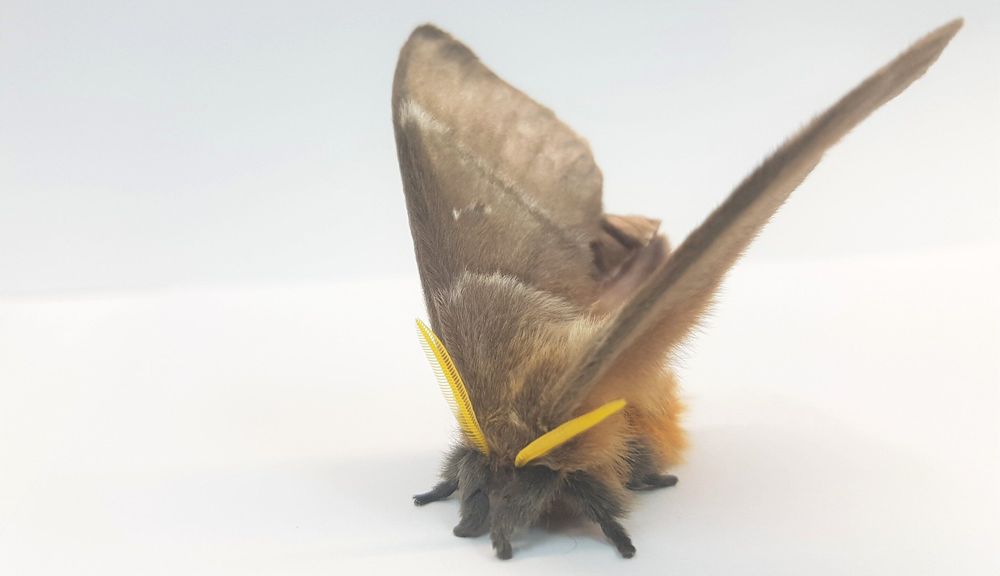
Some species of deaf moths can absorb as much as 85 per cent of the incoming sound energy from predatory bats—who use echolocation to detect them. The findings, published in the Journal of the Royal Society Interface today, reveal the moths, who are unable to hear the ultrasonic calls of bats, have evolved this clever defensive strategy to help it survive.
Bats hunt at night using echolocation. The technique, which is also known as biological sonar, first evolved around 65 million years ago and enables bats to search for and find prey putting huge predation pressure on nocturnal insects. One defence that many nocturnal insects evolved is the ability to hear the ultrasonic calls of bats, which allows them to actively evade approaching bats.
Many moth species, however, cannot hear. The team of researchers from the University of Bristol wanted to investigate the alternative defences against bats that some species of deaf moths might have evolved.