NASA has released this year’s photo of Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune taken by the Hubble Space Telescope.


We’ve been seeing a wave of innovations in solar panel technology, like perovskite solar cells, solar tiles and roofs, and organic panels. But what if we could harvest solar energy from the windows and skylights of our homes and skyscrapers, or even from our car windows and cellphone screens? Let’s explore transparent solar panels and how they stack up against conventional panels. Could transparent solar cells be the future of solar energy? Or does it remain to be unseen?
Watch Exploring Why This Nuclear Fusion Breakthrough Matters: h https://youtu.be/-KEwkWjADEA?list=PLnTSM-ORSgi7UWp64ZlOKUPNXePMTdU4d.
Video script and citations:
https://undecidedmf.com/episodes/exploring-why-transparent-s…isnt-clear.
Follow-up podcast:
Video version — https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC4-aWB84Bupf5hxGqrwYqLA
Audio version — http://bit.ly/stilltbdfm.
👋 Support Undecided on Patreon!
https://www.patreon.com/mattferrell.
⚙️ Gear & Products I Like.
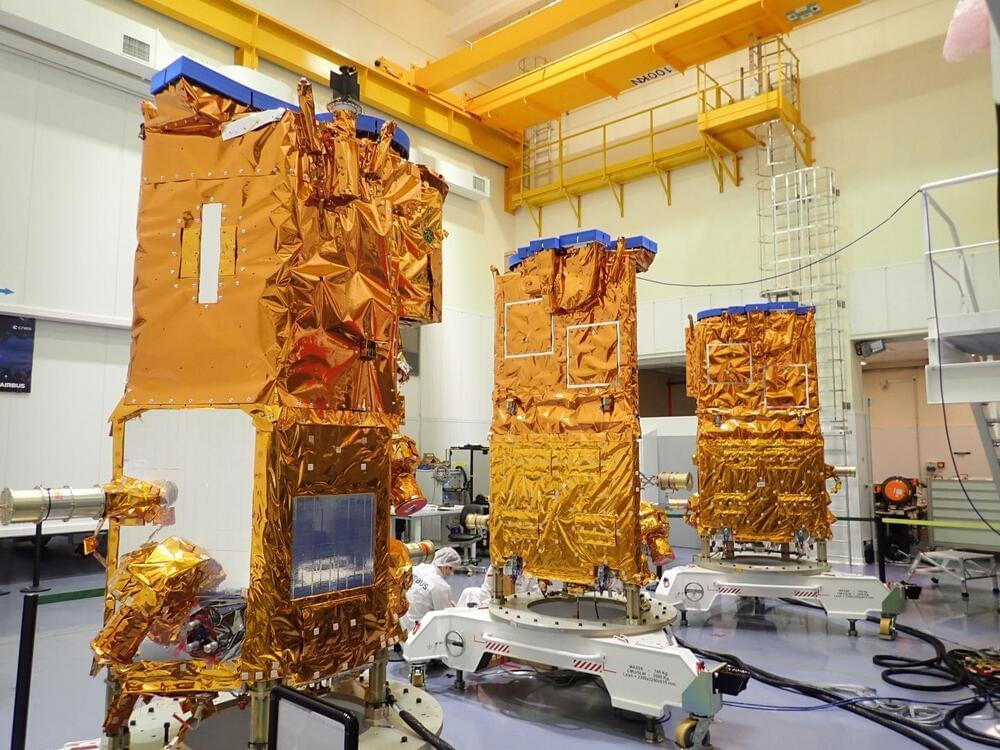

