Key findings Proofpoint researchers observed an increase in opportunistic cybercriminals using malware based on Stealerium, an open-source malware that is available for educational


Imagine a clock that doesn’t have electricity, but its hands and gears spin on their own for all eternity. In a new study, physicists at the University of Colorado Boulder have used liquid crystals, the same materials that are in your phone display, to create such a clock—or, at least, as close as humans can get to that idea. The team’s advancement is a new example of a “time crystal.” That’s the name for a curious phase of matter in which the pieces, such as atoms or other particles, exist in constant motion.
The researchers aren’t the first to make a time crystal, but their creation is the first that humans can actually see, which could open a host of technological applications.
“They can be observed directly under a microscope and even, under special conditions, by the naked eye,” said Hanqing Zhao, lead author of the study and a graduate student in the Department of Physics at CU Boulder.
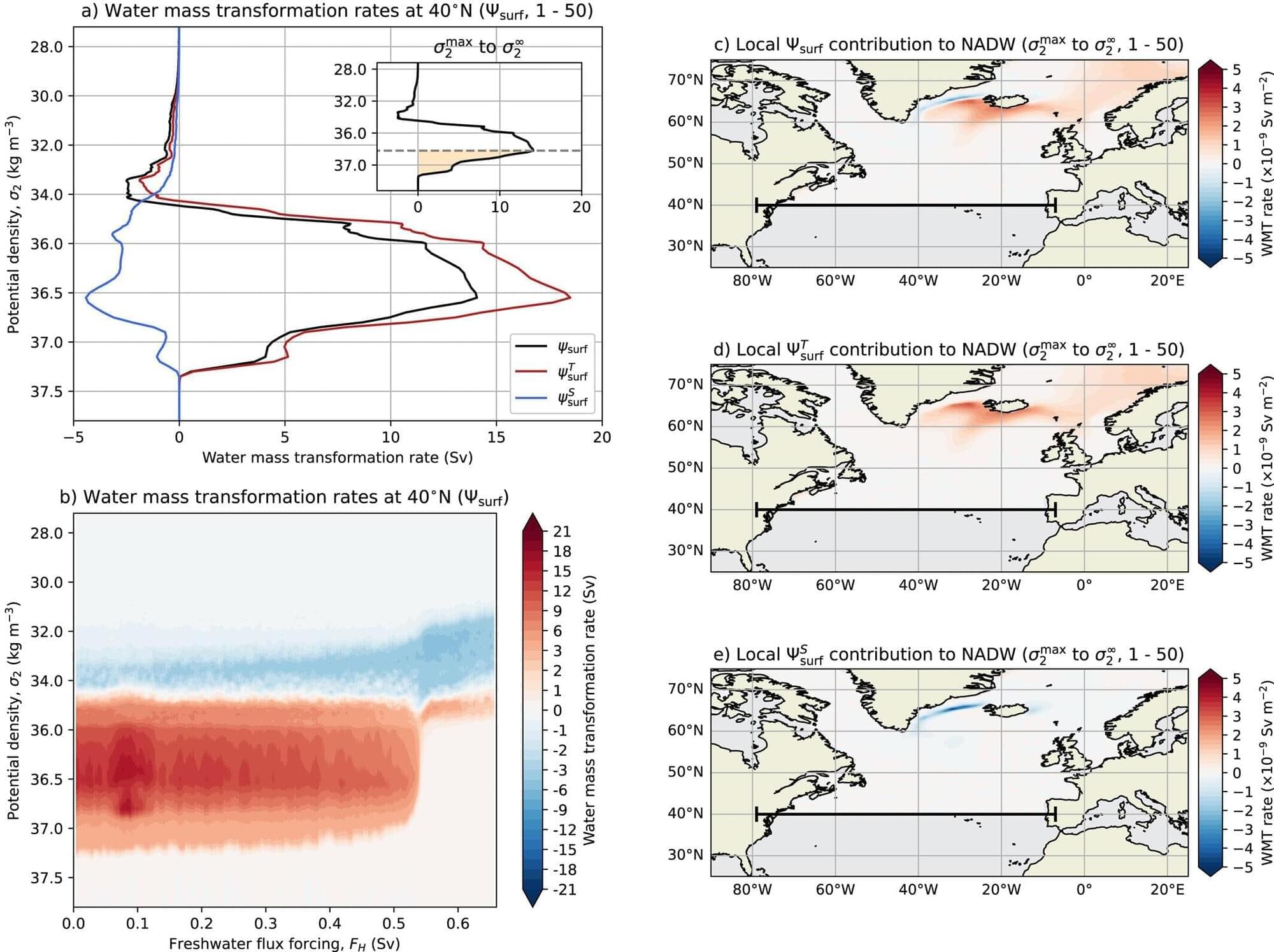
The Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) is an enormous loop of ocean current in the Atlantic Ocean that carries warmer waters north and colder waters south, helping to regulate the climate in many regions. The collapse of this critical circulation system has the potential to cause drastic global and regional climate impacts, like droughts and colder winters, especially in Northwestern Europe.

