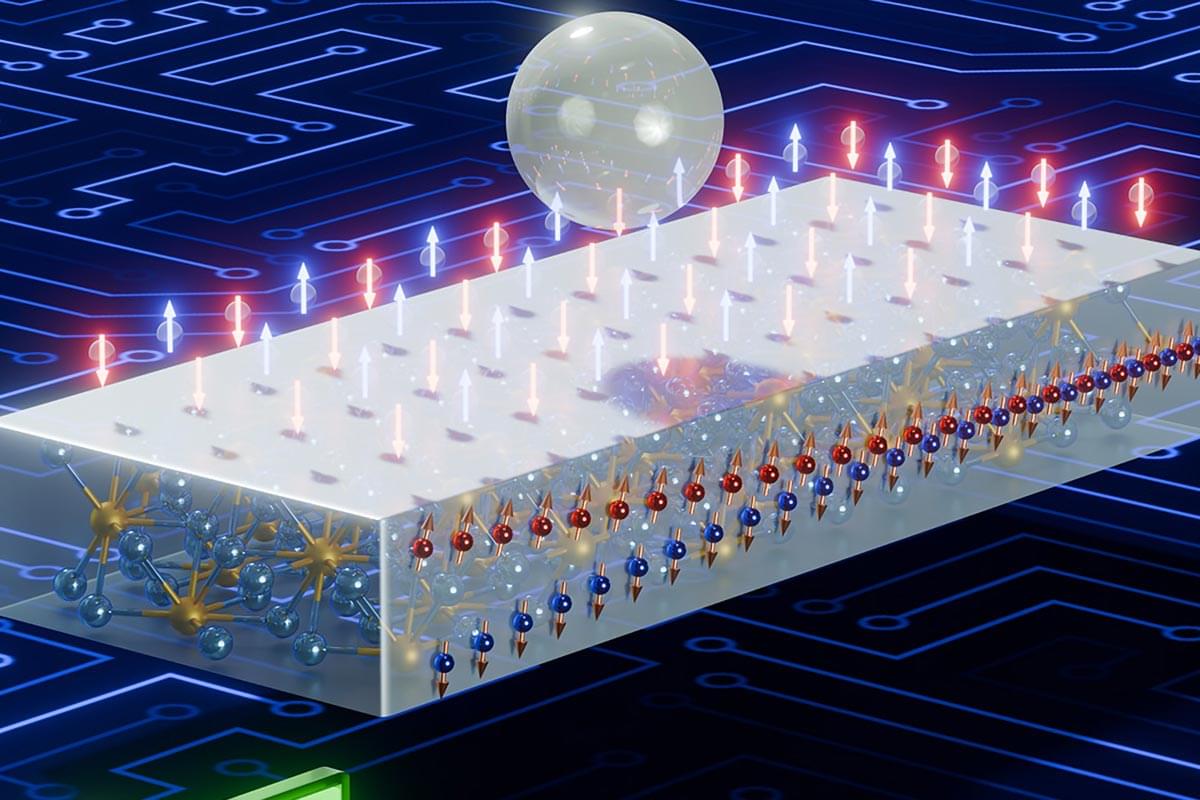
A common metal just unlocked a powerful, low-energy shortcut to faster electronics.



The hypertension drug rilmenidine has been shown to slow down aging in worms, an effect that in humans could hypothetically help us live longer and keep us healthier in our latter years.
Previous research has shown rilmenidine mimics the effects of caloric restriction on a cellular level. Reducing available energy while maintaining nutrition within the body has been shown to extend lifespans in several animal models.
Whether this translates to human biology, or is a potential risk to our health, is a topic of ongoing debate. Finding ways to achieve the same benefits without the costs of extreme calorie cutting could lead to new ways to improve health in old age.
An antibody treatment developed at Stanford Medicine successfully prepared patients for stem cell transplants without toxic busulfan chemotherapy or radiation, a Phase I clinical trial has shown.
While the researchers tested the protocol on patients with Fanconi anemia, a genetic disease that makes standard stem cell transplant extremely risky, they expect it may also work for patients with other genetic diseases that require stem cell transplants.
“We were able to treat these really fragile patients with a new, innovative regimen that allowed us to reduce the toxicity of the stem cell transplant protocol,” said the study’s co-senior author, Agnieszka Czechowicz, MD, Ph.D., assistant professor of pediatrics.
