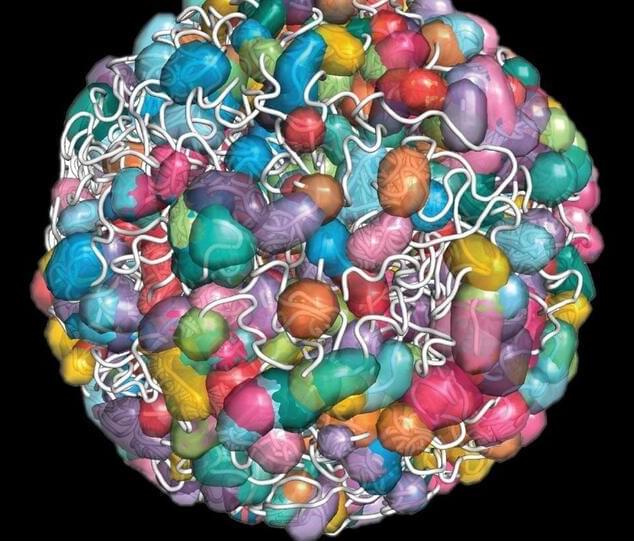
The human genome can be thought of as a massive library, containing over 20,000 different “instruction manuals”: your genes. For example, there are genes which contain information to build a brain cell, a skin cell, a white blood cell, and so on. There are even genes that contain information about regulating the genome itself—like books that explain how to organize a library. The ability to regulate gene expression —in other words, the cell’s ability to turn various constellations of genes on or off—is the basis of why different cells (such as a muscle cell or a brain cell) have different forms and functions.
For any library to be useful to a reader, it needs to be organized in an easily searchable way. For example, all the books pertaining to world history may be on one shelf, whereas the cookbooks may be in an entirely different section of the library. In a cellular nucleus, there is over six feet of genetic material packed into a space 50 times smaller than the width of a human hair. How is the “library” in the nucleus organized? When a cell needs to regulate certain genes, how does the cellular machinery find the right ones amongst 20,000 others?
A new paper from the laboratory of Mitchell Guttman, professor of biology, uses a powerful new tool that can peer into the world of the cell’s genetic material (DNA.