From the article:
Nipah virus outbreaks have been associated with a high death rate in the past, with fatality levels reported between 40 and 75 per cent depending on the outbreak and the viral strain involved.
The virus has been documented in Bangladesh, India, Malaysia, the Philippines and Singapore, with Bangladesh recording the highest number of 341 cases and 241 deaths, according to the International Society for Infectious Disease.
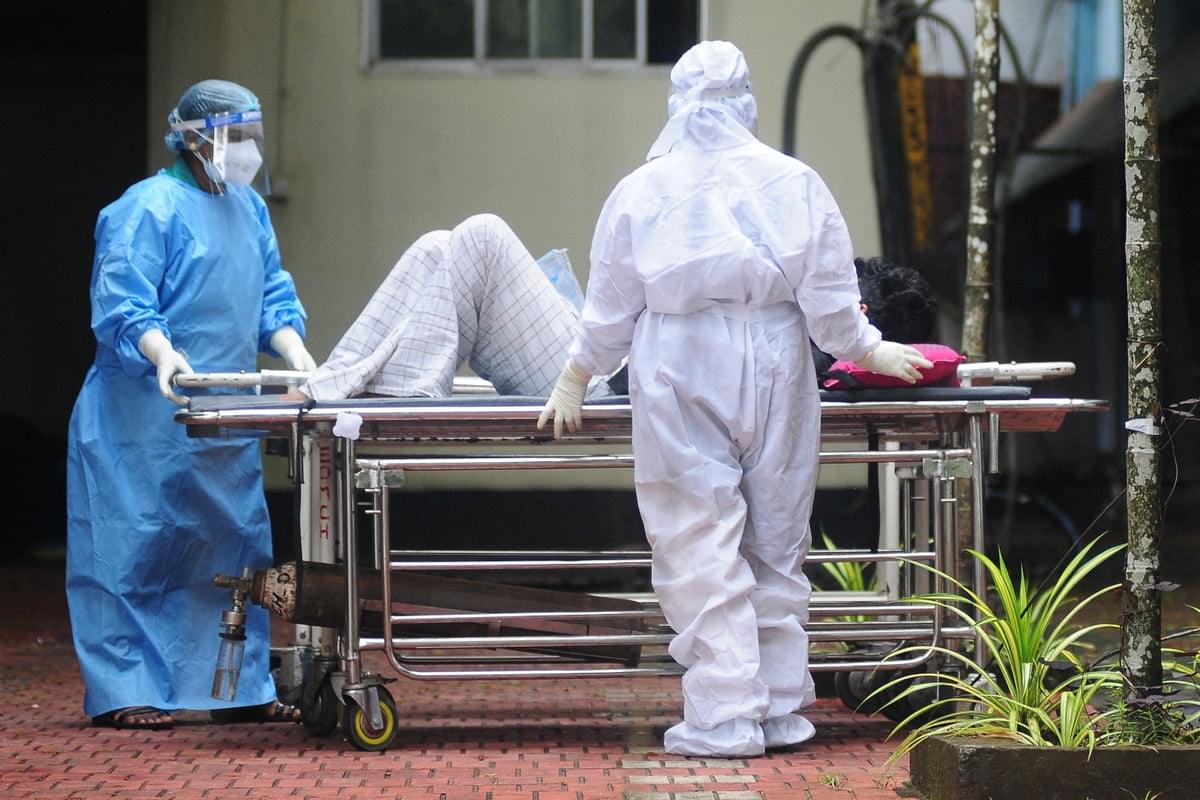
Airports across parts of Asia have begun tightening health surveillance and travel screening after an outbreak of Nipah virus in an Indian state.
Thailand, Nepal and Taiwan are among the countries and territories that have stepped up precautionary measures after five Nipah virus cases were confirmed in India’s West Bengal.
Nipah is a zoonotic disease that mainly spreads to humans from infected pigs and bats, but can also be passed on through close person-to-person contact.