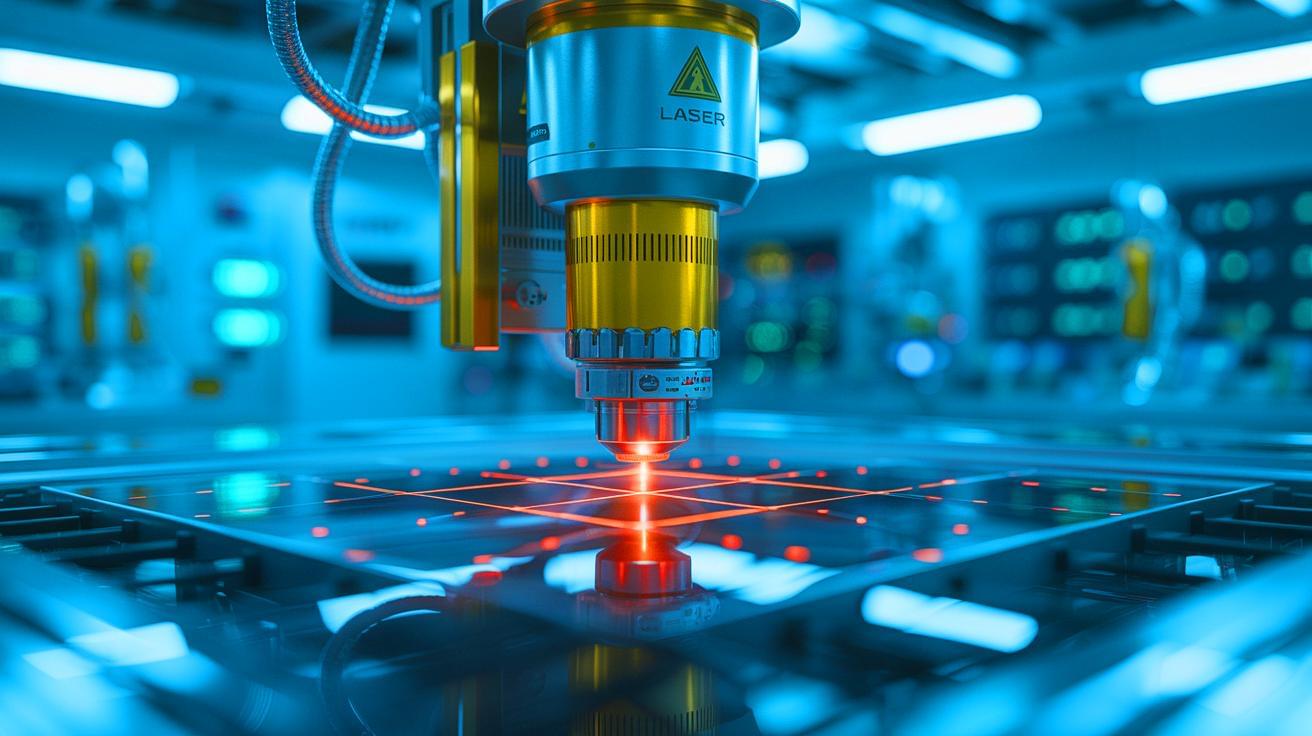


IN A NUTSHELL 🌟 Coherent Corp. unveils a powerful new laser to accelerate the production of high-temperature superconducting tape. ⚡ The LEAP 600C laser utilizes Pulsed Laser Deposition, offering twice the power and longer maintenance intervals. 🔬 HTS tape is essential for fusion energy and various technologies, including MRI machines and power grids. 🌍 This
“Historically, this has been a very challenging problem. People don’t know where to start,” said senior author Megan Dennis, associate director of genomics at the UC Davis Genome Center and associate professor in the Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Medicine and MIND Institute at the University of California, Davis.
In 2022, Dennis was a co-author on a paper describing the first sequence of a complete human genome, known as the ‘telomere to telomere’ reference genome. This reference genome includes the difficult regions that had been left out of the first draft published in 2001 and is now being used to make new discoveries.
Dennis and colleagues used the telomere-to-telomere human genome to identify duplicated genes. Then, they sorted those for genes that are: expressed in the brain; found in all humans, based on sequences from the 1,000 Genomes Project; and conserved, meaning that they did not show much variation among individuals.
They came out with about 250 candidate gene families. Of these, they picked some for further study in an animal model, the zebrafish. By both deleting genes and introducing human-duplicated genes into zebrafish, they showed that at least two of these genes might contribute to features of the human brain: one called GPR89B led to slightly bigger brain size, and another, FRMPD2B, led to altered synapse signaling.
“It’s pretty cool to think that you can use fish to test a human brain trait,” Dennis said.
The dataset in the Cell paper is intended to be a resource for the scientific community, Dennis said. It should make it easier to screen duplicated regions for mutations, for example related to language deficits or autism, that have been missed in previous genome-wide screening.
