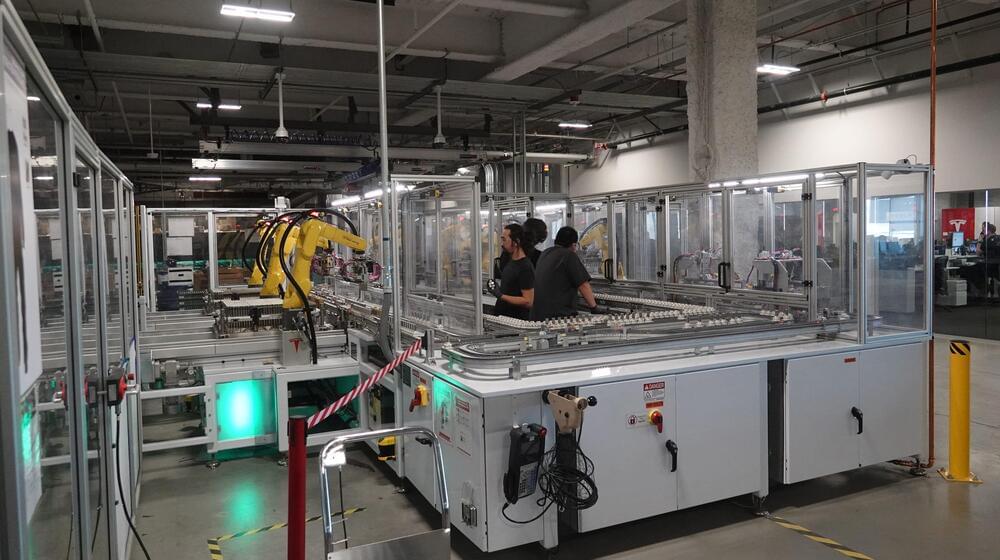
PENA, the division of Panasonic which produces lithium-ion batteries at the Sparks Gigafactory, will move into an existing building at 645 E. Plumb Lane, about half a mile east of the Reno-Tahoe International Airport. PENA’s headquarters will move from the Gigafactory to the Plumb Lane campus.
“Our new facility in Reno underscores our commitment to evolving and growing to stay at the forefront of the mobility market,” Allan Swan, president of PENA, said in a news release. “Investing in innovation and workforce initiatives in the local community supports our mission of creating a future powered by sustainable energy.”