With Ukraine’s proposed law recognizing bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies, the stage is set for the country to become a leader in the market.


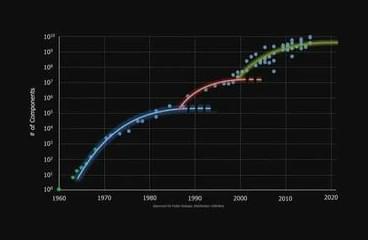
Some say that Moore’s Regulation, which tracks the exponential progress electronics during the last six a long time has stalled, and technological stagnation threatens. Mark Rosker, director of DARPA’s Microsystems Know-how Workplace (MTO), sees issues very in another way. In a new interview with Samuele Lilliu, he explains how the expansion described by Moore’s Regulation has been sustained by waves of innovation from DARPA and the way the following stage, what he calls the Fourth Wave, might be carried ahead by applied sciences his workplace is now creating.
The best model of Moore’s Regulation says that the variety of transistors on a silicon chip roughly doubles each two years. This was an commentary made by Gordon Moore – who later co-founded Intel – in 1965, and it proved to be remarkably correct. Yearly since then, an increasing number of highly effective computer systems and, later, laptops and smartphones have appeared in the marketplace. Low-cost chips have now grow to be important for vehicles, televisions, cameras and different units, which beforehand functioned with out electronics. They’re important throughout the financial system.
Describing the progress as a “Regulation” could also be deceptive. Moore’s Regulation is an outline of the development in semiconductor manufacturing, pushed by advances in science and know-how which requires fixed innovation to maintain going, not a pure course of.





Vitamin C has long been known as an essential nutrient for skin health and immune function, but it turns out its antioxidant activity plays a large role in those properties (among others).*.

Ion channels are crucial for neural communication; they control the flow and gradient of charged particles, creating electrical signals. Recent work report | Neuroscience.
In this study, the researchers assessed how dense ion channels were packed in the membranes of neuronal cells from ten species of mammals, including mice, rats, rabbits, ferrets, macaques, marmosets, macaques, humans, and one of the smallest known mammals, an animal called the Etruscan shrew. The team focused on a type of excitatory neuron typically found in the cortex of the brain, and three ion channels that are in the membranes of those cells; two are voltage-gated ion channels that control the movement of potassium, another is called the HCN channel and both potassium and sodium ions can flow through it.
Studies have suggested that the human brain is built like the brains of other mammals, said first study author Lou Beaulieu-Laroche, a former MIT graduate student. It was once thought that in mammals, these channels would be present at about the same density from one species to another.
Instead, the researchers determined that as the neurons got bigger, the density of ion channels increased. That was a notable finding, because as that density increases, more energy needed to move ions in and out of neurons, explained senior study author Mark Harnett, an associate professor of brain and cognitive sciences at MIT.