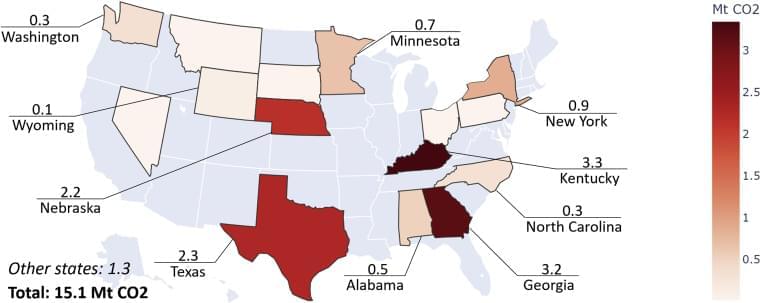
China’s government took U.S. intelligence provided to convince Beijing to join American-led efforts to head off a military attack on Ukraine and shared it with Russia, according to a person familiar with the activity.
Intelligence-sharing with a major U.S. adversary is unusual but was part of repeated diplomatic efforts by the Biden administration to gain support from China in dissuading Russian President Vladimir Putin from invading Ukraine.