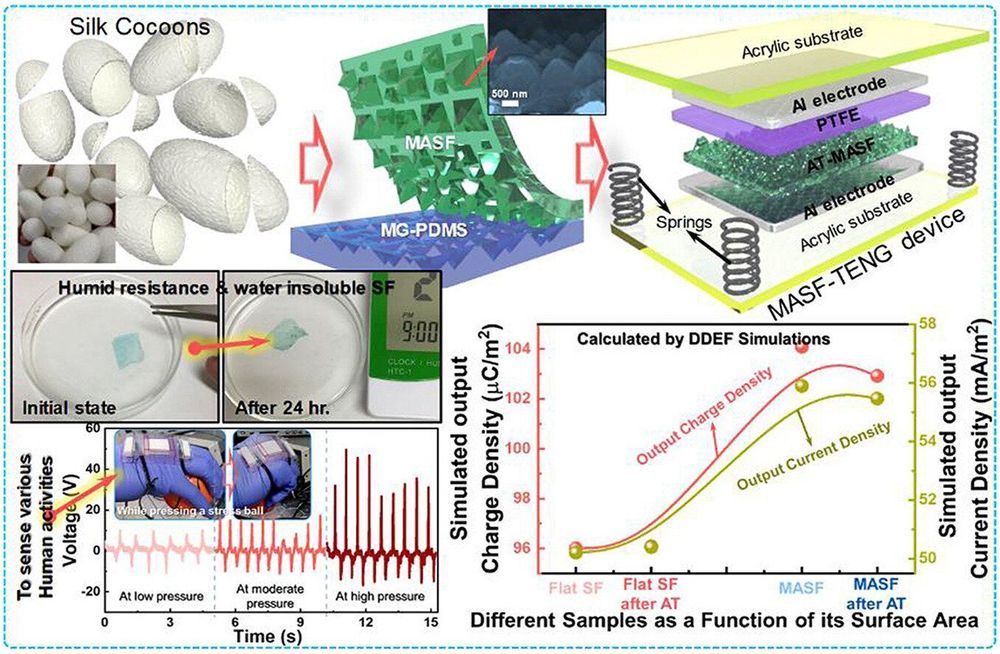
Researchers from the University of Surrey have revealed their new biodegradable motion sensor—paving the way for implanted nanotechnology that could help future sports professionals better monitor their movements to aid rapid improvements, or help caregivers remotely monitor people living with dementia.
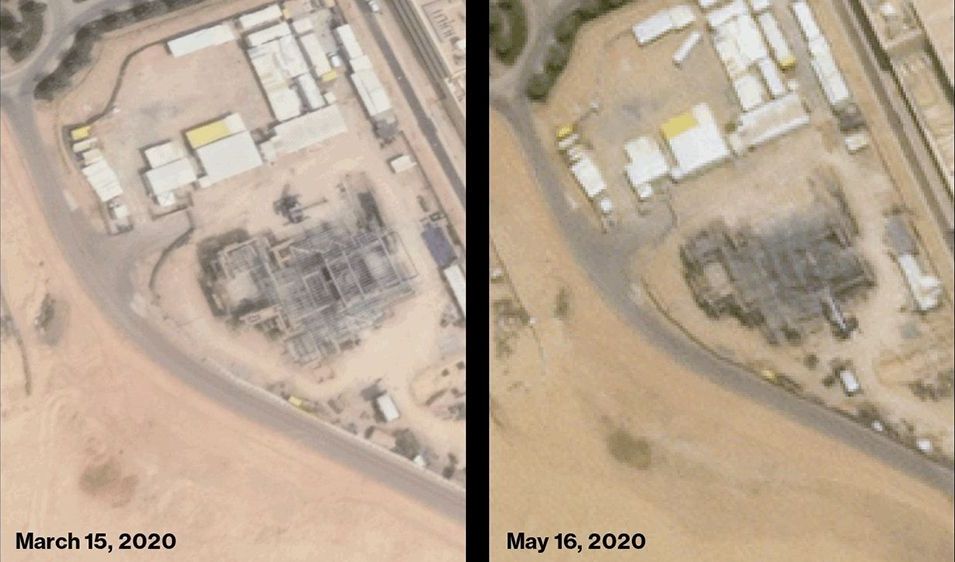
Saudi Arabia is pushing ahead to complete its first nuclear reactor, according to satellite images that have raised concern among arms-control experts because the kingdom has yet to implement international monitoring rules.
