Instead of requiring surgery to insert a solid scaffold, the gel could be simply injected into the knee, a much less invasive procedure



Elon Musk added that for a limited time, Grok Imagine video generation is free to all users in the US region.
(You can access anything in any region with a VPN 🙄)
Generative Artificial Intelligence (gen AI) firm xAI, earlier this week, introduced the Imagine video generation feature in the Grok AI app for iPhones.
Now, the company has expanded the availability of the video generation feature to the Android version of the Grok AI app. Elon Musk confirmed the news on his social media platform X. Also, Musk added that for a limited time, Grok Imagine video generation is free for a limited time for US region users.
AI Innovation: xAI brings Imagine video generation to Grok AI Android app, now free for US users for a limited time.
SpaceX is making significant progress towards establishing a human presence on Mars, with a major contract, advancements in technology, and plans for infrastructure development, potentially giving them a lead over competitors and raising questions about the future of space exploration and ownership ##
## Questions to inspire discussion.
Mars Exploration and Infrastructure.
🚀 Q: What is SpaceX’s breakthrough in Mars exploration? A: SpaceX’s Starship secured its first paying customer for Mars payloads: the Italian Space Agency, in a deal worth hundreds of millions of dollars.
🔬 Q: What experiments will the Italian Space Agency conduct on Mars? A: The payload includes plant growth, radiation, and local climate monitoring experiments, collecting data during the 6-month flight and on Mars’ surface.
🤖 Q: How will robots assist in Mars exploration? A: SpaceX plans to send 1,000–2,000 Optimus robots to Mars to fix rovers, run experiments, maintain equipment, and scout locations for future missions.
The newly developed device captures moments a quintillionth of a second long.

NVIDIA and OpenAI began pushing the boundaries of AI with the launch of NVIDIA DGX back in 2016. The collaborative AI innovation continues with the OpenAI gpt-oss-20b and gpt-oss-120b launch. NVIDIA has optimized both new open-weight models for accelerated inference performance on NVIDIA Blackwell architecture, delivering up to 1.5 million tokens per second (TPS) on an NVIDIA GB200 NVL72 system.
The gpt-oss models are text-reasoning LLMs with chain-of-thought and tool-calling capabilities using the popular mixture of experts (MoE) architecture with SwigGLU activations. The attention layers use RoPE with 128k context, alternating between full context and a sliding 128-token window. The models are released in FP4 precision, which fits on a single 80 GB data center GPU and is natively supported by Blackwell.
The models were trained on NVIDIA H100 Tensor Core GPUs, with gpt-oss-120b requiring over 2.1 million hours and gpt-oss-20b about 10x less. NVIDIA worked with several top open-source frameworks such as Hugging Face Transformers, Ollama, and vLLM, in addition to NVIDIA TensorRT-LLM for optimized kernels and model enhancements. This blog post showcases how NVIDIA has integrated gpt-oss across the software platform to meet developers’ needs.

