious as ever.