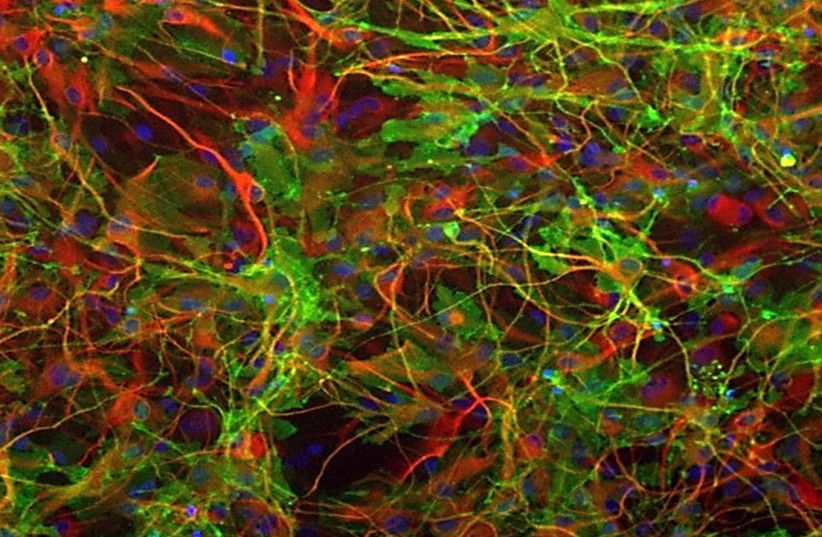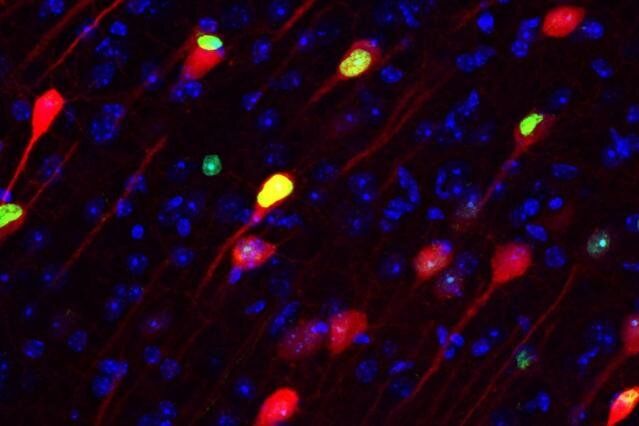
Experiments in rodents have revealed that engrams exist as multiscale networks of neurons. An experience becomes stored as a potentially retrievable memory in the brain when excited neurons in a brain region such as the hippocampus or amygdala become recruited into a local ensemble. These ensembles combine with others in other regions, such as the cortex, into an “engram complex.” Crucial to this process of linking engram cells is the ability of neurons to forge new circuit connections, via processes known as “synaptic plasticity” and “dendritic spine formation.” Importantly, experiments show that the memory initially stored across an engram complex can be retrieved by its reactivation but may also persist “silently” even when memories cannot be naturally recalled, for instance in mouse models used to study memory disorders such as early stage Alzheimer’s disease.
“More than 100 years ago Semon put forth a law of engraphy,” wrote Josselyn, Senior Scientist at SickKids, Professor of Psychology and Physiology at the University of Toronto and Senior Fellow in the Brain, Mind & Consciousness Program at the Canadian Institute for Advanced Research, (CIFAR) and Tonegawa, Picower Professor of Biology and Neuroscience at the RIKEN-MIT Laboratory for Neural Circuit Genetics at MIT and Investigator of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute. “Combining these theoretical ideas with the new tools that allow researchers to image and manipulate engrams at the level of cell ensembles facilitated many important insights into memory function.”
“For instance, evidence indicates that both increased intrinsic excitability and synaptic plasticity work hand in hand to form engrams and that these processes may also be important in memory linking, memory retrieval, and memory consolidation.”
Continue reading “Engrams emerging as the basic unit of memory” »
 We use a convolutional neural network (CNN) to study cosmic string detection in cosmic microwave background (CMB) flat sky maps with Nambu-Goto strings. On noiseless maps we can measure string tensions down to order $10^{-9}$, however when noise is included we are unable to measure string tensions below.
We use a convolutional neural network (CNN) to study cosmic string detection in cosmic microwave background (CMB) flat sky maps with Nambu-Goto strings. On noiseless maps we can measure string tensions down to order $10^{-9}$, however when noise is included we are unable to measure string tensions below.