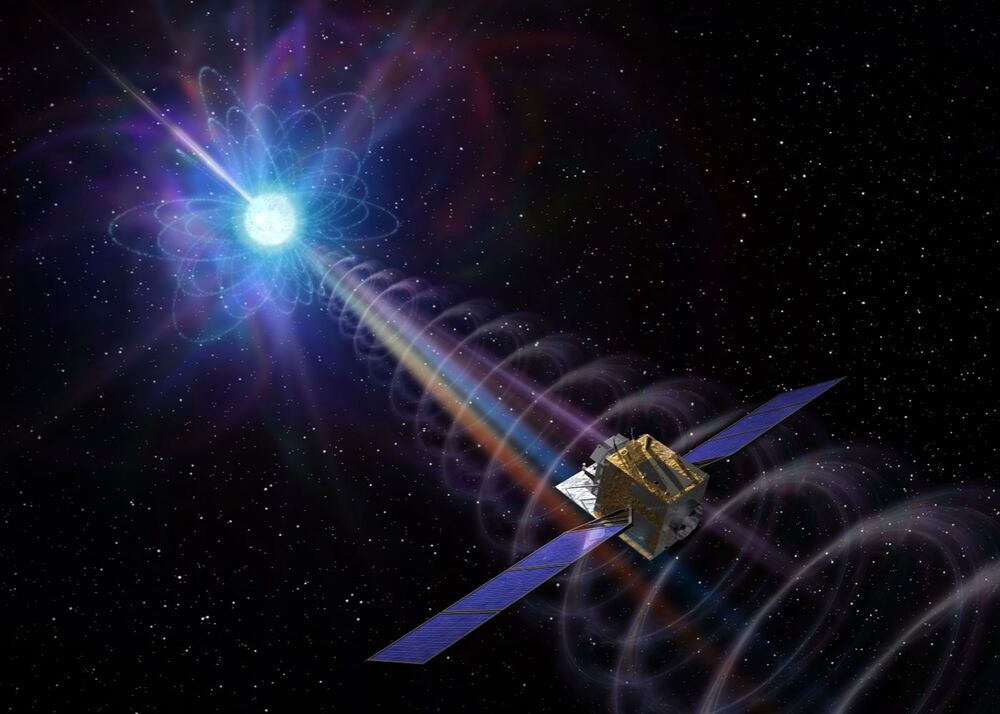
A new study of x-ray bursts from a local magnetar confirms the origin of a fast radio burst.
Every now and then there is a burst of radio light in the sky. It lasts for just milliseconds before fading. It’s known as a Fast Radio Burst (FRB), and they are difficult to observe and study. We know they are powerful bursts of energy, but we aren’t entirely sure what causes them.
The more we’ve learned about FRBs, the stranger they appear. Most occur outside our galaxy, but there are a few that seem to originate within the Milky Way. Most seem to appear at random in the sky, but a few of them are repeating FRBs. Some of them even repeat with surprising regularity. Because of this, astronomers generally think they can’t be caused by a cataclysmic event, such as the last radio burst of a neutron star as it collapses into a black hole.