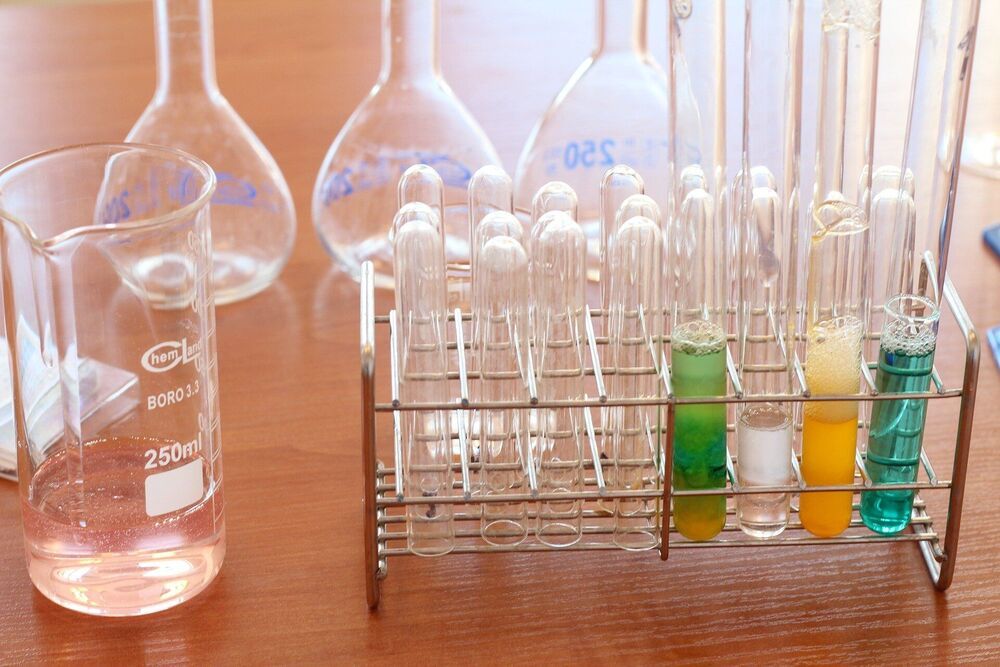
In the past few years, researchers have turned increasingly to data science techniques to aid problem-solving in organic synthesis.




We can immediately supersede the Mojo Vision approach for retinal projection, with an interim projection system using metalenses. The Mojo Lens approach is to try to put everything, including the television screen, projection method and energy source onto one contact lens. With recent breakthroughs in scaling up the size of metalenses, an approach utilizing a combination of a contact metalens and a small pair of glasses can be utilized. This is emphatically not the Google Glass approach, which did not use modern metalenses. The system would work as follows:
1)Thin TV cameras are mounted on both sides of a pair of wearable glasses.
2)The images from these cameras are projected via projection metalenses in a narrow beam to the center of the pupils.
3)A contact lens with a tiny metalens mounted in the center, directly over the pupil, projects this projected beam outwards, through the pupil, onto the full width of the curved retina.
The end result would be a 360 degree, full panorama image. This image can either be a high resolution real time vision of the wearer’s surroundings, or can be a projection of a movie, or augmented reality superimposed on the normal field of vision. It can inherently be full-color 3D. Of course such a system will be complemented with ear phones. Modern hearing aids are already so small they can barely be seen, and have batteries that last a week. A pair of ear phones will also allow full 3D sound and also will be the audible complement of augmented vision.
Cameras in cell phones using traditional lenses are already very thin, and even they could be used for an experimental system of this type, but the metalens cameras will make this drastically thinner. The projection lens system must work in combination with the lens over the pupil. This also means that when the glasses are removed, the contact lens must also be removed, or the vision will be distorted.
The end result will be a pair of glasses, not quite as thin as an ordinary pair of glasses, but still very thin and comfortable. Instead of trying to mount the power source in the contact lens, like Mojo Vision is trying to do, a small battery would be mounted in the glasses. Mojo Vision is probably going to have to do something similar for the power source: put the battery in a small pair of glasses that projects the energy onto its contact lens.

As commercial space companies increase the cadence of successful rocket launches, access to space is becoming more routine for both government and commercial interests. But even with regular launches, modern rockets impose mass and volume limits on the payloads they deliver to orbit. This size constraint hinders developing and deploying large-scale, dynamic space systems that can adapt to changes in their environment or mission.
DARPA’s Operational Fires (OpFires) program, which is developing a ground-launched intermediate-range hypersonic weapons system, is advancing to a new phase. Phase 3b will involve full-scale missile fabrication, assembly, and flight testing from a launch vehicle. Lockheed Martin Missiles and Fire Control was awarded this new contract modification after leading a successful Phase 3a integrated system preliminary design review that resulted in a comprehensive design and test plan.

DARPA’s Robotic Autonomy in Complex Environments with Resiliency — Simulation (RACER-Sim) project is seeking innovations in technologies that bridge the gap from simulation to the real world and significantly reduce the cost of off-road autonomy development. DARPA invites proposals for promising solutions that support these goals.

DARPA’s TRAnsformative DESign (TRADES) program, which began in 2017, set out to develop foundational design tools needed to explore the vast space opened by new materials and additive manufacturing processes commonly called 3D printing. The program recently concluded having successfully developed new mathematics and computational techniques, including artificial intelligence and machine learning, that will allow future designers to create previously unimaginable shapes and structures of interest to defense and commercial manufacturing.

After three months of reviewing more than 13000 hours of hacking exploits conducted by more than 580 cybersecurity researchers, DARPA today announced that its Finding Exploits to Thwart Tampering (FETT) Bug Bounty successfully proved the value of the secure hardware architectures developed under its System Security Integration Through Hardware and Firmware (SSITH) program while pinpointing critical areas to further harden defenses.
The U.S. military routinely deploys throughout the world where warfighters can potentially be exposed to regional endemic diseases as well as chemical, biological, radiological, or nuclear (CBRN) threats. Rapid access to medical countermeasures (MCMs) against these threats is critical to protect Defense Department (DoD) personnel and local populations; however, manufacturing, stockpiling, and distribution issues remain.

DARPA has executed contract options to continue the Manta Ray project that began in 2020. The effort seeks to demonstrate innovative technologies allowing payload-capable unmanned underwater vehicles (UUVs) to operate on long-duration, long-range missions in ocean environments. The three prime contractors will be Northrop Grumman Systems Corporation, Martin Defense Group, LLC (formerly Navatek, LLC), and Metron, Inc.