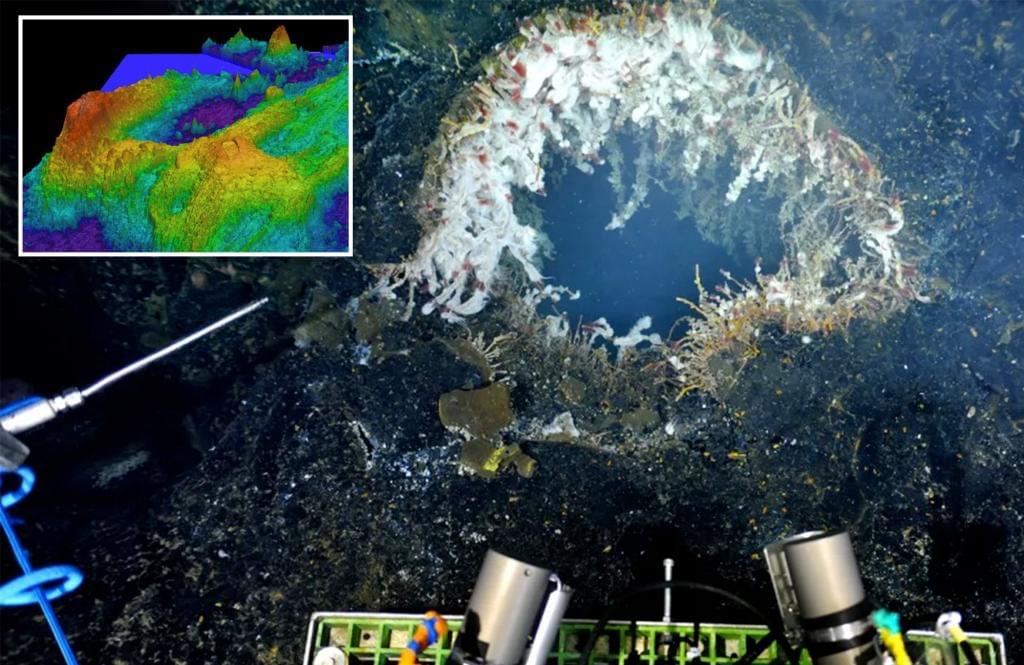
“The eruptions are pretty big,” said a volcanologist at Oregon State University.
Superionic materials are a class of materials that simultaneously present properties that are characteristic of solids and liquids. Essentially, a set of ions in these materials exhibits liquid-like mobility, even if the materials’ underlying atomic structure maintains a solid-like order.
Due to their unique ionic conductivity patterns, superionic materials could be promising for developing solid-state batteries. These are batteries that contain electrolytes based on solid materials instead of liquid electrolytes.
While various past studies have explored the potential of superionic materials as solid-state electrolytes, the physics underpinning their rapid ionic diffusion is not yet fully understood. Specifically, it is unclear whether this property results from liquid-like motion in the material or from the conventional lattice phonons (i.e., atom vibrations) in the material.
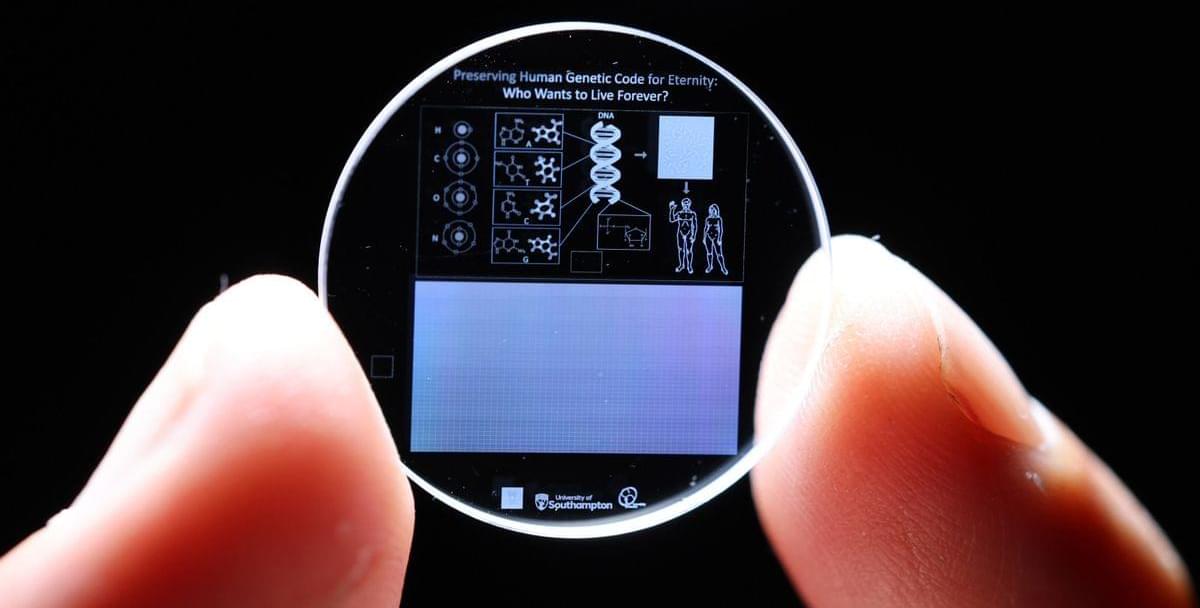
‘Eternal’ 5D memory crystal capable of storing 360 TB of data for billions of years now holds a full human genome
Posted in biotech/medical, chemistry, computing, existential risks, genetics, life extension | Leave a Comment on ‘Eternal’ 5D memory crystal capable of storing 360 TB of data for billions of years now holds a full human genome
The data inscribed into the crystal is carefully annotated with universal elements like hydrogen, oxygen, carbon, and nitrogen, as well as the four DNA bases—adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine—that make up the genetic code. Additionally, the molecular structure of DNA and the arrangement of genes within chromosomes are depicted, offering clear instructions on how to interpret the genetic information stored within.