The French Armament General Directorate’s (DGA) ‘Capacité de Renseignement Electromagnétique Spatiale/Space-based Signal Intelligence Capability’ satellites have been successfully launched.
An Arianespace Vega rocket lifted off with the satellites from the European spaceport in French Guiana.
Known by the French acronym CERES, the satellites were designed and built by Airbus Defence and Space, and Thales.
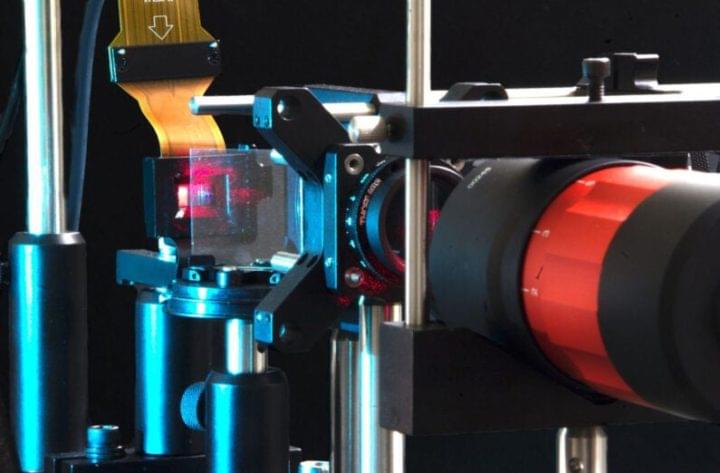
Working at the intersection of hardware and software engineering, researchers are developing new techniques for improving 3D displays for virtual and augmented reality technologies.
Virtual and augmented reality headsets are designed to place wearers directly into other environments, worlds and experiences.
While the technology is already popular among consumers for its immersive quality, there could be a future where the holographic displays look even more like real life. In their own pursuit of these better displays, the Stanford Computational Imaging Lab has combined their expertise in optics and artificial intelligence. Their most recent advances in this area are detailed in a paper published in Science Advances and work that will be presented at SIGGRAPH ASIA 2021 in December.
When Elon Musk has any news to share, you’re likely to hear about it first on Twitter. You’d think the guy who runs SpaceX, Neuralink, Tesla, The Boring Company wouldn’t have much time on his hands.
But as his companies grow, so do his number of tweets. They’ve been increasing steadily – as the Wall Street Journal notes in this graphic. His tweets are so frequent that when he announced he was taking a break from Twitter that one time, it made the news.
Ever since he opened up an account in 2009, he’s tweeted about 16,000 times. Other famous billionaires tweet far less. Bill Gates has sent 3,000 tweets. Jeff Bezos less than 300. This is said to be Mark Zuckerberg’s account which isn’t even verified. He’s sent 19 tweets.
Researchers at the USC Viterbi School of Engineering are using generative adversarial networks (GANs)—technology best known for creating deepfake videos and photorealistic human faces—to improve brain-computer interfaces for people with disabilities.
In a paper published in Nature Biomedical Engineering, the team successfully taught an AI to generate synthetic brain activity data. The data, specifically neural signals called spike trains, can be fed into machine-learning algorithms to improve the usability of brain-computer interfaces (BCI).
BCI systems work by analyzing a person’s brain signals and translating that neural activity into commands, allowing the user to control digital devices like computer cursors using only their thoughts. These devices can improve quality of life for people with motor dysfunction or paralysis, even those struggling with locked-in syndrome—when a person is fully conscious but unable to move or communicate.



Magnetic soft robots are systems that can change shape or perform different actions when a magnetic field is applied to them. These robots have numerous advantageous characteristics, including a wireless drive, high flexibility and infinite endurance.
In the future, micro-scale magnetic soft robots could be implemented in a variety of settings; for instance, helping humans to monitor the environment or to remotely perform biomedical procedures. Most of the systems developed so far, however, can only complete simple tasks and take on a limited number of shapes.
Researchers at the Chinese Academy of Sciences have recently devised a new technique for creating shape-programmable magnetic soft robots. This technique, outlined in a paper pre-published on arXiv and presented at the CCIR2021 conference, allowed them to create a new robot based on magnetic pixels that can change shapes and complete a variety of actions or tasks.
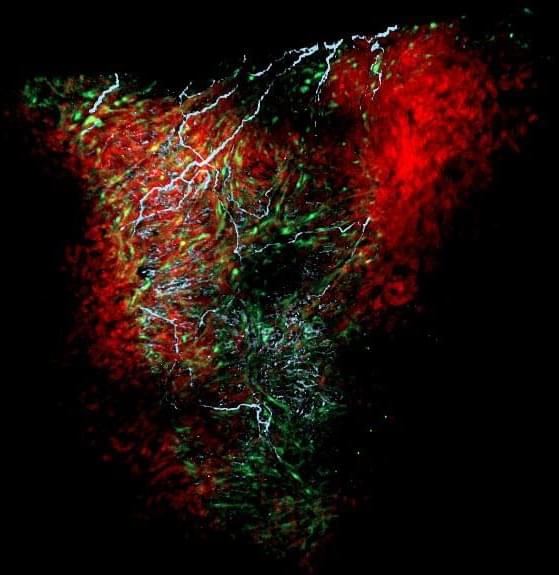
Discovery suggests glial cells may be important in other organs as well.
Glial cells in the heart help regulate heart rate and rhythm, and drive its development in the embryo, according to a new study publishing today (November 18th, 2021) in the open-access journal PLOS Biology by Nina Kikel-Coury, Cody Smith and colleagues at the University of Notre Dame. The discovery provides the most detailed portrait yet of a critical population of cells that had been previously poorly understood.
Glia are a diverse set of cell types, originally named after the Greek word for glue, and include cells that surround and nourish neurons, and others that mount immune responses within the central nervous system. In the peripheral nervous system, glia are present and presumably active in multiple organs, including the gut, pancreas, spleen, and lungs, although their function is not clear in most cases.