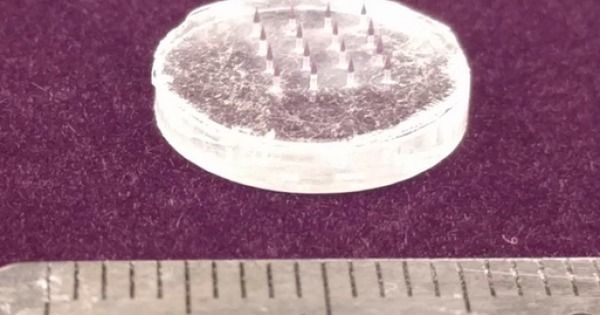
You really can not make this up The Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation has donated more than $21 million towards developing a vaccine technology that uses a tattoo-like mechanism which injects invisible nanoparticles under the skin that is now being tested in a vaccine against the virus that causes COVID-19.
Another study funded by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation and published in December, 2019 by researchers from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, the Institute of Chemistry of the Chinese Academy of Sciences in Beijing and the Global Good, Intellectual Ventures Laboratory in Bellevue, WA, describes how “near-infrared quantum dots” can be implanted under the skin along with a vaccine to encode information for “decentralized data storage and bio-sensing.”
“To maximize the utility of this technology for vaccination campaigns, we aimed to create a platform compatible with microneedle-delivered vaccines that could reliably encode data on an individual for at least five years after administration,” said the MIT paper, titled Biocompatible near-infrared quantum dots delivered to the skin by microneedle patches record vaccination. “In addition, this system also needed to be highly biocompatible, deliver a sufficient amount of dye after an application time of 2 min or less, and be detectable using a minimally adapted smartphone.”
Fridrik Laurusson, an author of the microchip study, is from The Global Good, Intellectual Ventures Labarotory . Its website features Microsoft founder Bill Gates on its front page and describes itself as a “collaboration between Bill Gates and Intellectual Ventures” a company founded by Nathan Myhrvold and Edward Jung of Microsoft. Wikipedia describes Intellectual Ventures in Gates’ home state as a private American company that “centers on the development and licensing of intellectual property” and “one of the top-five owners of U.S. patents, as of 2011.