“It opens up new areas,” Dennis said.
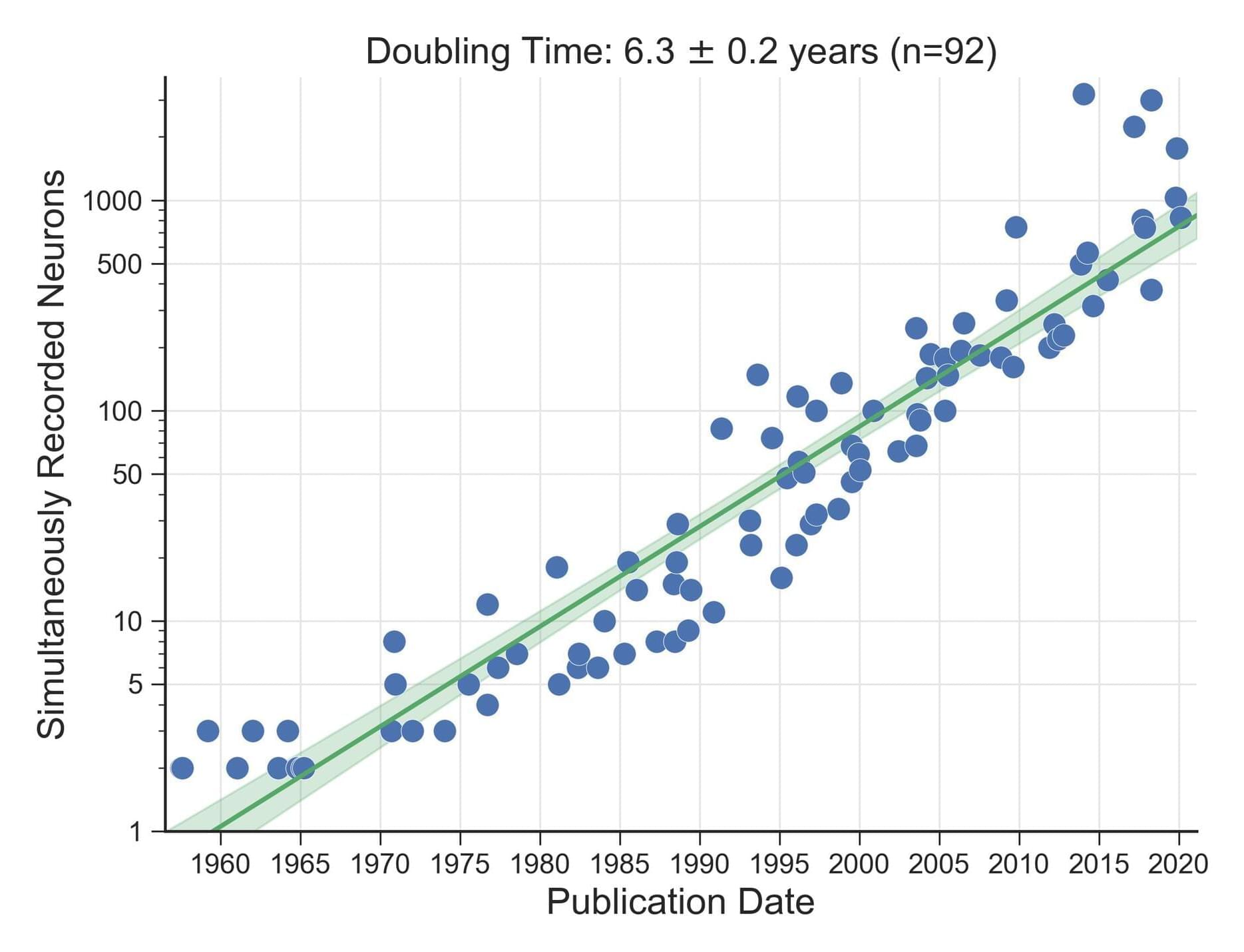
Over the last five decades, progress in neural recording techniques has allowed the number of simultaneously recorded neurons to double approximately every 7 years, mimicking Moore’s law. Following Stevenson and Kording (2011), this site aims to keep track of these advances in electrophysiology. If you notice a missing data point email me with a reference and the number of neurons recorded.

OpenAI recently told Axios that their AI tool ChatGPT handles over 2.5 billion user instructions every single day. That’s the equivalent of about 1.7 million instructions per minute or 29,000 per second.
This is a stark increase from December 2024, when ChatGPT was handling about 1 billion messages per day. Having launched in November 2022, it’s become one of the fastest growing consumer apps of all time.