The giant tectonic plate under the Indian Ocean is going through a rocky breakup … with itself.
In a short time (geologically speaking) this plate will split in two, a new study finds.
To humans, however, this breakup will take an eternity. The plate, known as the India-Australia-Capricorn tectonic plate, is splitting at a snail’s pace — about 0.06 inches (1.7 millimeters) a year. Put another way, in 1 million years, the plate’s two pieces will be about 1 mile (1.7 kilometers) farther apart than they are now.
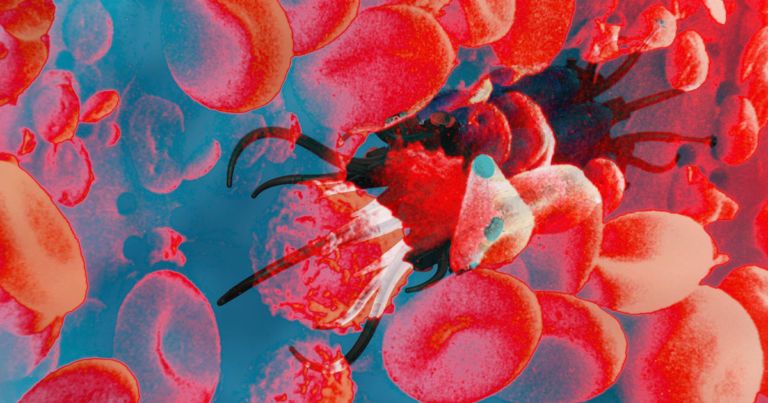
In order to find and treat cancerous tumors, a team of scientists is working on an aggressive new approach that involves a swarm of tiny, cancer-killing robots.
The idea is to inject the nanobots, which are engineered to look and travel like white blood cells, into a patient’s veins and move them around inside the body with powerful magnets.
“Our vision was to create the next-generation vehicle for minimally invasive targeted drug delivery that can reach even deeper tissues inside the body with even more difficult access routes than what was previously possible,” Metin Sitti, Director of Physical Intelligence at the Max Planck Society, said in a press release.
The robot could end up being an ideal ranch hand that acts like a sheep dog but doesn’t need to be fed.
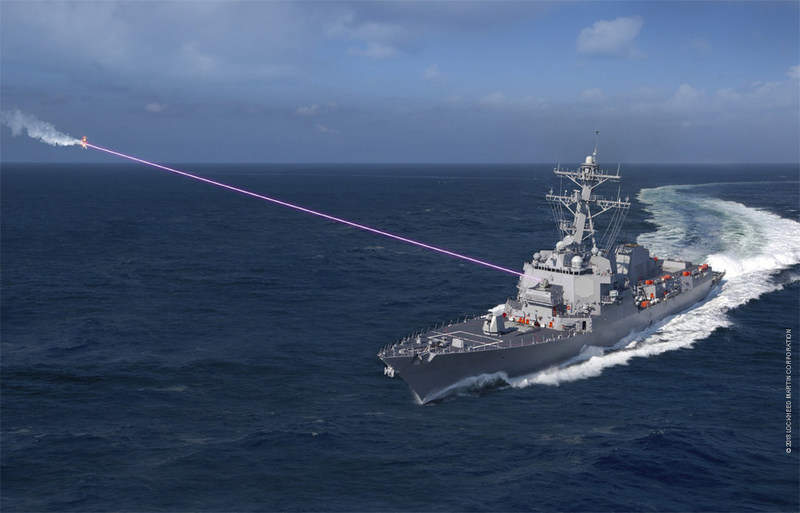
The US Navy has installed its first Optical Dazzling Interdictor, Navy (ODIN), a laser weapon designed to counter unmanned aerial systems (UAS).
The first ODIN laser system was installed on the Arleigh Burke-class guided-missile destroyer USS Dewey during a recent dry-docking.
Unlike hard-kill laser systems already deployed by the US Navy on vessels, ODIN uses a dazzling laser to confuse systems sensors and cameras or, in manned systems, potentially cause glare in a pilot’s vision.