However, it is important to note that the 5D memory crystals require a highly specialized skill set and advanced equipment to inscribe and read the data stored within the crystals, so those looking to re-establish the human race after an extinction event may have to refer to more traditional means.
The crystal, made from fused quartz, is one of the most chemically and thermally resilient materials known on Earth, and can endure temperatures as high as 1000°C, resist direct impact forces up to 10 tons per square centimeter, and is unaffected by long-term exposure to cosmic radiation. The longevity and storage capacity of the 5D memory crystal earned it a Guinness World Record in 2014 for being the most durable data storage material ever created.
The world of AI is evolving at a breakneck pace with new models constantly being created. With so much rapid innovation, it is essential to have the flexibility to quickly adapt applications to the latest models. This is where Azure Container Apps serverless GPUs come in.
Azure Container Apps is a managed serverless container platform that enables you to deploy and run containerized applications while reducing infrastructure management and saving costs.
With serverless GPU support, you get the flexibility to bring any containerized workload, including new language models, and deploy them to a platform that automatically scales with your customer demand. In addition, you get optimized cold start, per-second billing and reduced operational overhead to allow you to focus on the core components of your applications when using GPUs. All the while, you can run your AI applications alongside your non-AI apps on the same platform, within the same environment, which shares networking, observability, and security capabilities.
OpenAI, the company behind ChatGPT, says it has proof that the Chinese start-up DeepSeek used its technology to create a competing artificial intelligence model — fueling concerns about intellectual property theft in the fast-growing industry.
OpenAI believes DeepSeek, which was founded by math whiz Liang Wenfeng, used a process called “distillation,” which helps make smaller AI models perform better by learning from larger ones.
While this is common in AI development, OpenAI says DeepSeek may have broken its rules by using the technique to create its own AI system.
Figure AI is launching a Center for Humanoid Safety for transparency, testing, and third-party certification.
Figure AI announces plans for a Center for Humanoid Safety, focusing on transparency, rigorous testing, and third-party certification for safer robots.
While DeepSeek makes AI cheaper, seemingly without cutting corners on quality, a group is trying to figure out how to make tests for AI models that are hard enough. It’s ‘Humanity’s Last Exam’
If you’re looking for a new reason to be nervous about artificial intelligence, try this: Some of the smartest humans in the world are struggling to create tests that AI systems can’t pass.
For years, AI systems were measured by giving new models a variety of standardized benchmark tests. Many of these tests consisted of challenging, SAT-calibre problems in areas like math, science and logic. Comparing the models’ scores over time served as a rough measure of AI progress.
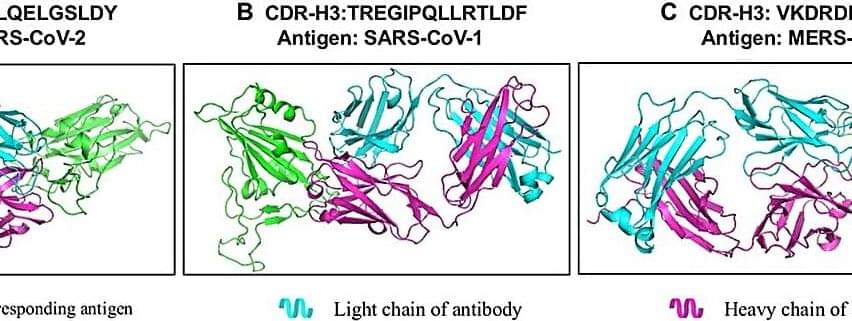
Researchers from Zhejiang University and HKUST (Guangzhou) have developed a cutting-edge AI model, ProtET, that leverages multi-modal learning to enable controllable protein editing through text-based instructions. This innovative approach, published in Health Data Science, bridges the gap between biological language and protein sequence manipulation, enhancing functional protein design across domains like enzyme activity, stability, and antibody binding.
Proteins are the cornerstone of biological functions, and their precise modification holds immense potential for medical therapies, synthetic biology, and biotechnology. While traditional protein editing methods rely on labor-intensive laboratory experiments and single-task optimization models, ProtET introduces a transformer-structured encoder architecture and a hierarchical training paradigm. This model aligns protein sequences with natural language descriptions using contrastive learning, enabling intuitive, text-guided protein modifications.
The research team, led by Mingze Yin from Zhejiang University and Jintai Chen from HKUST (Guangzhou), trained ProtET on a dataset of over 67 million protein–biotext pairs, extracted from Swiss-Prot and TrEMBL databases. The model demonstrated exceptional performance across key benchmarks, improving protein stability by up to 16.9% and optimizing catalytic activities and antibody-specific binding.
We could soon live to the age of 150, medics claim.
They say more of us will reach the massive milestone thanks to modern tech, new medicines and healthy living. Longevity medicine expert Dr Debonneuil said: If the current trend continues, we could see individuals living to 140 or 150 in good health.
While that might sound sensational, it’s grounded in science and the longevity field is booming because of these breakthroughs.” Dr Debonneuil spoke after a first-of-its-kind study, Rejuvenation Olympics, produced promising anti-ageing results. He continued: “One of the guys taking part is in his 60’s but biologically he resembles someone in their later 30’s.
A 2024 study is facing skepticism, so the people behind that study are diving back underwater.