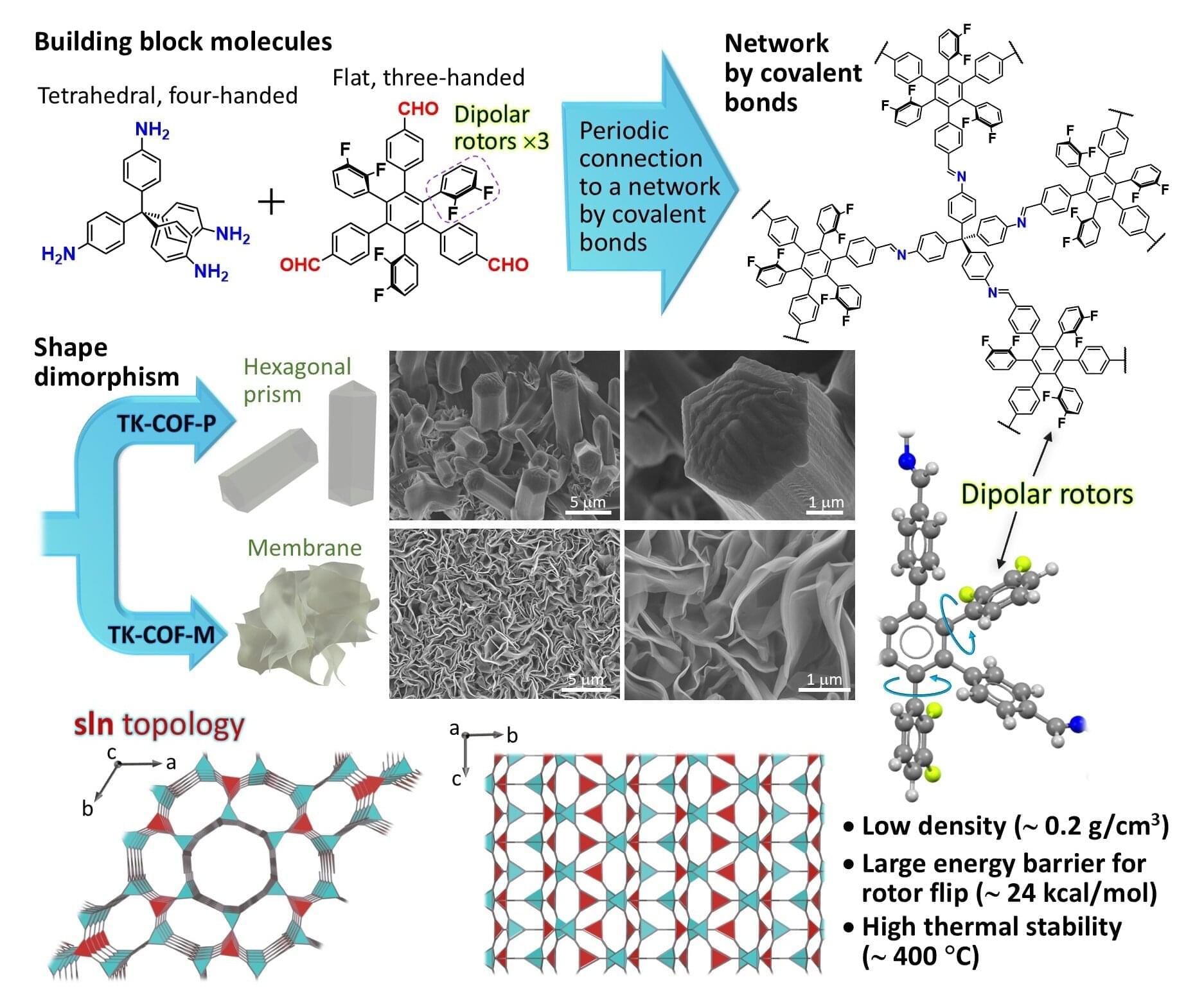
Researchers at Institute of Science Tokyo have created a new material platform for non-volatile memories using covalent organic frameworks (COFs), which are crystalline solids with high thermal stability. The researchers successfully installed electric-field-responsive dipolar rotors into COFs.
