Industrial farming practices often deplete the soil of important nutrients and minerals, leaving farmers to rely on artificial fertilizers to support plant growth. In fact, fertilizer use has more than quadrupled since the 1960s, but this comes with serious consequences. Fertilizer production consumes massive amounts of energy, and its use pollutes the water, air, and land.
Plant biologists at the Salk Institute are proposing a new solution to help kick this unsustainable fertilizer habit.
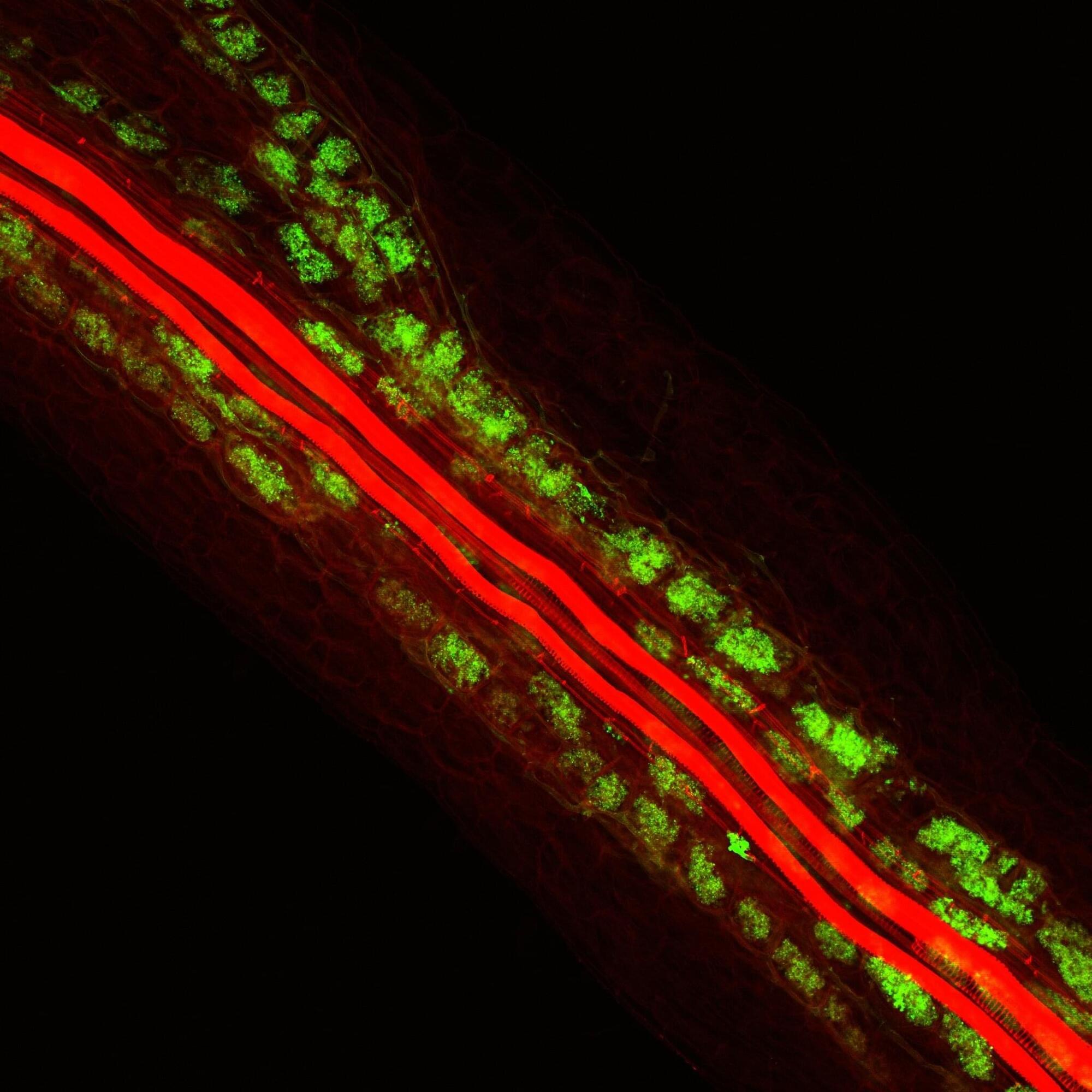
In a new study, the researchers identified a key molecule produced by plant roots, a small peptide called CLE16, that encourages plants and beneficial soil fungi to interact with each other. They say boosting this symbiotic relationship, in which the fungi provide mineral nutrients to the plants through CLE16 supplementation, could be a more natural and sustainable way to encourage crop growth without the use of harmful artificial fertilizers.