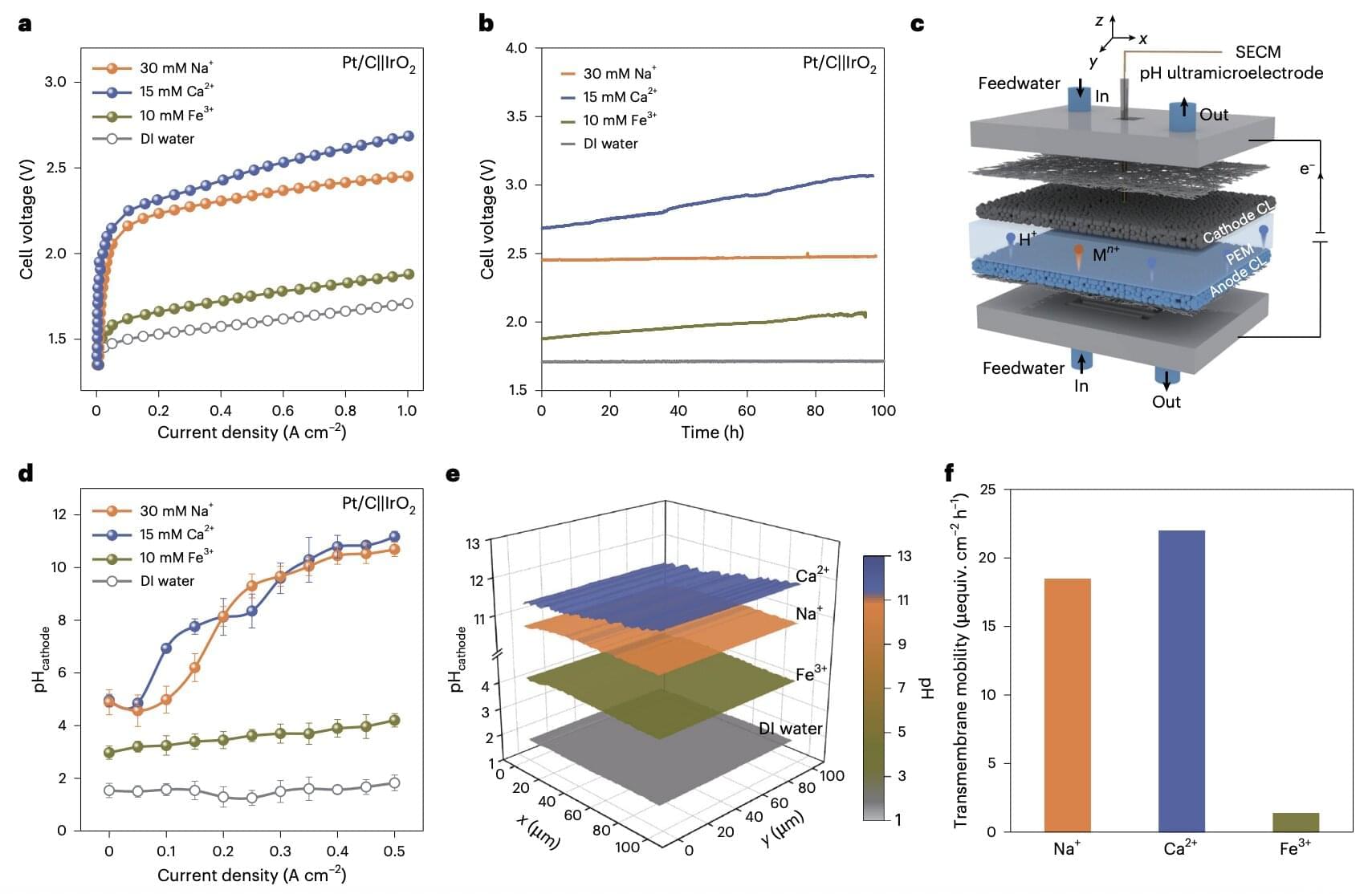
A drug commonly used to treat type 2 diabetes may reduce excess fluid in the brains of patients with hydrocephalus, which could help treat the disease less invasively than current treatments, according to a Northwestern Medicine study published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation.
Stephen Magill, MD, Ph.D., assistant professor of Neurological Surgery, was senior author of the study.
Normal pressure hydrocephalus occurs when excess cerebrospinal fluid builds up inside the skull and puts pressure on the brain. The cause of the condition is elusive and affects up to 3% of individuals over the age of 65, with symptoms including cognitive decline, difficulty walking and bladder problems.