Due to the unique structure of the COFs, the dipolar rotors can flip in response to an electric field without being hampered by a steric hindrance from the surroundings, and their orientation can be held at ambient temperature for a long time, which are necessary conditions for non-volatile memories. The study is published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
Humans have made great efforts to record information by inventing recording media such as clay, paper, compact disks, and semiconductor memories. As the physical entity that holds information—such as indentations, characters, pits, or transistors—becomes smaller and its areal density becomes higher, the information is stored with higher density. In rewritable memories, the class called “non-volatile memories” are suitable for storing data for a long time, such as for days and years.
In 3D bioprinting, researchers use living cells to create functional tissues and organs. Instead of printing with plastic, they print with living cells. This comes with great challenges. Cells are fragile and wouldn’t survive a regular 3D printing process. That’s why Levato’s team developed a special bio-ink, a mix of living cells and nourishing gels that protect the cells during the printing process.
With the advancements in bio-inks, layer-by-layer 3D bioprinting became possible. But this method is still time-consuming and puts a lot of stress on the cells. Researchers from Utrecht came up with a solution: volumetric bioprinting.
Volumetric bioprinting is faster and gentler on cells. Using cell-friendly laser light, a 3D structure is created all at once. “To build a structure, we project a series of light patterns into a spinning tube filled with light-sensitive gel and cells,” Levato explains. “Where the light beams converge, the material solidifies. This creates a full 3D object in one go, without having to touch the cells.” To do this, it is crucial to know exactly where the cells are in the gel. GRACE now makes that possible.
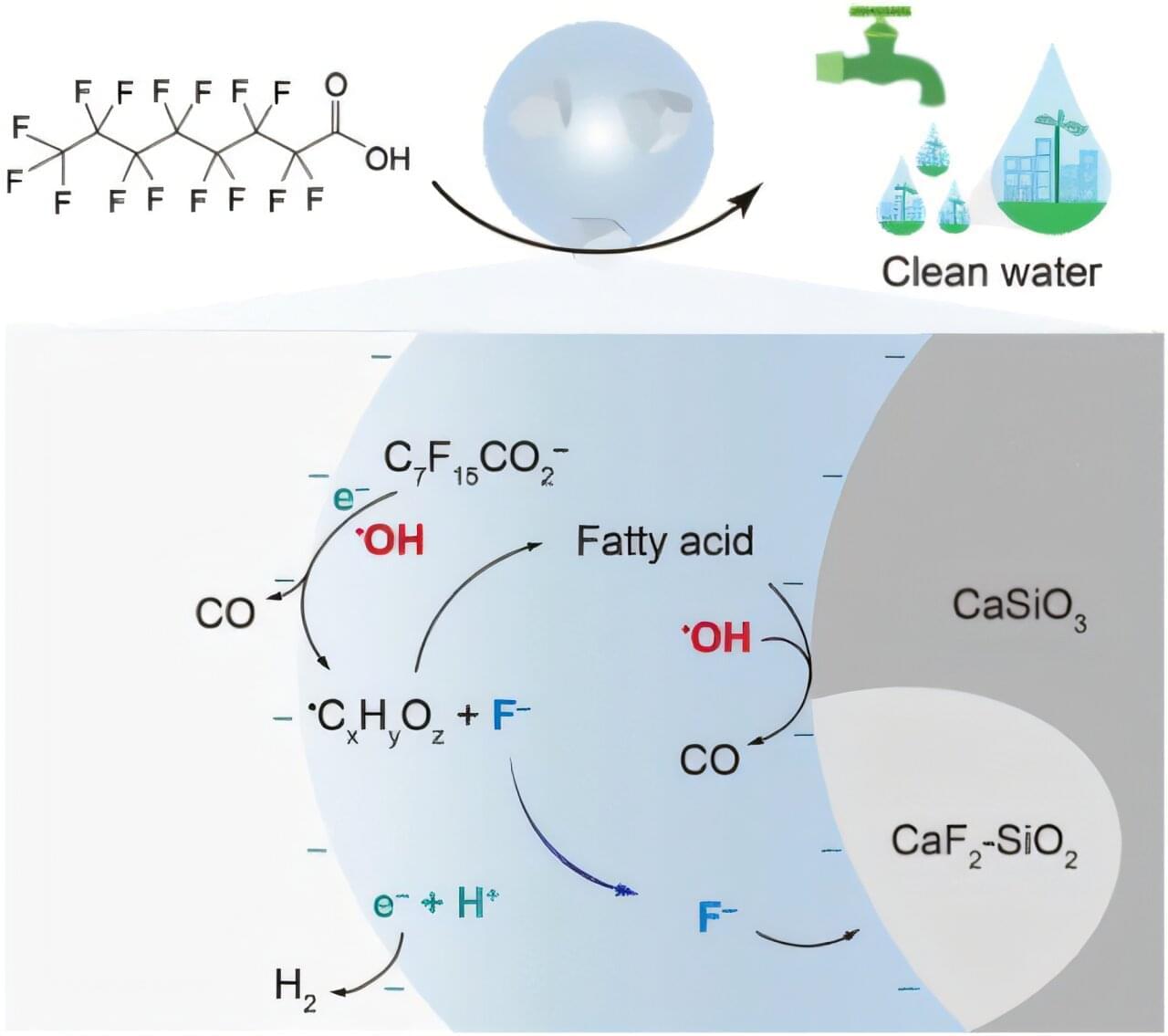
Anthropogenic perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are widespread and persistent pollutants that are increasingly subject to stringent regulatory thresholds in water resources. Current nonthermal defluorination strategies have limitations including incomplete mineralization, leaving behind short-chain PFAS byproducts and residual fluoride ions, thereby posing challenges to meeting water quality standards.
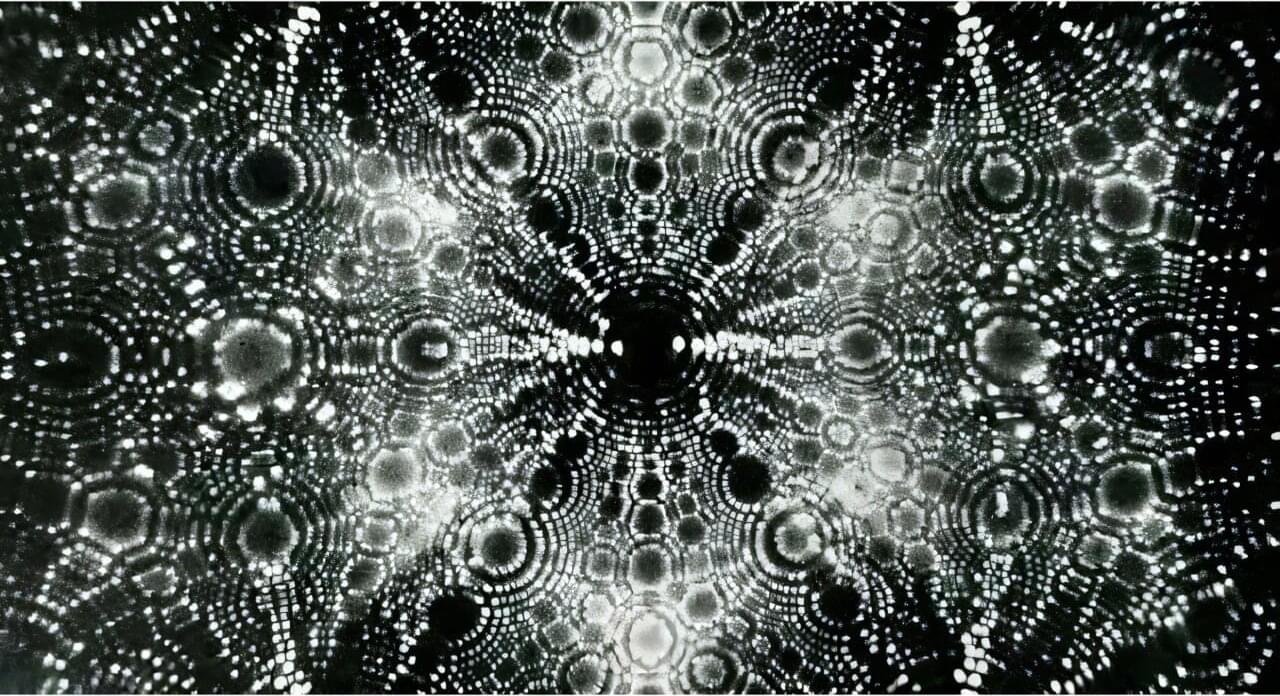

Seventy years ago, in Osmond Laboratory on Penn State’s University Park campus, Erwin W. Müller, Evan Pugh Research Professor of Physics, became the first person to “see” an atom. In doing so, Müller cemented his legacy, not only at Penn State, but also as a pioneer in the world of physics and beyond.
