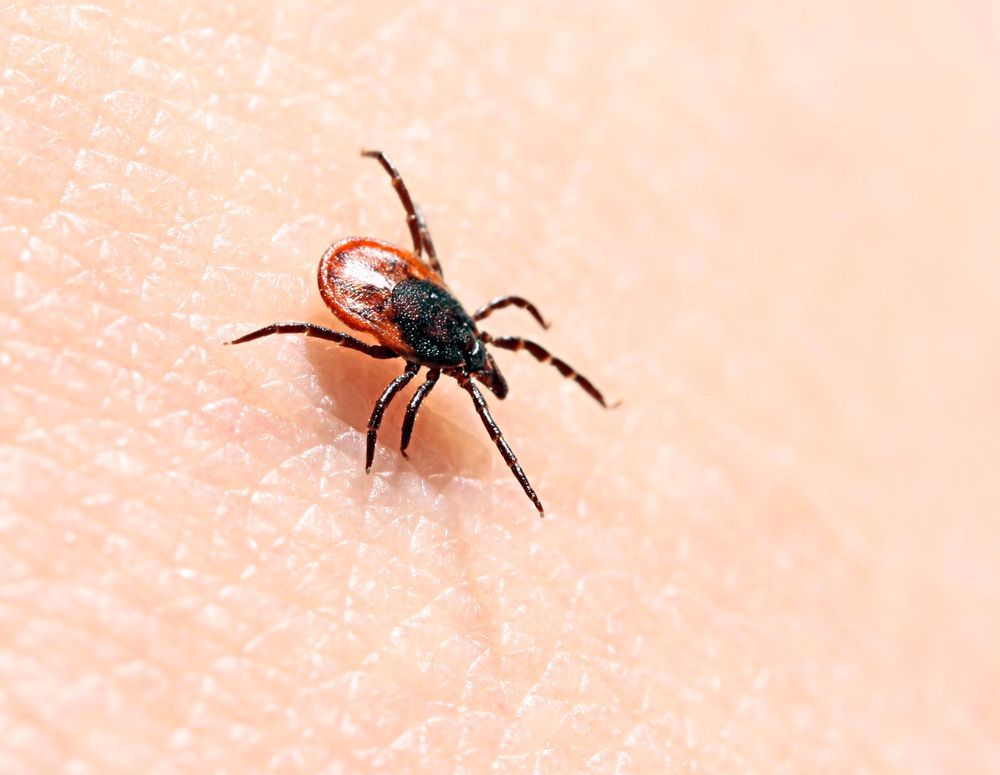
Lyme disease is an infectious condition spread by ticks that affects as many as 300,000 people in the US every year, according to the Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Today’s treatment is largely effective in treating the infection, but a good portion of patients do not respond and go on to endure lingering symptoms. A new study has revealed that an already-approved antibiotic can completely eliminate the underlying bacteria that causes the disease in mice, offering new hope of a more comprehensive therapy for humans.
While the standard antibiotics used to treat Lyme disease do the job for the majority of patients, somewhere between 10 and 20 percent go on to experience its symptoms. These include muscle pain, fatigue, fever, headaches and heart problems. There are couple of theories for why this might be.
“Some researchers think this may be due to drug-tolerant bacteria living in the body and continuing to cause disease,” said study author Jayakumar Rajadas. “Others believe it’s an immune disorder caused by bacteria during the first exposure, which causes a perpetual inflammation condition. Whatever the cause, the pain for patients is still very real.”