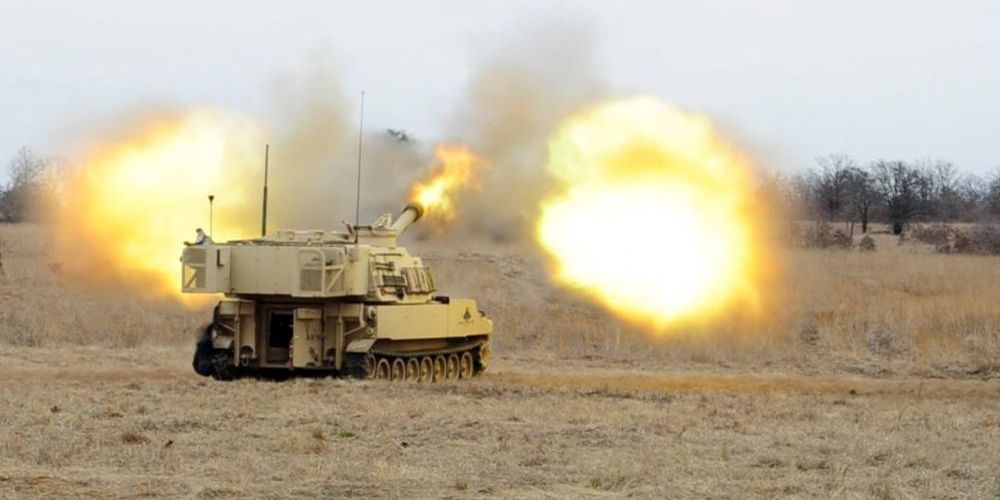
The U.S. Army is working on a new artillery shell capable of locating enemy targets, including moving tanks and armored vehicles. The shell, called Cannon-Delivered Area Effects Munition (C-DAEM), is designed to replace older weapons that leave behind unexploded cluster bomblets on the battlefield that might pose a threat to civilians. The shell is designed to hit targets even in situations where GPS is jammed and friendly forces are not entirely sure where the enemy is.
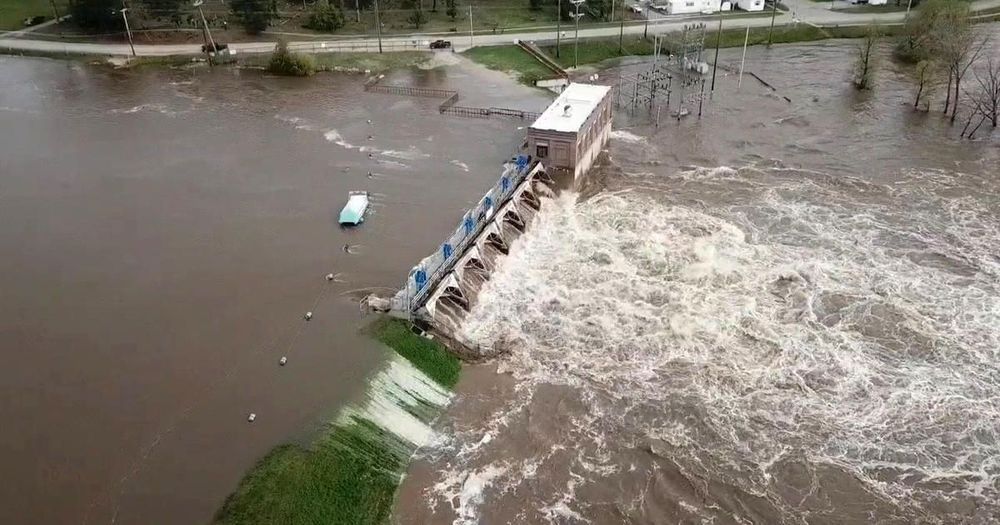
The National Weather Service on Tuesday evening urged anyone near the river to seek higher ground following “castastrophic dam failures” at the Edenville Dam, about 140 miles north of Detroit and the Sanford Dam, about seven miles downriver.
The Tittabawassee River rose another four feet by Wednesday morning, to 34.4 feet in Midland. According to the National Weather Service, the height has set a new record for the river, beating the previous record of 33.9 feet set during flooding in 1986.
Whitmer said downtown Midland, a city of 42,000 about 8 miles downstream from the Sanford Dam, faced an especially serious flooding threat. Dow Chemical Co.’s main plant sits on the city’s riverbank.
Transparent solar panels are regarded as the “wave of the future” for new solar technologies. Ubiquitous Energy and Physee are 2 pioneers.