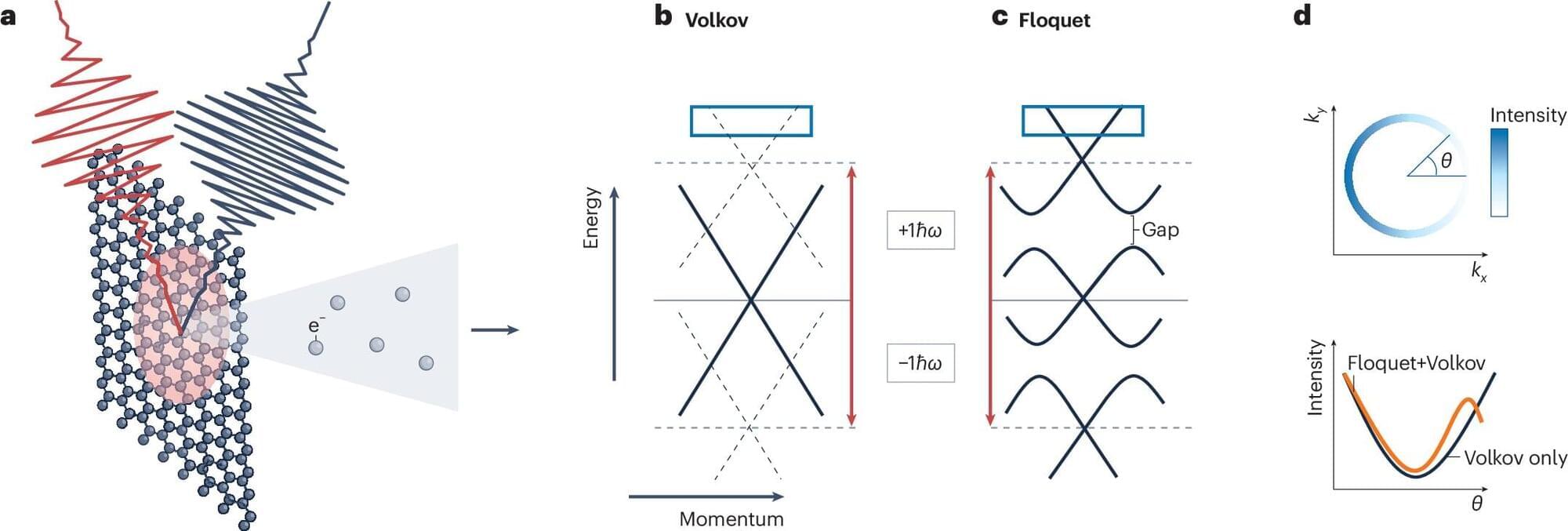
Graphene is an extraordinary material—a sheet of interlocking carbon atoms just one atom thick that is stable and extremely conductive. This makes it useful in a range of areas, such as flexible electronic displays, highly precise sensors, powerful batteries, and efficient solar cells.
A new study—led by researchers from the University of Göttingen, working together with colleagues from Braunschweig and Bremen in Germany, and Fribourg in Switzerland—now takes graphene’s potential to a whole new level. The team has directly observed “Floquet effects” in graphene for the first time.
This resolves a long-standing debate: Floquet engineering—a method in which the properties of a material are very precisely altered using pulses of light—also works in metallic and semi-metallic quantum materials such as graphene. The study is published in Nature Physics.