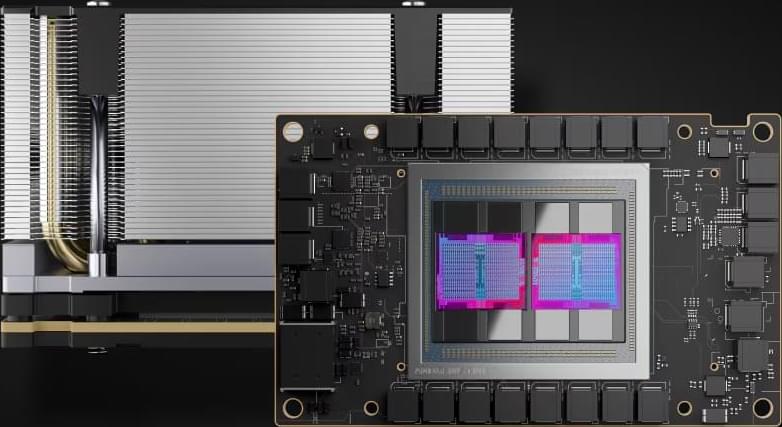
A quantum leap for antimatter measurements.


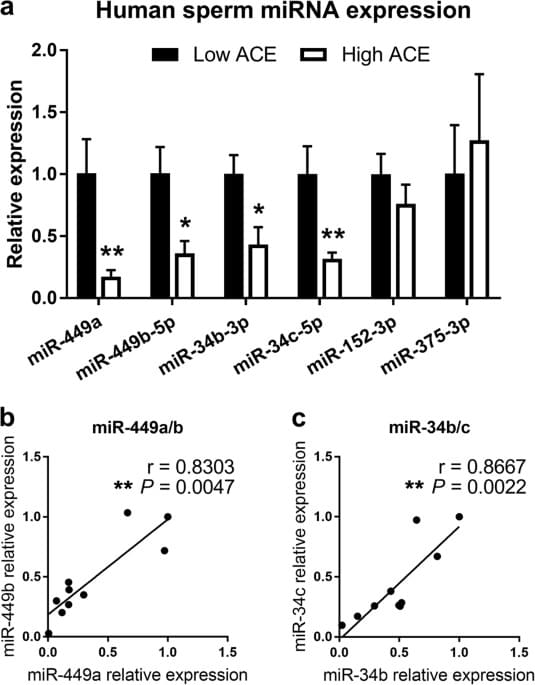
Many studies have confirmed that exposure to severe stress during childhood has long-lasting negative health effects. One of the most convincing has been the Adverse Childhood Experience (ACE) Study, which is supported by over 100 publications1. It was initiated by collaboration between the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and Kaiser Permanente’s Department of Preventive Medicine. It led to the ACE Study Questionnaire (see http://www.acestudy.org/index.html), where anonymous yes or no answers to 10 questions involving participant’s experiences at home until the age of 18 are quantified. Five are personal questions about physical abuse, verbal abuse, sexual abuse, physical neglect, and emotional neglect. Five relate to other family members: an alcoholic parent, a victim of domestic violence, incarceration, diagnosed with a mental illness, and the disappearance of a parent through divorce, death, or abandonment. A score ≥4 puts one at serious risk for future mental and physical health problems, such as a 4.6-fold increased rate of depression2 and a ~30-fold increased rate of suicidal ideation and attempts in adults3. Remarkably, 10% of the population reports scores of ≥4.
There is a growing appreciation that clinicians should be aware of patients’ traumatic experiences, particularly when young, because they add to their risk for physical and psychiatric maladies4,5. Moreover, sensitivity to PTSD has been shown to correlate with ACE score6,7,8 implying it can be used as a screening tool to identify people who should take extra precaution to avoid trauma. However, some may not answer the ACE questionnaire accurately due to suppressed memories or because of the sensitive nature of many of the questions, particularly in settings that do not allow anonymity. Thus, discovery of unbiased markers for early trauma could complement ACE surveys in some clinical settings.
Moreover, offspring of those exposed to early life trauma are at elevated risk for psychiatric disorders9. This phenomena has also been demonstrated in rodents10,11. For example, transmission of the effects of stress across generations has been observed after exposing male mice to a wide variety of psychological stresses, including social defeat12, chronic physical restraint13, multiple variable perturbations in adults14, social instability beginning in adolescence15, and early maternal separation16. While some evidence in mice points to environmentally induced changes in sperm DNA methylation as a mechanism for transmission of stress phenotypes16, the best evidence to date supports small RNA species in sperm. Recent studies show that sperm contain various types of cytoplasmic RNAs (e.g., mRNAs, miRNAs, siRNAs, lnc-RNAs, piwi-interacting RNAs, and fragments of tRNAs) that have the potential to contribute to embryo development17,18,19.

#ArtificialIntelligence #CyberSecurity #QuantumComputing
The transformative effects of emerging technologies in this year by artificial intelligence and quantum computing will be hugely impactful; however, their cybersecurity challenges on society will require the need for proactive security adaptation and collaboration to mitigate new threats.

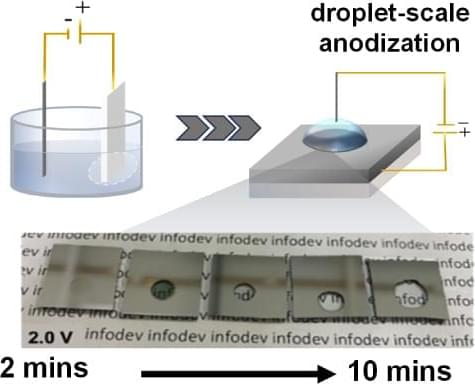
Transparent aluminum oxide (TAlOx), a real material despite its sci-fi name, is incredibly hard and resistant to scratches, making it perfect for protective coatings on electronics, optical sensors, and solar panels. On the sci-fi show Star Trek, it is even used for starship windows and spacefaring aquariums.
Current methods of making TAlOx are expensive and complicated, requiring high-powered lasers, vacuum chambers, or large vats of dangerous acids. That may change thanks to research co-authored by Filipino scientists from Ateneo de Manila University.
Instead of immersing entire sheets of metal into acidic solutions, the researchers applied microdroplets of acidic solution onto small aluminum surfaces and applied an electric current. Just two volts of electricity—barely more than what’s found in a single AA household flashlight battery—was all that was needed to transform the metal into glass-like TAlOx.
Rumelhart, D., Hinton, G. & Williams, R. Learning representations by back-propagating errors. Nature 323, 533–536 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1038/323533a0