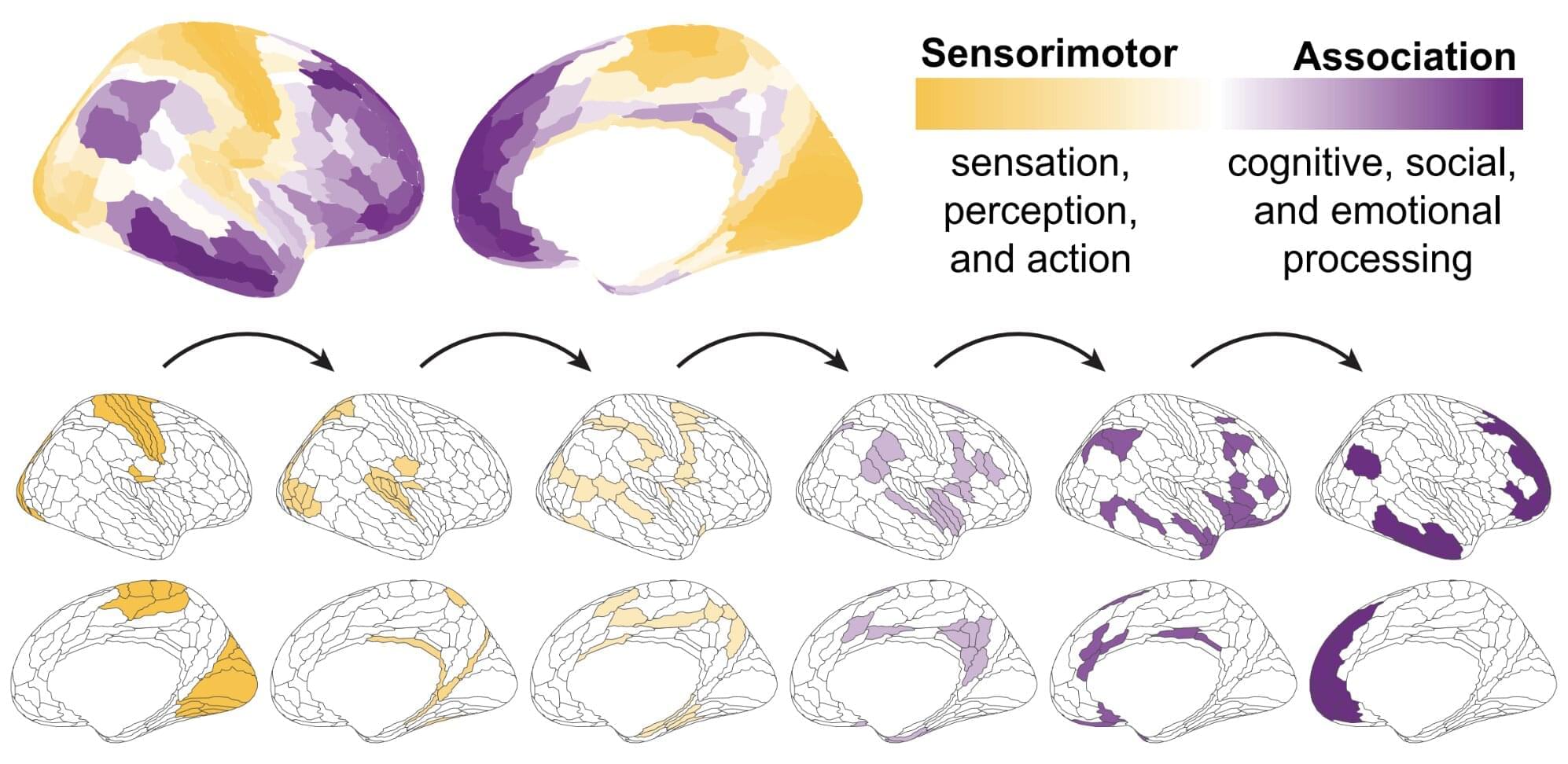
The brain is known to develop gradually throughout the human lifespan, following a hierarchical pattern. First, it adapts to support basic functions, such as movement and sensory perception, then it moves onto more advanced human abilities, such as decision-making.
Researchers at the University of Pennsylvania and other institutes, led by Principal Investigator Dr. Theodore Satterthwaite, recently carried out a study aimed at better understanding how the thalamus, a structure deep within the brain known to be involved in the processing and routing of sensory information, could contribute to the brain’s development over time.
Their findings, published in Nature Neuroscience, suggest that the thalamus is more than a relay station for sensory and motor signals, and also plays a role in regulating the hierarchical pattern and timeline of brain development.
Questions to inspire discussion.
👥 Q: What is the ratio of robo taxis to supervisors in Tesla’s network? A: Tesla’s robo taxi network operates with a 10:1 ratio of robo taxis to supervisors, enabling efficient management and cost-effective operations.
Market Disruption.
📊 Q: How is Whim, a Tesla competitor, performing in the market? A: As of April 2025, Whim has 25% of San Francisco gross bookings, surpassing Lyft, with an average price of $20 per mile compared to Uber’s $15 and Lyft’s $14.
Technology Superiority.
🤖 Q: How does Tesla’s robo taxi software compare to human drivers? A: Tesla’s robo taxi software has crossed the uncanny valley, providing a smooth and comfortable driving experience similar to a human chauffeur, outperforming Uber’s inconsistent service.